Unveiling the Options Market: A Gateway to Risk and Reward
Venture into the captivating world of options trading, where strategic choices intertwine with calculated risks, paving the path to potential profits. An option contract offers a right, not an obligation, to buy (call option) or sell (put option) an underlying asset, such as stocks, at a specified price (strike price) on a predefined date (expiration date). This flexibility allows traders to tailor their strategies to their risk tolerance and market outlook, making options an indispensable tool in the financial landscape.
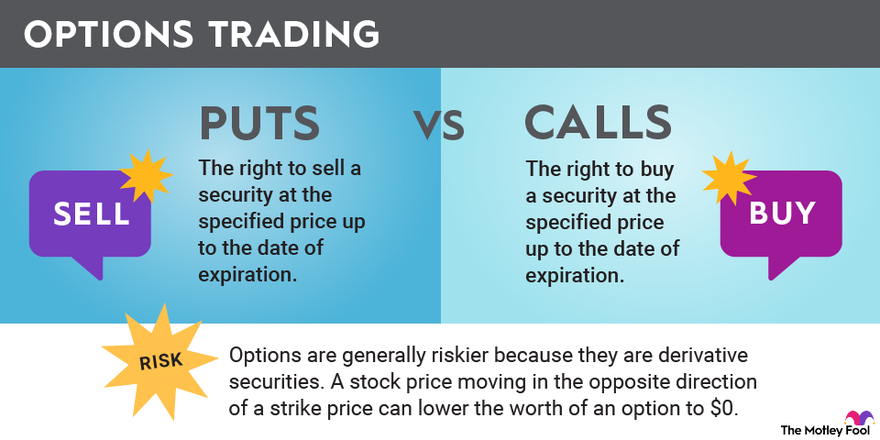
Image: www.fool.com
Deciphering the Nuances of Option Characteristics
Options are multifaceted financial instruments, each possessing a unique set of characteristics that influence their value. Understanding these characteristics is crucial for effective options trading:
- Type: Options fall into two distinct types: call and put. A call option grants the holder the right to buy the underlying asset, while a put option confers the right to sell.
- Strike Price: This predefined price represents the price at which the trader can buy or sell the underlying asset.
- Expiration Date: The contract’s expiration date marks the day beyond which the option becomes worthless. Options typically expire on the third Friday of each month.
- Premium: The price paid to acquire an option contract is called the premium. This non-refundable payment represents the value of the option’s potential rights.
- Volume and Open Interest: Volume refers to the number of option contracts traded in a given period, while open interest measures the number of contracts outstanding at any given time. These indicators provide insights into market sentiment and liquidity.
Navigating Options Trading: The Risks Involved
While options provide opportunities for substantial gains, they also carry inherent risks that traders must carefully consider:
- Unlimited Loss Potential for Call Options: The potential loss for a call option buyer is theoretically unlimited, as the underlying asset can rise indefinitely.
- Limited Profit Potential for Put Options: In contrast, the profit potential for a put option buyer is limited to the premium paid, as the underlying asset cannot fall below zero.
- Time Decay: As the expiration date approaches, the option’s value decays due to the declining probability of it being exercised profitably.
- Volatility Risk: Options are sensitive to changes in the underlying asset’s price volatility. High volatility increases option premiums but also amplifies potential losses.
- Liquidity Risk: Some options may have low trading volume, making it difficult to enter or exit positions quickly without incurring significant slippage.
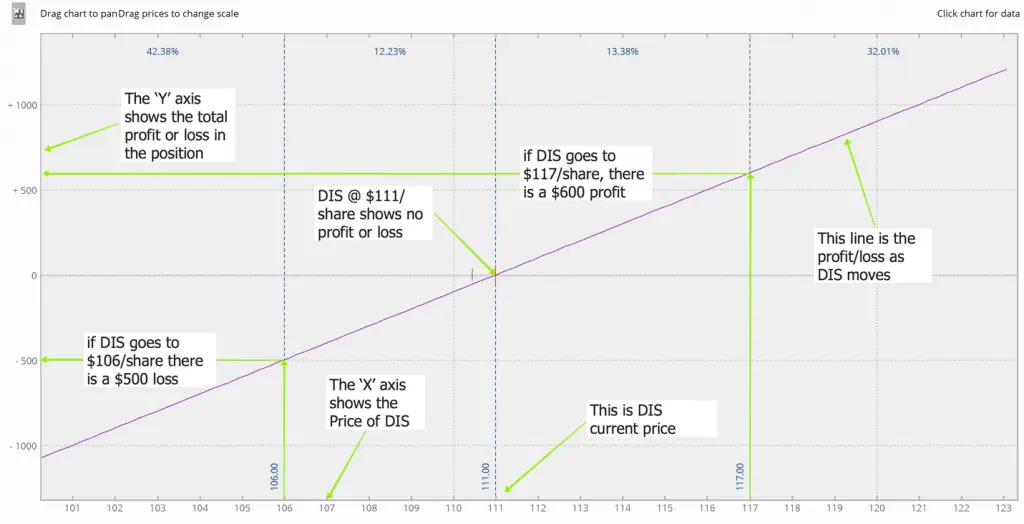
Image: www.newtraderu.com
Options Trading Characteristics And Risks

Image: www.tradingmadeez.com
Conclusion: Mastering Options Trading
Venturing into options trading demands a thorough understanding of the instrument’s characteristics and an acknowledgment of the risks involved. With a deep understanding of the option’s anatomy, traders can craft strategies that align with their risk tolerance and market predictions. Embrace the complexities of options trading, traverse its challenges with calculated measures, and unlock its potential for substantial rewards.






