Are you ready to step into the fast-paced world of options trading? Embarking on this financial adventure requires a solid understanding of the basics. This beginner’s guide is your roadmap to unravel the complexities of option trading, equipping you with the knowledge to navigate this dynamic market.
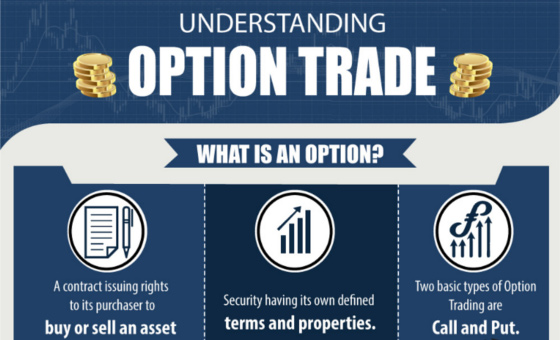
Image: www.visualcapitalist.com
Demystifying Options Trading: A Beginner’s Perspective
Options trading involves contracts that grant you the right, but not the obligation, to buy (call option) or sell (put option) an underlying asset, such as a stock, at a specified price (strike price) on or before a certain date (expiration date). Unlike futures contracts, which obligate you to complete the transaction, options provide you with flexibility and the potential for both profit and loss.
Call Options: A Right to Buy, Limitless Profits
Call options give you the right to purchase the underlying asset at the strike price. If the market price of the asset exceeds the strike price, you can exercise your option and buy the asset, potentially profiting from the price difference. However, if the asset’s price remains below the strike price, you lose the premium you paid for the option but retain the right to sell it to another trader.
Put Options: A Right to Sell, Capped Profits
Put options grant you the right to sell the underlying asset at the strike price. When the market price of the asset falls below the strike price, you can exercise your option and sell the asset, profiting from the price difference. If the asset’s price remains above the strike price, you lose the premium you paid for the option.

Image: savoteur.com
Understanding Option Premiums: The Price of Flexibility
Option premiums are the price you pay to purchase an option contract. They reflect the market’s perception of the underlying asset’s price movement and the time remaining until expiration. Premiums can fluctuate rapidly, influenced by factors such as market volatility, interest rates, and supply and demand.
Essential Terminology: Navigating the Option Market
- Strike Price: The price at which you can buy (call option) or sell (put option) the underlying asset.
- Expiration Date: The date on which your option contract expires.
- Premium: The cost of purchasing an option contract.
- Underlying Asset: The asset (e.g., stock, commodity, currency) on which an option contract is based.
- In-the-Money (ITM): When the market price of the underlying asset is above the strike price (for call options) or below the strike price (for put options), making it profitable to exercise the option.
- Out-of-the-Money (OTM): When the market price of the underlying asset is below the strike price (for call options) or above the strike price (for put options), making it unprofitable to exercise the option.
Getting Started: Choosing Your Options Trading Strategy
Options trading strategies vary widely, ranging from simple to complex. Newbies should start with strategies that minimize risk, such as:
- Covered Call: Selling a call option against shares you own.
- Cash-Secured Put: Selling a put option with the cash to cover potential assignment.
- Bull Call Spread: Buying a call option with a lower strike price and simultaneously selling a call option with a higher strike price.
- Bear Put Spread: Selling a put option with a higher strike price and simultaneously buying a put option with a lower strike price.
Risk Management: Understanding the Potential Drawbacks
Option trading involves inherent risks that can lead to financial losses. It’s crucial to practice risk management techniques to mitigate potential pitfalls:
- Set Trading Limits: Determine a budget for option trading to avoid excessive risk.
- Diversify Your Portfolio: Spread your trades across different options and underlying assets.
- Use Stop-Loss Orders: Set orders that automatically exit your positions if they reach a certain loss threshold.
- Avoid Leverage: Trading options on margin can amplify both profits and losses.
Option Trading Newbies Pdf
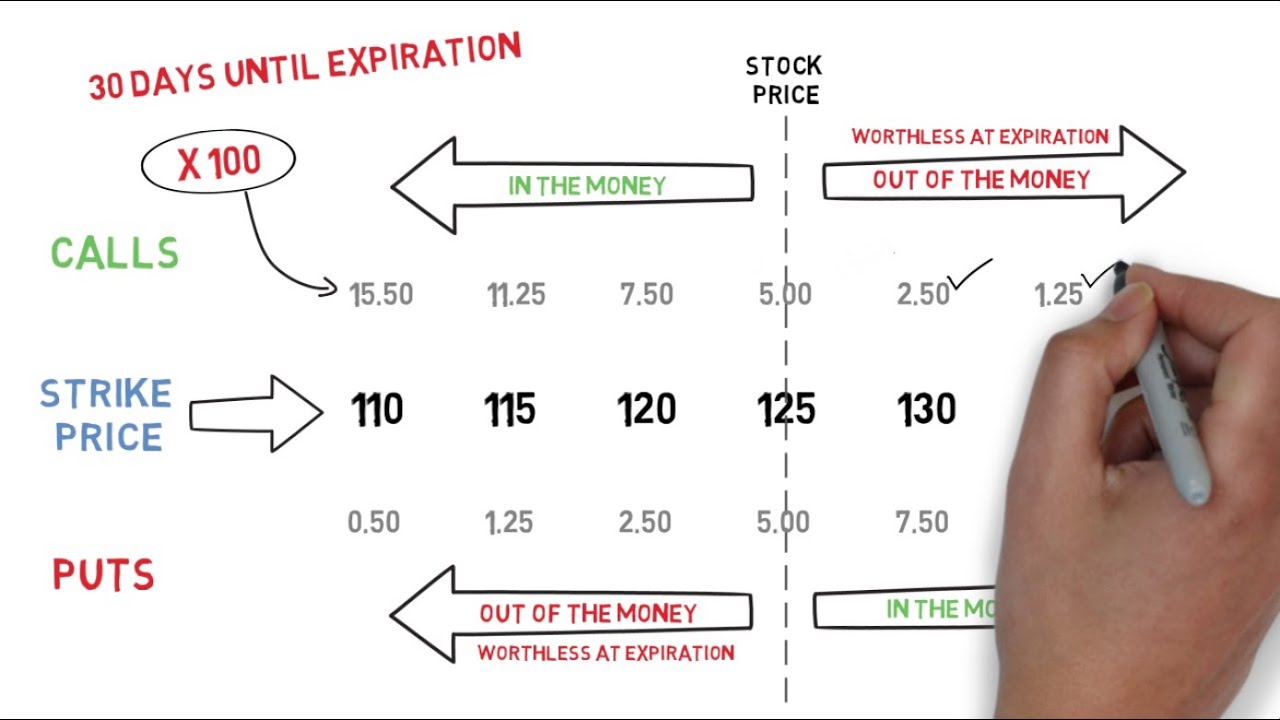
Image: www.youtube.com
Conclusion
Navigating the option trading landscape as a newbie requires a comprehensive understanding of basic concepts, strategies, and risk management. This guide has provided a solid foundation for your option trading journey. By leveraging the knowledge presented here, you can unlock the potential for financial success while mitigating associated risks. Remember to consult with financial professionals for personalized advice and always approach options trading with a thoughtful and strategic mindset.






