Introduction

Image: www.youtube.com
In the realm of investing, options trading stands out as a dynamic and potentially lucrative avenue. Yet, for many, its complexities can be daunting, shrouded in jargon and abstract concepts. This comprehensive guide aims to demystify the world of options trading, providing you with the foundational knowledge to embark on your financial journey with confidence.
Demystifying Options Trading
An option is a financial contract that grants the holder the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a predetermined price (strike price) on or before a specific date (expiration date). By understanding these fundamental elements, you can lay the groundwork for understanding the intricate mechanisms of options trading.
Types of Options
1. Call Options: Call options grant the holder the right to buy the underlying asset at the strike price. When the market price of the asset exceeds the strike price, call options typically gain value.
2. Put Options: Put options give the holder the right to sell the underlying asset at the strike price. If the market price of the asset falls below the strike price, put options usually increase in value.
Understanding Options Premiums
The premium is the amount paid by the buyer to the seller of an option contract. The premium incorporates factors such as the underlying asset’s price, time to expiration, interest rates, and volatility. It’s crucial to consider these factors when determining the potential profitability of an options trade.
Leveraging Options Trading Strategies
1. Covered Call: This strategy involves selling (writing) a call option against an already-owned stock. It generates potential income from the premium while maintaining exposure to potential upside in the stock’s price.
2. Protective Put: Buying a put option complements a stock purchase, offering protection against a decline in the stock’s price beyond a certain point. It reduces risk but limits the potential upside compared to owning the stock outright.
3. Vertical Spread: Vertical spreads involve buying and selling options with the same underlying asset but different strike prices and/or expiration dates. They allow for tailored risk-reward profiles.
Expert Insights and Actionable Tips
- Seek Professional Guidance: Before initiating options trades, it’s prudent to consult with a financial advisor who can provide personalized guidance based on your risk tolerance and investment objectives.
- Start Gradually: Begin with small-scale trades to gain experience and confidence. Gradually increase your trading volume as your knowledge and risk appetite grow.
- Manage Risk: Options trading involves inherent risk. Establish a robust risk management plan, including stop-loss orders and position sizing strategies, to protect your capital.
Conclusion
Learning the basics of options trading opens a gateway to a world of enhanced investment opportunities. By embracing the concepts outlined in this guide, you can unlock the potential to diversify your portfolio, generate potential income, and effectively navigate the complexities of the financial markets. Embrace the journey of options trading with a thirst for knowledge and a calculated approach, and you’ll be well-equipped to reap the rewards it holds.
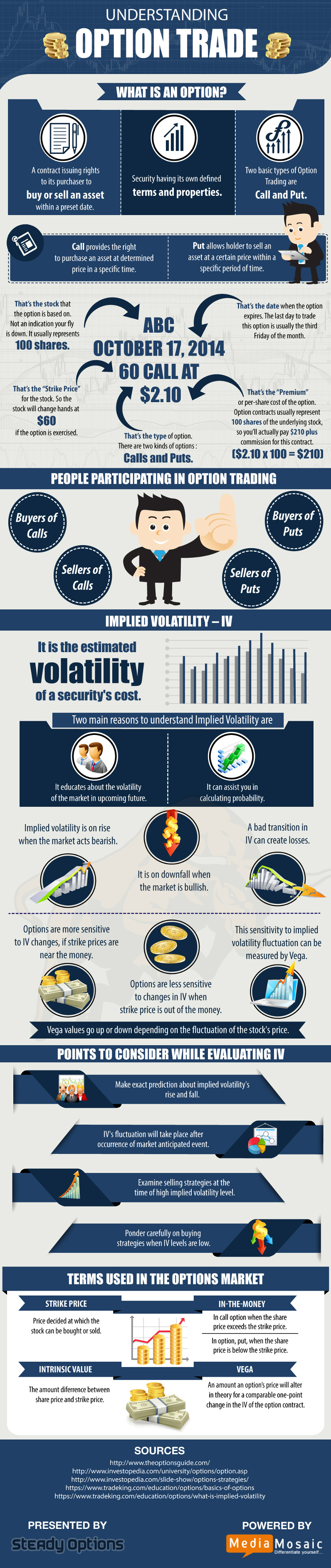
Image: progresswealthmanagement.com
Learning Basic Options Trading

Image: www.youtube.com






