In the fast-paced and ever-evolving world of finance, options trading has emerged as a powerful tool for savvy investors seeking to amplify their returns. However, mastering the intricacies of option trading accounting is crucial to maximizing profits and navigating potential risks.
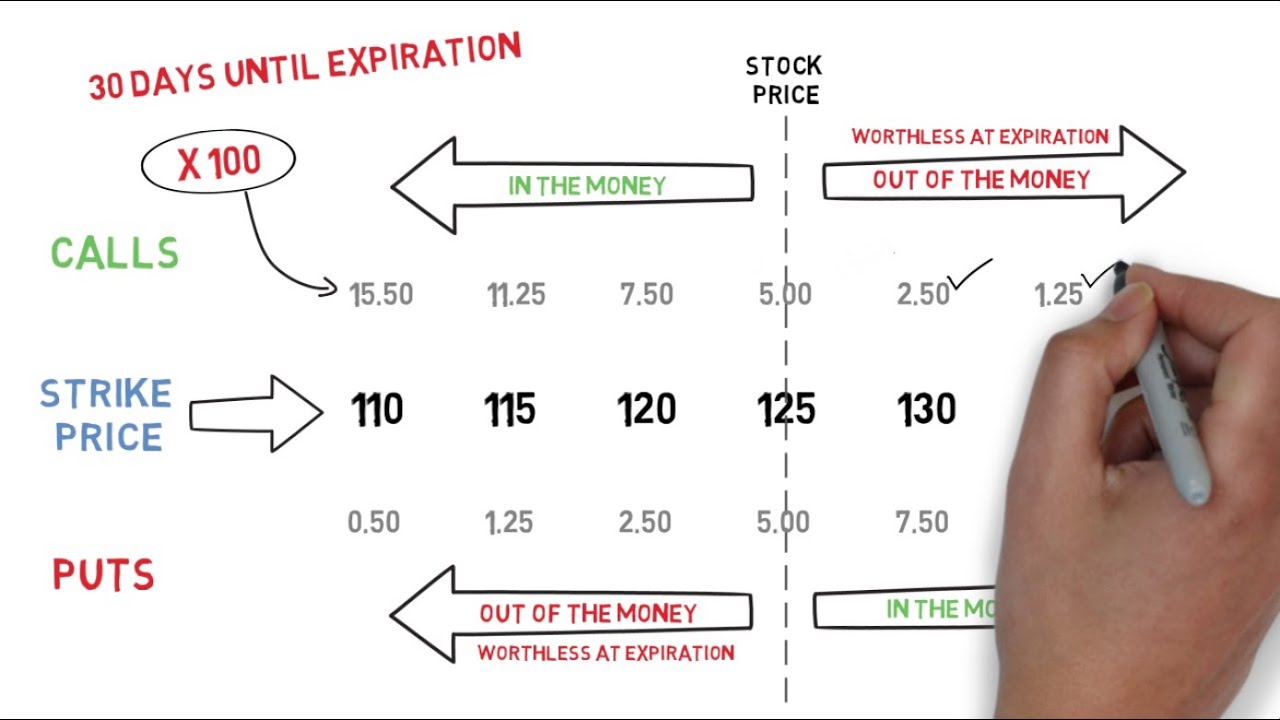
Image: tikloenglish.weebly.com
Option trading involves the buying and selling of options, which are contracts that grant the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a specified price on or before a certain date. The accounting treatment of options can be complex, but with a clear understanding, investors can optimize their trading strategies.
Understanding the Basics of Option Trading Accounting
At the heart of option trading accounting lies the concept of recognizing gains and losses. When an option is purchased, it is recorded as an asset on the investor’s balance sheet. If the option expires worthless, the entire cost of the option is recognized as a loss. However, if the option is exercised or sold for a profit, the difference between the proceeds and the original cost is recorded as a gain.
The timing of the recognition of gains and losses depends on whether the option is classified as a “short-term investment” or a “long-term investment.” Short-term investments are generally those held for less than one year, and their gains and losses are recognized in the income statement. Long-term investments are held for more than one year, and their gains and losses are recognized in other comprehensive income (OCI).
Marked-to-Market Accounting for Options
To ensure the accurate valuation of options, the concept of marked-to-market accounting is employed. This process involves adjusting the carrying value of options on the balance sheet to reflect their current market price. Mark-to-market accounting provides investors with an up-to-date assessment of their portfolio’s value and allows them to react accordingly to market fluctuations.
Accounting for the Different Types of Options
Option trading encompasses various types of options, each with specific accounting implications. Some of the most common options include:
- Call Options: Grant the buyer the right to buy the underlying asset at a specified price. Calls are recorded as assets and can result in gains if exercised or sold for a profit.
- Put Options: Grant the buyer the right to sell the underlying asset at a specified price. Puts are recorded as liabilities and can lead to gains if exercised or sold for a profit.
- Covered Calls: Involve selling a call option while owning the underlying asset. Covered calls are considered short-term investments and are accounted for under the income statement.
- Cash-Settled Options: Do not involve the physical delivery of the underlying asset. Cash-settled options are settled in cash, and their gains and losses are recognized at the time of settlement.
Image: db-excel.com
Expert Insights into Option Trading Accounting
Jeff Willard, a renowned option trading expert, emphasizes the importance of understanding the tax implications of option trading. He advises consulting with a tax professional to optimize tax strategies and minimize liabilities.
Furthermore, Mark J. Walsh, a seasoned options trader and author, stresses the significance of maintaining accurate records. Meticulous documentation of all option trading activities facilitates tax reporting and enhances portfolio monitoring.
Proven Strategies for Success
To enhance profitability in option trading, investors can adopt the following strategies:
- Utilize Market Orders: Market orders ensure the immediate execution of trades at the current market price, saving investors valuable time and minimizing the risk of unfavorable price movements.
- Maximize Volatility: Options gain value from volatility, so selecting options with high implied volatility can increase profit potential. However, investors should exercise caution and manage risk accordingly.
- Consider Technical Analysis: Technical analysis techniques, such as charting and indicators, can provide valuable insights into market trends and support informed trading decisions.
Option Trading Accounting

Image: s3.amazonaws.com
Conclusion
Option trading accounting is an indispensable aspect of successful option trading. By embracing accurate accounting practices, investors can not only enhance their profitability but also mitigate potential risks. Understanding the nuances of option trading accounting empowers investors to make informed decisions, optimize their portfolios, and achieve their financial goals.






