Option trading has emerged as a popular investment strategy for its potential to generate high returns. However, understanding the tax implications of option trading is crucial to avoid unexpected liabilities. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the nuances of capital gains tax as they apply to option trading, providing insights into the latest trends and developments, and sharing expert advice to help you optimize your tax strategy.

Image: www.basunivesh.com
**Capital Gains Tax: A Primer**
Capital gains tax is levied on the profits realized from the sale of an asset, such as stocks or options. The tax rate applicable to capital gains depends on several factors, including the holding period of the asset and your taxable income. Short-term capital gains, derived from assets held for less than one year, are taxed at your ordinary income tax rate. Conversely, long-term capital gains, arising from assets held for over a year, are taxed at a lower rate. It’s important to note that the tax rates for long-term capital gains vary depending on your overall income.
**Option Trading and Capital Gains Tax**
Option trading involves buying or selling contracts that provide the holder the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a specified price within a certain period. When an option is sold for a profit, the gain is subject to capital gains tax. The tax treatment of option gains largely depends on whether the option is classified as a short-term or long-term asset.
Short-term option gains, generated from options held for less than one year, are treated as short-term capital gains and taxed at ordinary income tax rates. Long-term option gains, resulting from options held for over a year, qualify as long-term capital gains and are taxed at preferential rates. It’s important to note that the holding period for options begins on the day following the date of purchase and ends on the day of sale, regardless of the expiration date of the option.
**Latest Trends and Developments**
The taxation of option trading has undergone several changes in recent years. The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017 significantly altered the capital gains tax landscape, introducing new tax rates and modifying the holding period requirements. Additionally, the IRS has issued guidance clarifying the classification of certain option strategies, such as the sale of covered call options and the purchase of protective puts.
To stay abreast of the latest developments, it’s advisable to monitor updates from the IRS and consult with a qualified tax professional. Keeping up with the regulatory changes can help you navigate the tax implications of option trading more effectively.
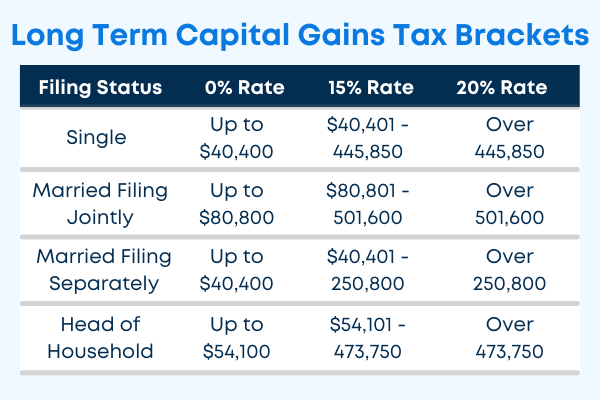
Image: www.aiohotzgirl.com
**Expert Advice: Optimizing Your Tax Strategy**
To optimize your tax strategy for option trading, consider implementing the following tips:
- Plan your trades strategically, identifying opportunities to offset short-term gains with long-term losses.
- Utilize tax-advantaged accounts, such as IRAs or 401(k)s, to defer or avoid capital gains tax on option trading profits.
By incorporating these strategies, you can potentially reduce your tax liability and enhance the overall returns on your option trading activities.
**Frequently Asked Questions**
Q: What is the difference between short-term and long-term capital gains?
A: Short-term capital gains are taxed at ordinary income tax rates, while long-term capital gains are taxed at preferential rates.
Q: How do I determine the holding period for options?
A: The holding period for options begins on the day following the date of purchase and ends on the day of sale.
Q: Can I use tax-advantaged accounts for option trading?
A: Yes, you can use IRAs or 401(k)s to defer or avoid capital gains tax on option trading profits.
Option Trading Capital Gains Tax

Image: www.youtube.com
**Conclusion**
Understanding the tax implications of option trading is essential for informed decision-making and maximizing your returns. By navigating the complexities of capital gains tax, you can optimize your tax strategy, plan your trades strategically, and potentially reduce your tax liability. Remember to consult with a qualified tax professional for personalized guidance and stay abreast of the latest regulatory changes to ensure compliance and leverage the most up-to-date tax-saving strategies. As you embark on the journey of option trading, remember to assess your own interest and risk tolerance before making any investment decisions.






