Navigating the world of options trading can be daunting, but understanding the nuances of specific strategies is crucial for success. Buying put options is a technique that provides both protection from potential losses and opportunities for income generation. In this in-depth guide, we’ll delve into the essentials of buying put options, exploring their definition, purpose, and powerful applications.
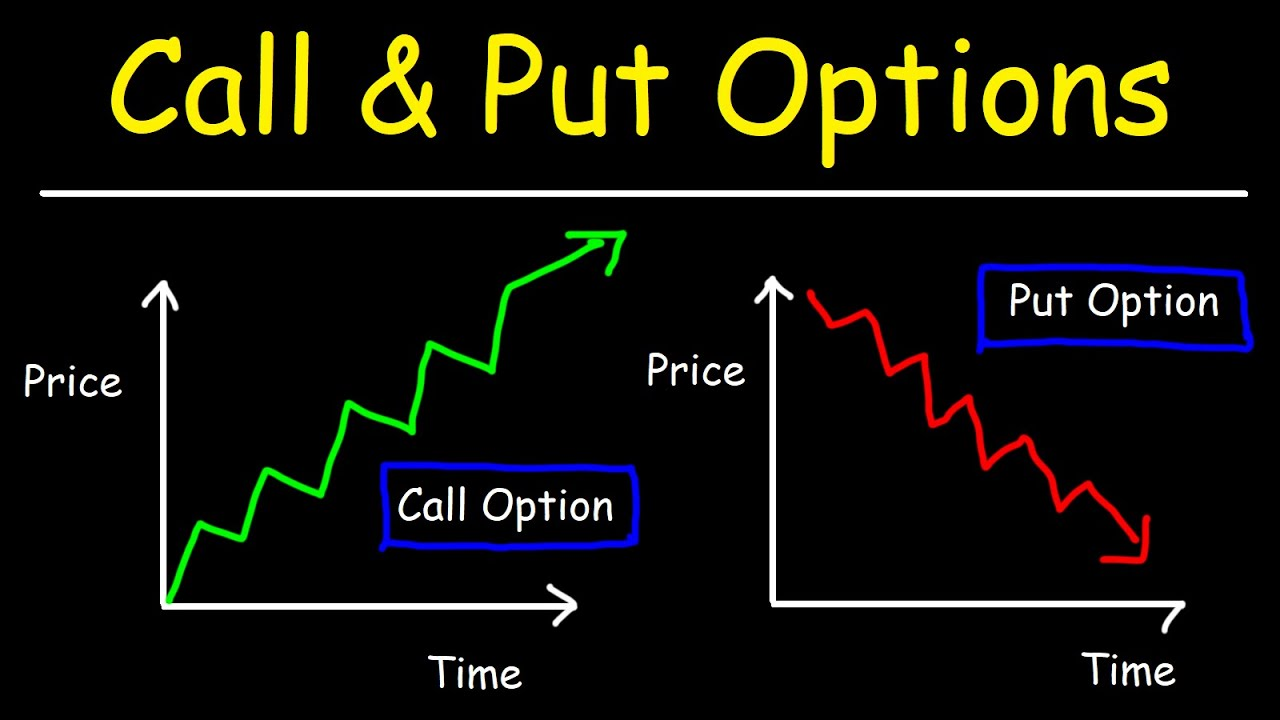
Image: tradewithmarketmoves.com
What Are Put Options?
Put options convey the right, but not the obligation, to sell a specific asset at a predetermined price (the strike price) on or before a certain date (the expiration date). When you buy a put option, you’re essentially acquiring the right to sell the underlying asset at the strike price, regardless of its actual market value. This strategy is commonly employed for two primary purposes: hedging and profit generation.
Hedging against Risk
Buying put options offers a valuable tool for risk management in options trading. By establishing a floor price for your assets, put options provide downside protection, limiting your potential losses in case of an unfavorable market movement. This hedging strategy is particularly beneficial for investors seeking to safeguard their portfolios from potential downturns.
Profit Generation through Option Premiums
Beyond hedging, buying put options can also generate profits through option premiums. When the underlying asset’s price falls below the strike price, the put option holder has the right to exercise their option and sell at the strike price. This creates an opportunity to profit from the asset’s price decline, which can be especially lucrative in volatile markets.

Image: www.pinterest.co.uk
How to Buy Put Options
To execute a put option purchase, follow these steps:
- Select the underlying asset: Identify the asset or security you intend to hedge or profit from.
- Determine the strike price: Specify the price at which you have the right to sell the asset.
- Choose the expiration date: Establish the period during which you can exercise your option.
- Buy the put option: Purchase the put option contract at the agreed-upon premium.
Current Trends and Developments
The options trading market continues to evolve, propelled by technological advancements and market volatility. Here are some emerging trends:
- Virtual trading platforms: Online platforms empower traders with user-friendly interfaces and advanced trading tools.
- Increased algorithmic trading: Computers employ complex algorithms to execute trades based on predefined parameters.
- Rise of exotic options: Options with non-standard features, such as barrier options and binary options, gain popularity.
Tips and Expert Advice
Follow these tips from seasoned traders to enhance your put option trading strategy:
- Understand the risks: Grasp the potential risks associated with buying put options and determine your risk appetite.
- Manage your premiums wisely: Calculate the premiums and consider the potential rewards to make informed decisions.
- Set clear profit goals: Establish realistic profit targets before entering an options trade.
- Monitor market conditions: Stay abreast of market news and economic data that may impact the underlying asset’s price.
- Seek professional guidance: Consult with a financial advisor or broker to ascertain which options trading strategies align with your risk tolerance and investment objectives.
Remember, experience plays a crucial role in mastering any trading technique. Practice paper trading or start with smaller investments to hone your skills gradually.
FAQs
Q: What determines the premium of a put option?
A: The premium is influenced by factors such as the current price of the underlying asset, strike price, time to expiration, and market volatility.
Q: What is the difference between buying a put option and selling a covered put?
A: Buying a put option grants you the right to sell, while selling a covered put obligates you to sell the underlying asset if the option is exercised.
Q: What are the potential drawbacks of buying put options?
A: The option may expire worthless if the underlying asset’s price doesn’t fall below the strike price, resulting in a loss of the premium paid.
Options Trading Buy Put
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/BuyingPuts-d28c8f1326974c16807f23cb32854501.png)
Image: www.investopedia.com
Conclusion
Buying put options is a multifaceted strategy with both risk management and profit generation capabilities. By understanding the fundamentals, current trends, and expert advice, you can harness the power of options trading to expand your portfolio’s defensive and offensive capabilities. If you’re intrigued by the potential benefits of this technique, we encourage you to delve deeper into the world of options trading and explore the numerous opportunities it offers.






