Trading options can be a lucrative avenue for generating income, but it also carries inherent risks that must be thoroughly understood before diving in. One crucial aspect to grasp is the obligation to pay for trading options. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the ins and outs of this obligation, empowering you with the knowledge to navigate the world of options trading confidently.

Image: financetrain.com
Understanding the Basics: What is an Option Contract?
An option contract is a derivative instrument granting the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a predetermined price (strike price) on or before a specific date (expiration date). Buyers of options pay a premium to the seller for this right, while sellers receive the premium in exchange for the obligation to fulfill the contract if the buyer exercises it.
Types of Options Contracts
There are two main types of options contracts: calls and puts.
-
Call options give the buyer the right to buy the underlying asset at the strike price. If the asset’s market price rises above the strike price, the call option becomes “in the money” (profitable) and can be exercised for a profit.
-
Put options give the buyer the right to sell the underlying asset at the strike price. When the asset’s market price falls below the strike price, the put option becomes “in the money” and can be exercised for a profit.
The Obligation to Pay: Key Considerations for Option Sellers
As the seller of an option contract, you have the obligation to fulfill the terms of the contract if the buyer exercises it. This means you must be prepared to buy or sell the underlying asset at the agreed-upon strike price, regardless of the market conditions at that time.
Several factors determine the extent of the seller’s obligation:
-
Type of option contract: The obligation differs based on whether the option is a call or a put. Call sellers are obligated to sell the underlying asset at the strike price if the call option is exercised. Put sellers are obligated to buy the underlying asset at the strike price if the put option is exercised.
-
Exercise price: The strike price will determine the extent of the seller’s obligation. If the market price of the underlying asset is significantly different from the strike price when the option is exercised, the seller may face substantial financial losses or gains.
-
Expiration date: The expiration date specifies the timeframe within which the option can be exercised. If the option is not exercised by the expiration date, it expires worthless, and the seller retains the premium received at the time of the sale.

Image: www.clipartpanda.com
Managing the Risks: Strategies for Sellers
Managing the risks associated with the obligation to pay is crucial for option sellers to protect their financial interests. Several strategies can be employed to mitigate potential losses:
-
Position sizing: Carefully determine the number of option contracts to sell based on your risk tolerance and financial capacity. Selling more contracts increases the potential obligation and risks.
-
Hedging: Implement hedging strategies to reduce exposure to market fluctuations. Common hedging techniques include buying or selling opposite options or using futures contracts.
-
Selling covered options: Consider selling covered calls or puts where you own or have the ability to borrow the underlying asset. This limits the risk by ensuring you can fulfill the obligation if the option is exercised.
-
Margin account: If using a margin account, be aware that your broker may require you to maintain a certain level of margin (funds) in your account to cover potential losses arising from the obligation to pay.
Obligation To Pay For Trading Options
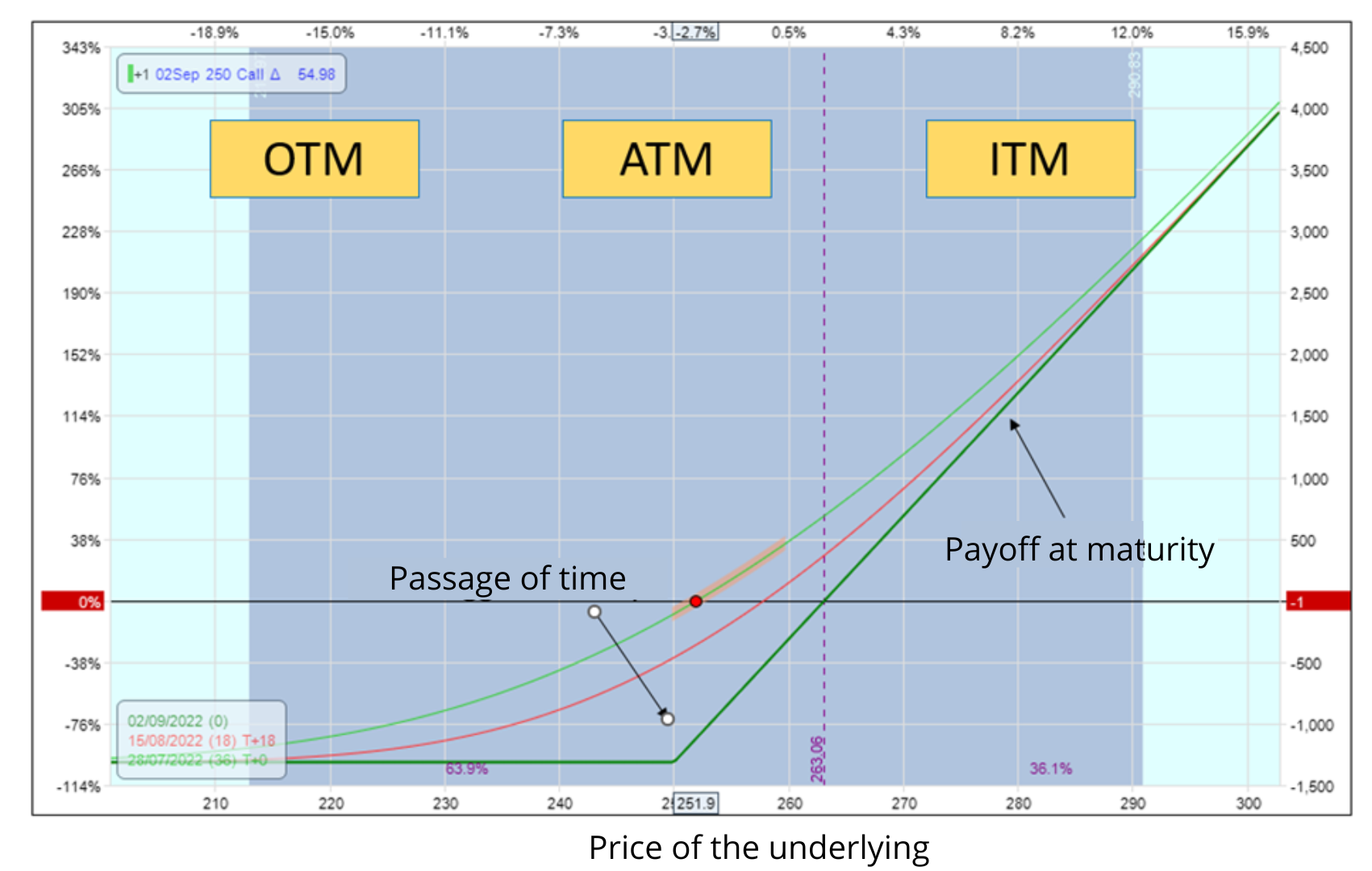
Image: ungeracademy.com
Conclusion
The obligation to pay for trading options is an essential aspect that option sellers must fully comprehend and manage effectively. By understanding the types of option contracts, the extent of the obligation, and employing risk management strategies, sellers can navigate the options market with greater confidence and protect their financial interests. Remember, informed decision-making and responsible trading practices are key to success in the world of options trading.






