Introduction: The Allure of Options Trading
In the fast-paced world of financial markets, options trading stands out as a formidable tool for investors seeking greater control over their investment decisions and the potential to enhance their returns. An option contract grants the holder the right, but not the obligation, to buy (call option) or sell (put option) an underlying asset, such as a stock, at a specified price (strike price) on or before a set date (expiration date). This unique feature opens up a world of strategic possibilities for investors, from hedging risks to amplifying gains. Options trading software, such as Microsoft Excel, provides a valuable platform for analyzing and executing options strategies with ease.
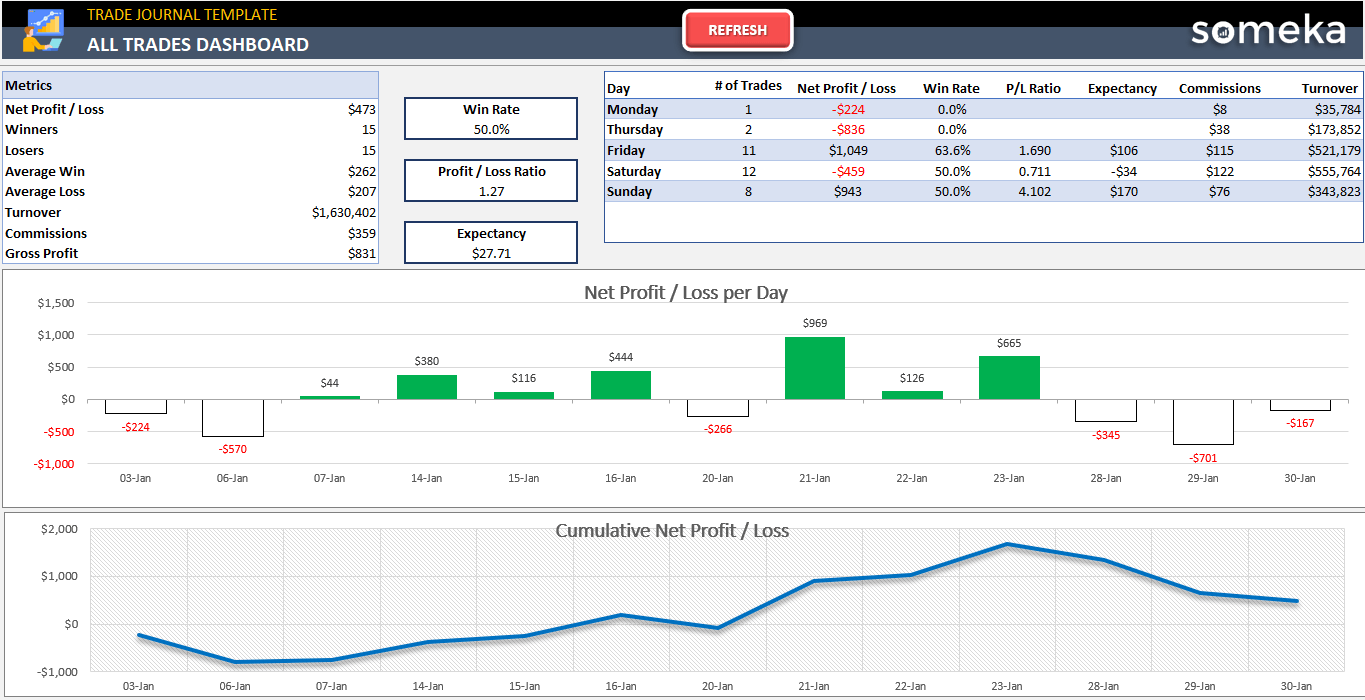
Image: www.ppgbbe.intranet.biologia.ufrj.br
Unveiling the Power of Excel for Options Trading
Excel, renowned for its versatility and analytical prowess, has emerged as a preferred choice for options traders. Its intuitive interface and robust functionality allow traders to quickly and efficiently analyze market data, perform complex calculations, and optimize their trading strategies. With Excel’s built-in options pricing models and customizable templates, traders can effortlessly value options, simulate scenarios, and make informed decisions based on real-time market conditions. Whether you’re a novice trader seeking to navigate the world of options or a seasoned veteran looking to refine your techniques, Excel serves as an invaluable ally.
