Unlocking the World of Options Trading
In the labyrinthine world of financial markets, options trading stands as an alluring yet intricate realm. Options, financial instruments derived from underlying assets like stocks or indices, offer a sophisticated means to speculate on price movements, hedge against risks, and augment income. However, as aspiring traders delve into this intriguing domain, it is imperative to decipher the nuanced complexities surrounding options trading costs. This comprehensive guide illuminates the intricate web of expenses associated with options trading, empowering readers with the knowledge to navigate this financial landscape with precision and efficiency.
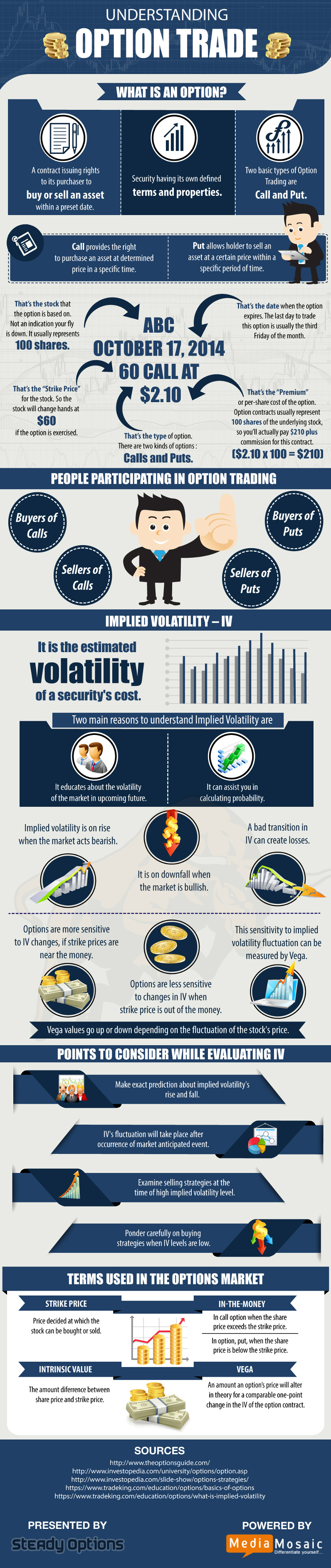
Image: www.visualcapitalist.com
Deconstructing Options Trading Costs
To fully comprehend the multifaceted nature of options trading costs, it is essential to dissect the individual components that contribute to the overall expenses involved in these transactions. These costs can be broadly categorized into two primary types: commissions and premiums.
Commissions
Commissions represent the fees charged by brokerage firms or trading platforms for facilitating options trades. These costs can vary significantly depending on the broker, the type of option, and the trading volume. Discount brokers typically offer lower commissions than full-service brokers, while complex options strategies may incur higher commission rates. It is crucial to compare commission structures across different brokers before selecting a trading platform to optimize cost efficiency.
Premiums
Premiums, on the other hand, encompass the price paid to acquire options contracts. The premium reflects the market’s assessment of the likelihood that the option will expire in-the-money, granting the holder the right to exercise the option at a predetermined price. Premiums are directly influenced by factors such as the underlying asset’s price, time until expiration, volatility, and interest rates. Understanding how premiums are calculated is essential for evaluating the potential profitability of options trades.

Image: www.tradethetechnicals.com
Options Trading Costs

Image: www.tradestation.com
Additional Considerations
Along with commissions and premiums, there are several ancillary costs associated with options trading that warrant consideration. These include:
- Exercise fees: Fees charged when an option holder exercises the right to buy or sell the underlying asset.
- Assignment fees: Fees paid by the option writer if an option is assigned (exercised) before expiration.
- Regulatory fees: Government-imposed fees associated with options trading, such as the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) fee.
It is imperative to factor in these additional costs when calculating the overall expenses associated with options trading.






