Introduction
The allure of options trading lies in its potential for significant returns. Traders are drawn to this financial instrument due to its ability to amplify gains and hedge against market fluctuations. Understanding monthly returns in options trading is crucial for investors seeking success in this dynamic arena.
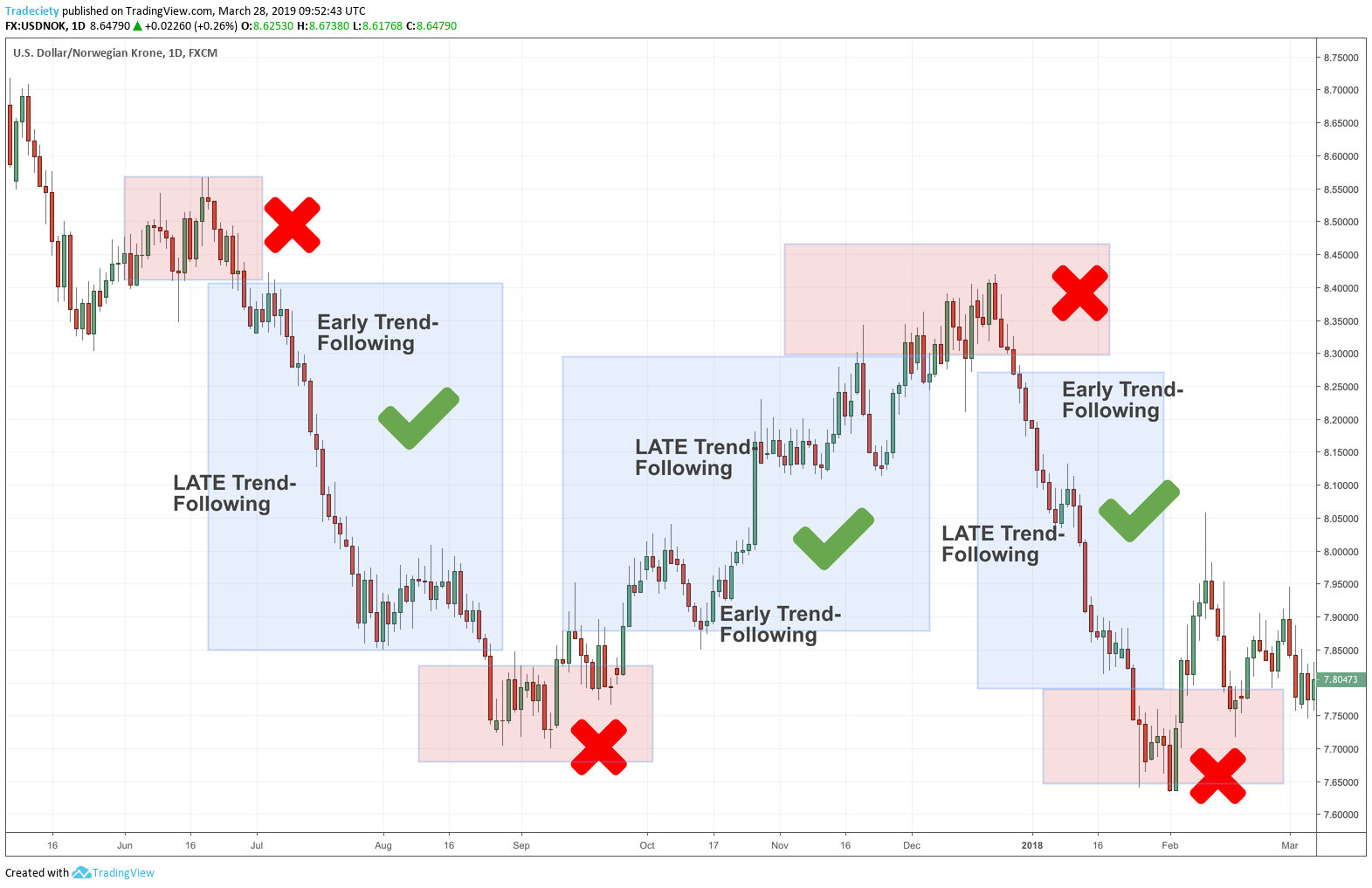
Image: tradeciety.com
Monthly returns in options trading represent the profit or loss incurred during a one-month period. Several factors contribute to these returns, including the underlying asset’s price movement, volatility, and time decay. Traders aiming to optimize monthly returns must navigate these variables and develop a comprehensive trading plan.
The Impact of Underlying Asset’s Price Movement
The fundamental driver of options returns is the movement of the underlying asset’s price. Call options grant the buyer the right to buy the asset at a predetermined price (strike price), while put options confer the right to sell. If the underlying asset’s price rises (falls) above (below) the strike price, the call (put) option will be profitable.
Traders can strategize based on their market outlook. For instance, if they anticipate a surge in the underlying asset’s price, they may purchase call options with a lower strike price. Conversely, if they expect a decline, they may acquire put options with a higher strike price.
Volatility’s Influence on Monthly Returns
Volatility, a measure of price fluctuations, significantly affects options premiums. Higher volatility equates to more expensive options premiums, as it increases the probability of the option expiring in-the-money. Traders can leverage this to their advantage by selling options during periods of high volatility and purchasing them during periods of low volatility.
Time Decay’s Role in Diminuishing Premium
An unavoidable aspect of options trading is time decay, which erodes the premium’s value as time passes. Each day that an option remains unexercised, its value decreases. Traders must consider this when selecting the expiration date of their options and adjust their positions accordingly.
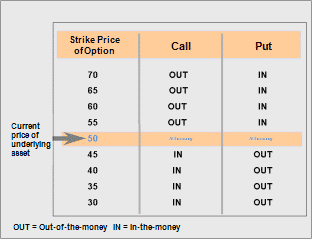
Image: optionstradingiq.com
Hedging Strategies for Risk Management
In addition to seeking potential returns, options trading offers robust risk management strategies. Hedging involves using options to reduce the risk of an existing portfolio. For example, an investor holding a long position in a stock can purchase put options with a strike price slightly below the current market price. This creates a downside hedge, mitigating potential losses in case the stock’s price falls.
Options Trading Montly Returns

Image: www.youtube.com
Conclusion
Monthly returns in options trading are a multifaceted subject, influenced by various factors. Traders seeking success in this domain must possess a comprehensive understanding of the impact of underlying asset’s price movement, volatility, and time decay. By embracing a strategic approach and implementing sound risk management practices, traders can harness the potential of options trading to generate consistent monthly returns. Remember, thorough research, diligent planning, and a disciplined execution are key ingredients in the pursuit of successful options trading.






