Introduction:
The world of options trading offers a plethora of opportunities to savvy investors seeking to enhance their portfolios. However, understanding the nuances of the Wash Sale Rule is crucial to avoid costly missteps. This rule prohibits traders from claiming tax losses on sold securities if they have acquired similar or identical securities within a specific timeframe.
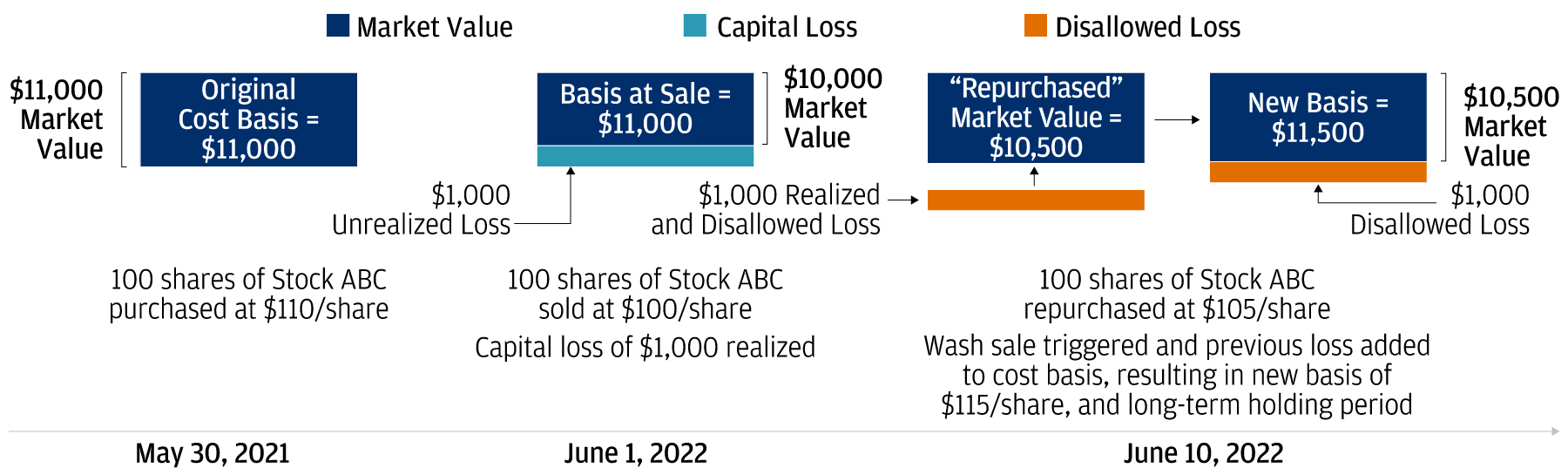
Image: privatebank.jpmorgan.com
In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the fundamentals of option trading, unraveling the complexities of the Wash Sale Rule, and providing strategies to avoid its potential pitfalls.
Delving into Option Trading:
Option trading involves the buying and selling of contracts that grant investors the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a predetermined price and date. Options can be categorized as calls or puts, depending on whether the trader anticipates an increase or decrease in the asset’s value.
Calls confer the right to buy, while puts offer the right to sell an asset. Options provide investors with the potential for significant gains, but they also carry varying degrees of risk based on factors such as time decay, market volatility, and the underlying asset’s performance.
Navigating the Wash Sale Rule:
The Wash Sale Rule was enacted to curb tax avoidance tactics where traders sold an asset at a loss and then immediately repurchased the same or similar asset to claim the loss as a tax deduction.
According to the rule, a wash sale occurs when:
- The taxpayer sells a security or option at a loss.
- Within 30 days before or after the sale, the taxpayer acquires a substantially identical security or option.
When a wash sale occurs, the disallowed loss is added to the taxpayer’s cost basis in the new security. This means the trader will recoup less when they eventually sell the replacement security.
Exceptions to the Wash Sale Rule:
There are a few exceptions to the Wash Sale Rule:
- If the transaction is part of an estate, it won’t trigger a wash sale.
- If the original security or option sold was worthless, it also won’t trigger a wash sale.

Image: fomo-investor.com
Avoiding Wash Sales in Option Trading:
To avoid wash sales while trading options, adhere to the following guidelines:
- Ensure there is a gap of more than 30 days between the sale and the purchase of the same or a similar option.
- Avoid selling an option at a loss and acquiring shares of the underlying asset within 30 days.
- If a wash sale has occurred, consider the impact on your tax returns carefully.
Impact of Wash Sales on Option Trading Strategies:
The Wash Sale Rule can impact option trading strategies in various ways. For instance, it may prevent investors from harvesting losses for tax purposes. This stipulation can affect strategies that involve frequent trading and profit-taking.
Additionally, traders need to be mindful of the implications when rolling over options contracts due to the potential for triggering a wash sale.
Option Trading Basics Against Wash Sale Rule
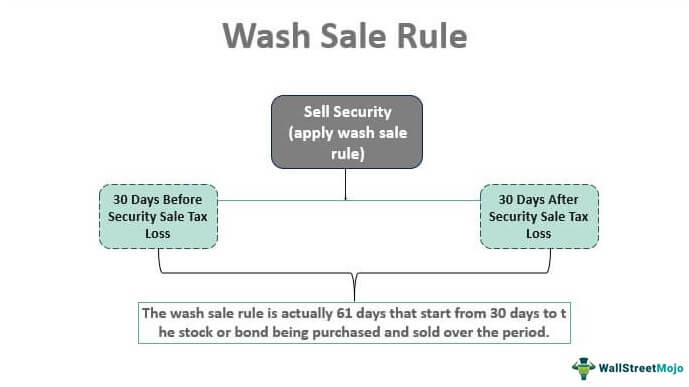
Image: usefidelity.com
Conclusion:
Understanding the Wash Sale Rule and exercising due diligence to avoid its pitfalls is paramount for successful option trading. By adhering to the guidelines and staying informed about any changes to the rule, traders can reap the benefits of options trading while minimizing tax implications.
Remember, it’s always prudent to consult with a tax professional before engaging in any substantial trading activity to receive personalized advice based on your financial situation.






