Introduction
In the realm of financial markets, options trading stands as a powerful tool that empowers investors to gain exposure to underlying assets without the need for immediate ownership. This versatile instrument has captivated traders for decades, offering the potential for both hefty returns and measured risks. Yet, navigating the complexities of option trading can seem daunting, especially for those new to the investment arena. This comprehensive guide will unravel the intricacies of option trading, providing a clear understanding of how it operates with real-world examples to illuminate its practical applications.

Image: www.plafon.id
What are Options?
Options, in the financial context, are contracts that confer upon their purchaser the right, but not the obligation, to buy (call option) or sell (put option) an underlying asset at a predetermined price (strike price) before a set date (expiration date). The holder of a call option has the privilege to acquire the asset if its market price ascends above the strike price by the expiration date while the owner of a put option benefits from the right to sell the asset if its market price falls below the strike price by the expiration date.
How Do Options Work?
To initiate an options trade, one party (the buyer) pays a premium to the other party (the seller) in exchange for the option contract. The premium represents the price of the option and compensates the seller for assuming the obligation to fulfill the contract if the buyer chooses to exercise their right.
The buyer of an option possesses two fundamental choices: they can either exercise their right to buy or sell the underlying asset at the strike price before the expiration date or let the option expire worthless if it becomes unprofitable to do so. The seller of an option, on the other hand, is obligated to honor the contract if the buyer decides to exercise their right, potentially resulting in the purchase or sale of the underlying asset at the predetermined price.
Types of Options
The world of options trading encompasses two primary types of contracts: call options and put options. While both confer upon the buyer similar rights to buy or sell the underlying asset, they differ in their strategic objectives.
Call options are employed when an investor anticipates an upswing in the underlying asset’s price. If the price of the asset ascends above the strike price before the expiration date, the holder of the call option can exercise their right to purchase the asset at the strike price, potentially generating a profit.
Put options, on the other hand, are utilized when an investor expects the underlying asset’s price to decline. In this scenario, the holder of the put option can exercise their right to sell the asset at the strike price before the expiration date, potentially profiting from the asset’s decreased value.
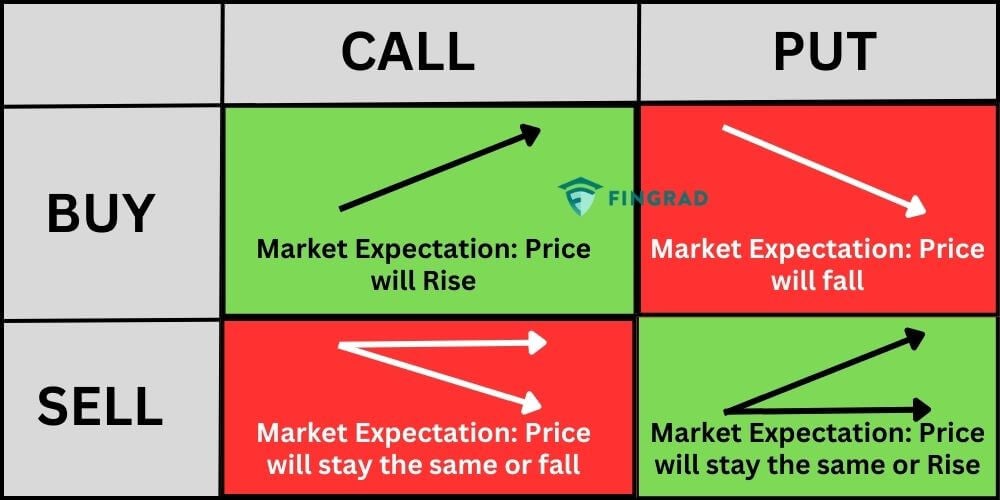
Image: tradebrains.in
Real-World Example of Option Trading
Let’s consider a hypothetical stock option to illustrate how option trading works in practice. Assume that a company’s stock is currently trading at $50 per share. An investor, optimistic about the company’s prospects, purchases a three-month call option with a strike price of $55 for a premium of $5 per share.
If the stock price rises to $60 before the expiration date, the investor can exercise their right to buy the stock at the strike price of $55, resulting in a profit of $5 per share or a total return of $500 (excluding brokerage fees). However, if the stock price falls below $55, the option will expire worthless, and the investor will lose the $5 premium paid for the option.
Key Considerations in Option Trading
Though option trading presents tantalizing prospects for financial gain, it also entails inherent risks that must be carefully weighed. Here are some critical factors to keep in mind when venturing into option trading:
Time decay: The value of an option dwindles over time as it approaches its expiration date. This phenomenon, known as time decay, reduces the likelihood of profit as the option nears its end.
Volatility: The volatility of the underlying asset significantly influences option pricing. Higher volatility typically leads to higher option premiums as investors demand a greater premium to compensate for the increased risk.
Leverage: Options provide a form of leverage, amplifying both potential gains and potential losses. It is essential to exercise caution when employing leverage and to trade within one’s risk tolerance.
How Option Trading Works With Example
The Role of Expert Insights
Seasoned experts in the field of options trading can provide invaluable insights that can enhance your understanding of options trading strategies and help you make informed decisions. Consider seeking guidance from financial advisors, reputable brokers, or experienced traders who can share their expertise and help you navigate the complexities of option trading.
Successful option trading hinges upon a disciplined approach, thorough research, and astute decision-making. While this guide offers a comprehensive overview of how option trading works, it is imperative to invest time in further education, practice, and seeking expert guidance to empower yourself with the knowledge and skills necessary for successful option trading.






