Jump-starting my foray into options trading, the stakes were high. After meticulously researching viable opportunities, I cautiously executed a few trades, and to my surprise, I witnessed a significant surge in my brokerage account’s balance. However, amidst the euphoria, I realized I was oblivious to the tax implications. This realization prompted me to delve into the intricate world of capital gains on options trading, an essential aspect often overlooked by aspiring traders. Thus, let’s embark on this comprehensive guide to unriddle the mysteries surrounding this intriguing topic.
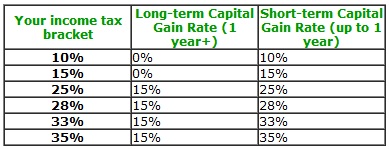
Image: laqenyberegi.web.fc2.com
Demystifying Capital Gains on Options Trading
Capital gains, simply put, represent profits accrued during an investment period. In the context of options trading, these gains result from the sale of options contracts at a price higher than their initial purchase price. Options, financial instruments that bestow the right to buy (call options) or sell (put options) an underlying asset at a predetermined price, offer a myriad of strategies that can yield substantial profits. However, it’s imperative to understand how capital gains on options differ from those made via stock trading.
Unveiling the Nuances of Capital Gains on Options
- Holding Period: Unlike stocks, which are subjected to long-term capital gains tax rates if held for over a year, options possess a shorter holding period. Any profits from options held for less than a year will be taxed as short-term capital gains, often at the trader’s ordinary income tax rate, potentially resulting in a higher tax bill.
- Expiration Date: The expiration date of an option contract plays a pivotal role in determining capital gains. If the contract expires worthless, it doesn’t confer any taxable gains or losses. However, if the option is exercised or sold prior to expiration, capital gains may arise.
- Income Reporting: Options traders must meticulously track their trades, including all realized gains and losses. This information is reported on Schedule D of Form 1040, which serves as the tax return for capital gains and losses. The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) expects traders to maintain accurate records for tax filing purposes.
Exploring Tax Strategies to Optimize Capital Gains
Navigating the labyrinth of tax implications in options trading unveils the judicious use of strategies to optimize capital gains. Here are some insights and expert advice to maximize your returns:

Image: www.warriortrading.com
- Embrace Long-Term Strategies: Consider holding options for longer than a year to qualify for the favorable long-term capital gains tax rates. This approach entails exercising patience while nurturing investments for a potentially more significant payoff down the road.
- Harvest Tax Losses: Capital losses, while undesirable outcomes, can provide valuable tax benefits. By intentionally selling losing options, traders can offset capital gains, thereby reducing their overall tax liability.
- Put Options and Short Strategies: Explore the utilization of put options or short-selling techniques, which enable traders to potentially reap profits even in declining markets.
- Consult with Professionals: Seek guidance from a qualified tax advisor or financial advisor to navigate the complex tax landscape of options trading. Their expertise can help you make informed decisions while adhering to all regulatory requirements.
FAQ: Unraveling Common Queries on Capital Gains
To alleviate lingering uncertainties, let’s delve into a comprehensive FAQ section that addresses common queries surrounding capital gains on options trading:
- Q: How do I calculate capital gains on options?
A: Subtract the cost basis (purchase price) of the option from its sale price. The resulting figure represents the capital gain or loss. - Q: What happens if I exercise an option?
A: Exercising an option entails converting it into an underlying stock or asset. The capital gain or loss is determined by comparing the exercise price to the sale price of the underlying asset. - Q: Do I need to pay taxes on unexercised options?
A: No, unexercised options that expire worthless are not subject to capital gains tax. - Q: Are capital gains on options reported on the same form as stock gains?
A: Yes, both capital gains on options and stocks are reported on Schedule D of Form 1040.
Capital Gains On Options Trading
Conclusion
Navigating the intricacies of capital gains on options trading requires a thorough understanding of tax implications and optimization strategies. By embracing a proactive approach, traders can maximize their profits while adhering to regulatory guidelines. As you delve further into this exciting domain, remember that knowledge is your most valuable asset. Engage with resources, seek expert advice, and stay abreast of industry updates to stay ahead of the curve.
Would you like to know more about capital gains on options trading? Share your queries in the comments section, and let’s explore this multifaceted topic together.






