Embarking on the exhilarating world of options trading can be akin to navigating a labyrinthine maze, fraught with uncharted terrains and potential pitfalls. However, with the right knowledge and a steadfast approach, you can unravel its complexities and reap the rewards it offers. This article serves as a comprehensive guide to options trading basics, designed to equip you with the fundamental understanding necessary to embark on this transformative financial journey.
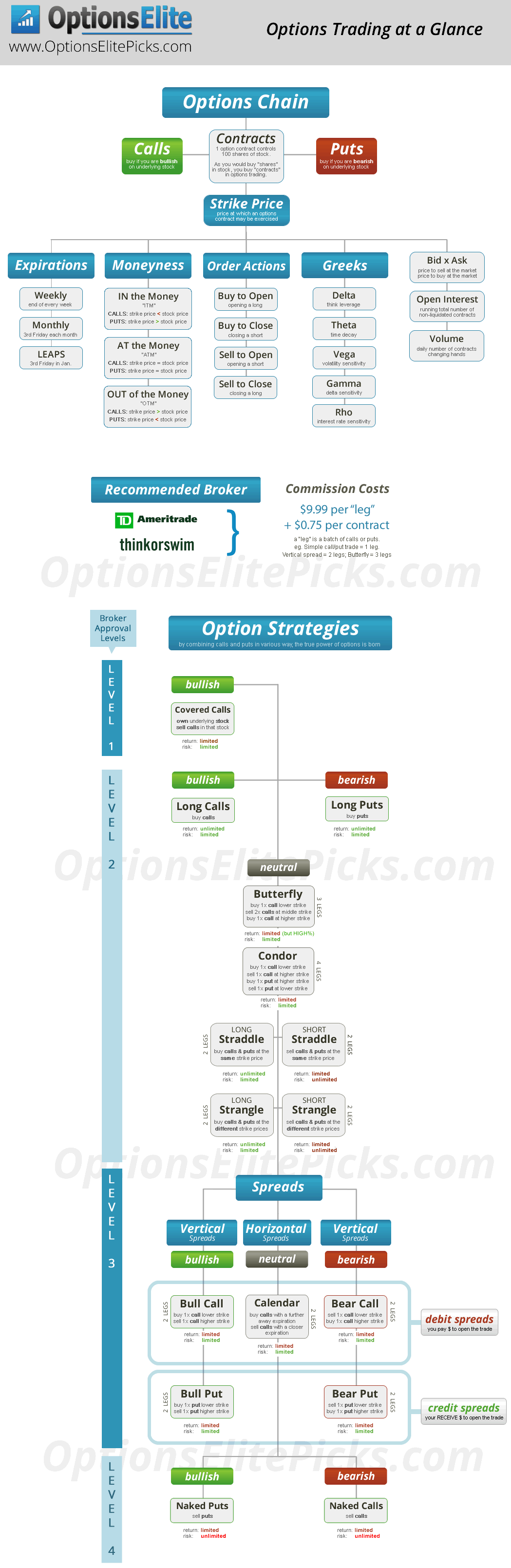
Image: thestockmarketwatch.com
What Options Trading Entails
Options, in the realm of finance, are contracts that grant the holder the right, but not the obligation, to buy (in the case of call options) or sell (in the case of put options) a specified asset (known as the underlying asset) at a predetermined price (the strike price) on or before a specific date (the expiration date). The buyer of an option pays a premium to the seller in exchange for this right, without any further obligation.
The significance of options trading stems from its versatility and potential for profit generation. Call options provide the opportunity to capitalize on anticipated price increases in the underlying asset, while put options offer protection against potential declines in value. This flexibility allows investors to tailor their trading strategies to their specific risk tolerance and financial goals.
Anatomy of an Options Contract
At the heart of every options contract lies a constellation of essential elements that determine its characteristics and value. These elements serve as the building blocks of options trading and a thorough understanding of each is crucial for informed decision-making.
-
Underlying Asset: Options contracts derive their value from the performance of an underlying asset. This asset could be a stock, bond, index, commodity, or even a basket of assets.
-
Strike Price: The strike price represents the price at which the buyer has the right to buy (call option) or sell (put option) the underlying asset.
-
Expiration Date: This date marks the end of the contract’s life. The option can be exercised up until the expiration date.
-
Call Option: A call option grants the holder the right to buy the underlying asset at the strike price on or before the expiration date.
-
Put Option: Conversely, a put option confers the right to sell the underlying asset at the strike price on or before the expiration date.
-
Premium: The premium is the price paid by the buyer to the seller in exchange for the option contract. The premium is determined by factors such as the strike price, time to expiration, volatility, and supply and demand.
Types of Options Strategies
The realm of options trading offers a vast array of strategies, each meticulously crafted to align with specific market conditions and investment objectives. Whether you seek to harness market momentum, hedge against potential losses, or generate income through premiums, there’s a strategy designed to meet your needs.
-
Covered Call: This conservative strategy involves selling (writing) a call option while simultaneously owning the underlying asset. Suitable for bullish or neutral market views, it generates income from the sale of the premium while limiting potential upside gains.
-
Cash-Secured Put: Similar to a covered call, this strategy entails selling (writing) a put option while holding cash equal to the strike price in your trading account. It provides a source of income and protects against potential declines in the underlying asset’s value.
-
Bull Call Spread: This bullish strategy combines the purchase of a lower-strike call option with the sale (writing) of a higher-strike call option. It offers limited profit potential but provides protection against large market swings.
-
Bear Put Spread: Tailored for bearish market views, this strategy involves the sale (writing) of a lower-strike put option coupled with the purchase of a higher-strike put option. It benefits from market declines but has limited profit potential.
-
Straddle: This neutral strategy involves purchasing both a call option and a put option with the same strike price and expiration date. It profits from significant price movements in either direction but requires a large upfront investment.

Image: www.pinterest.es
Trading Options: A Step-by-Step Guide
Embarking on your options trading journey can be an exhilarating yet daunting experience. To ensure a smooth and informed start, follow these steps:
-
Select a Broker: The first step involves choosing a reputable options brokerage firm. Look for a platform that offers a user-friendly interface, competitive pricing, and a wide range of options contracts.
-
Open an Account: Create an account with your chosen broker, providing personal information and financial details for verification.
-
Deposit Funds: Transfer funds into your trading account to cover the purchase price of options contracts and any applicable commissions and fees.
-
Research and Select Contracts: Meticulously research underlying assets and identify options contracts that align with your investment objectives and risk tolerance. Consider factors such as strike price, expiration date, and implied volatility.
-
Place an Order: Once you’ve selected an options contract, place an order through your broker’s platform. Specify the type of option (call or put), the strike price, the expiration date, and the quantity you wish to trade.
-
Monitor and Manage Positions: Regularly monitor your options positions by tracking their value and risk profile. Adjust your strategy if necessary based on market conditions and performance against预期。
Options Trading Basics Free

Image: kingtradingsystems.com
Conclusion
Mastering the intricacies of options trading requires a steadfast commitment to learning, disciplined risk management, and a refined understanding of market dynamics and option contract characteristics. By adhering to the principles outlined in this guide, you can navigate the ever-changing financial landscape, empowering yourself with the tools to capitalize on market opportunities and safeguard your investments. Remember to approach this endeavor with a thirst for knowledge and a willingness to continually evolve your strategies. As you embark on this path, you may encounter formidable challenges, but with perseverance and an insatiable curiosity for financial markets, you can unlock the transformative potential that options trading has to offer.