Navigating the Alphabet Soup of Options Terminology
To fully appreciate the world of options trading, it’s essential to master the language spoken by market veterans. Options contracts are characterized by a unique vocabulary that may initially sound like an alphabet soup of terms. Here’s a quick glossary to help you decode the jargon:
- Call Option: Grants the holder the right to buy the underlying asset.
- Put Option: Grants the holder the right to sell the underlying asset.
- Strike Price: The specified price at which the underlying asset can be bought (call) or sold (put).
- Expiration Date: The last date on which the option contract can be exercised.
- Premium: The price paid by the option buyer to acquire the contract.
- Intrinsic Value: The difference between the underlying asset’s current price and the strike price of the option (positive for in-the-money options).
- Time Value: The portion of the option premium attributed to the remaining time until expiration.
Unveiling the Secrets of Options Pricing
Understanding the factors that determine the price of an option is paramount to making informed trading decisions. Options prices are influenced by a dynamic interplay of underlying asset’s price, strike price, time to expiration, volatility, and interest rates. As the underlying asset’s price moves in favorable directions, the intrinsic value of the option increases, boosting its price. Closer proximity to the expiration date also enhances the option’s value due to the diminishing time premium. Higher volatility, indicating greater uncertainty in the underlying asset’s price movements, generally translates to higher option prices. Interest rates play a role in determining the cost of carry for the option, impacting its overall price.

Image: www.pinterest.com
Exploring the Spectrum of Options Trading Strategies
Options trading offers a vast array of strategies, catering to diverse risk appetites and market conditions. Here’s a glimpse into some of the most popular strategies:
- Covered Calls: Selling call options against a long position in the underlying asset to generate income while limiting upside potential.
- Protective Puts: Buying put options to hedge against potential losses in a long position.
- Bull Put Spreads: Buying a call option at a higher strike price and selling a call option at a lower strike price, benefiting from a bullish outlook.
- Bear Put Spreads: Selling a put option at a higher strike price and buying a put option at a lower strike price, profiting from a bearish market view.
- Iron Condors: Selling a bull put spread and a bear put spread with different strike prices, aiming for limited gains in a range-bound market.
Mastering the Art of Options Risk Management
While options trading presents immense opportunities, it also comes with inherent risks. Effective risk management strategies are crucial to mitigate potential losses and protect one’s capital. Here are some essential risk management principles:
- Understand Your Risk Profile: Assess your financial situation, risk tolerance, and investment goals before venturing into options trading.
- Diversify Your Portfolio: Spread your risk across multiple underlying assets and option strategies to reduce exposure to any single position.
- Adopt Protective Measures: Utilize hedging strategies, such as buying put options or selling covered calls, to minimize potential losses.
- Set Stop-Loss Orders: Predetermine the maximum loss you’re willing to tolerate and place orders to automatically exit positions if the price moves against you.
- Monitor Your Positions Regularly: Stay vigilant about market conditions and adjust your strategies as needed to manage risk.
Options Trading Xls Edu
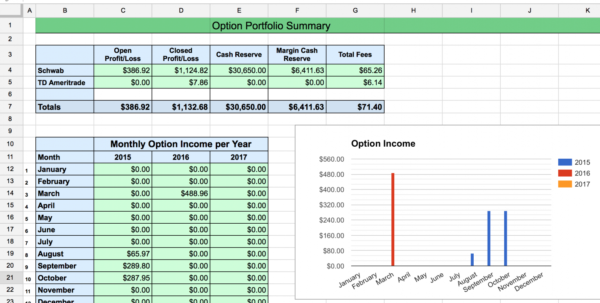
Image: db-excel.com
Conclusion: Options Trading XLs EDU – Empowering Informed Decisions
Options trading, enhanced by the versatility of Excel, has emerged as a powerful tool for investors seeking to amplify their gains, manage risk, and navigate market volatility. This comprehensive guide has provided a solid foundation for understanding the concepts, strategies, and risk management techniques associated with options trading. By leveraging Excel’s analytical prowess, traders can unlock the full potential of options trading and make informed decisions to achieve their financial goals. Remember, the journey of mastering options trading is an ongoing process that requires continued learning and market observation. Embrace the learning curve, embrace the challenges, and make the most of the opportunities that options trading offers.






