Options trading has emerged as a prevalent financial strategy among investors seeking leverage and risk management. At its core, options offer an array of trading opportunities, two prominent types being call options and put options. This article delves into the intricacies of call vs. put options trading, empowering you with the knowledge to navigate this dynamic financial landscape.

Image: www.simplertrading.com
Call Options: The Power to Buy Assets
A call option grants the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to buy an underlying asset at a predetermined price (strike price) on or before a specified expiration date. In essence, call options allow investors to capitalize on potential price increases in the asset. For example, if you believe that Apple’s stock is poised to rise in the coming months, you could purchase a call option that gives you the right to buy 100 shares of Apple at $120 per share within the next three months. If Apple’s stock price climbs to $130, you can exercise your call option and purchase the shares at the lower strike price, thereby profiting from the stock’s appreciation.
Put Options: The Privilege to Sell Assets
In contrast to call options, put options confer upon the buyer the right, not the obligation, to sell an underlying asset at a predetermined strike price on or before the expiration date. Essentially, put options empower investors to capitalize on potential price declines in the asset. Using the previous example, if you anticipate a decline in Apple’s stock price, you could acquire a put option that gives you the right to sell 100 shares of Apple at $120 per share within the next three months. If Apple’s stock price drops to $110, you can exercise your put option and sell the shares at the higher strike price, generating a profit from the stock’s decrease in value.
The Role of Expiration Dates: Time is of the Essence
One crucial aspect of options trading is the concept of expiration dates. Every option contract bears an expiration date, which defines the end of the period during which the option can be exercised. Once the expiration date passes, the option becomes worthless if it has not been exercised. The time value of options decays as the expiration date approaches, affecting the premium price.
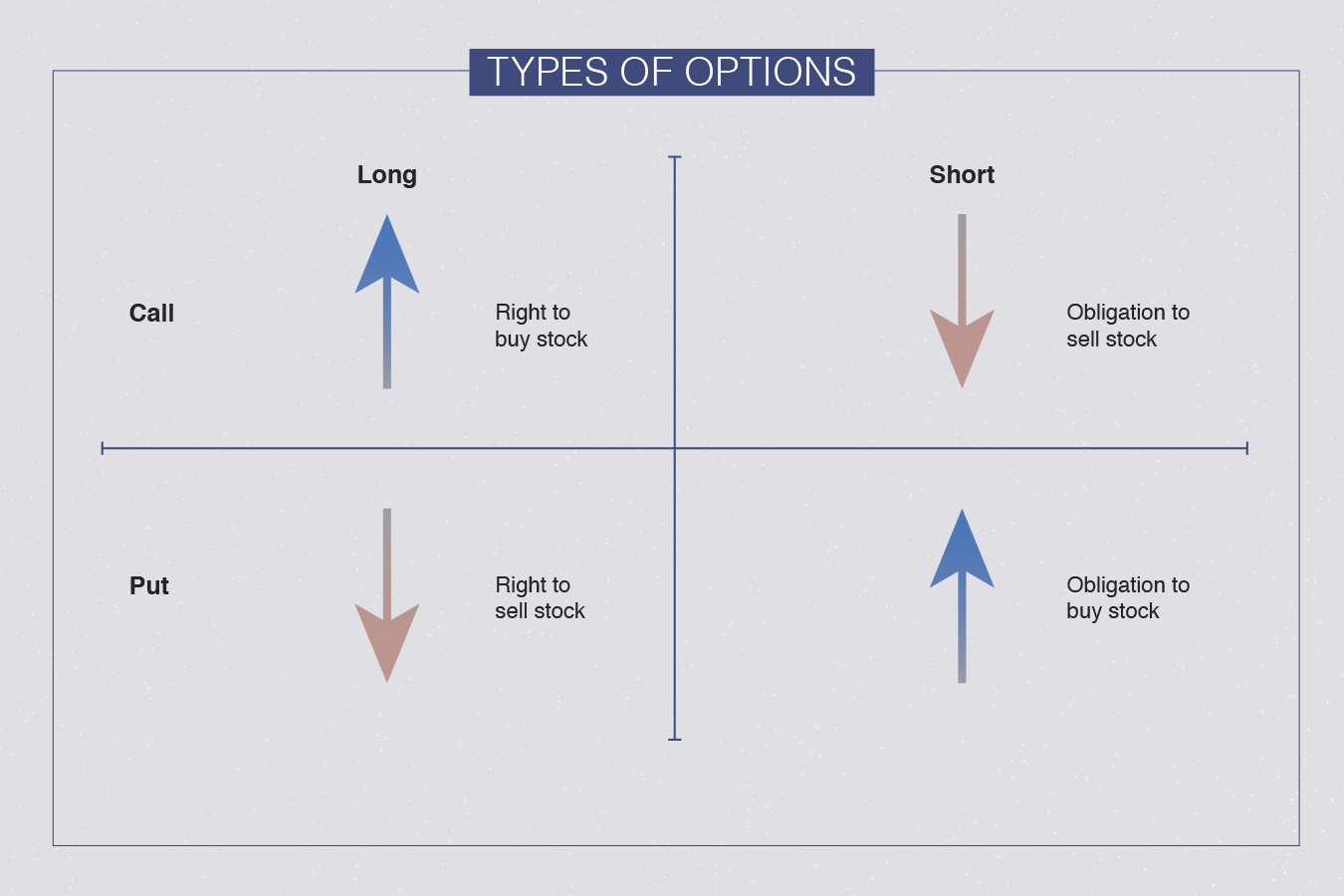
Image: internaljapan9.bitbucket.io
Premiums, the Currency of Options
Options do not come free of charge. To acquire an option contract, the buyer must pay a premium to the seller, which represents the price of the option. The premium amount is determined by factors such as the strike price, expiration date, volatility of the underlying asset, and current market conditions.
Call Vs Put Options Trading
Conclusion
Understanding the nuances of call vs. put options trading equips investors with valuable tools to navigate the financial markets. By carefully weighing the potential rewards and risks associated with each option strategy, investors can harness the power of options to enhance their investment portfolio and pursue financial success. Whether it’s speculating on future price movements, hedging against risks, or generating income streams, call and put options offer investors a vast array of possibilities.






