Introduction
In the tumultuous waters of option trading, where every move can be a gamble, gamma-hedging emerges as a lighthouse of stability. This risk management strategy empowers traders to navigate the market with confidence, mitigating the potential perils and unlocking the path to success.
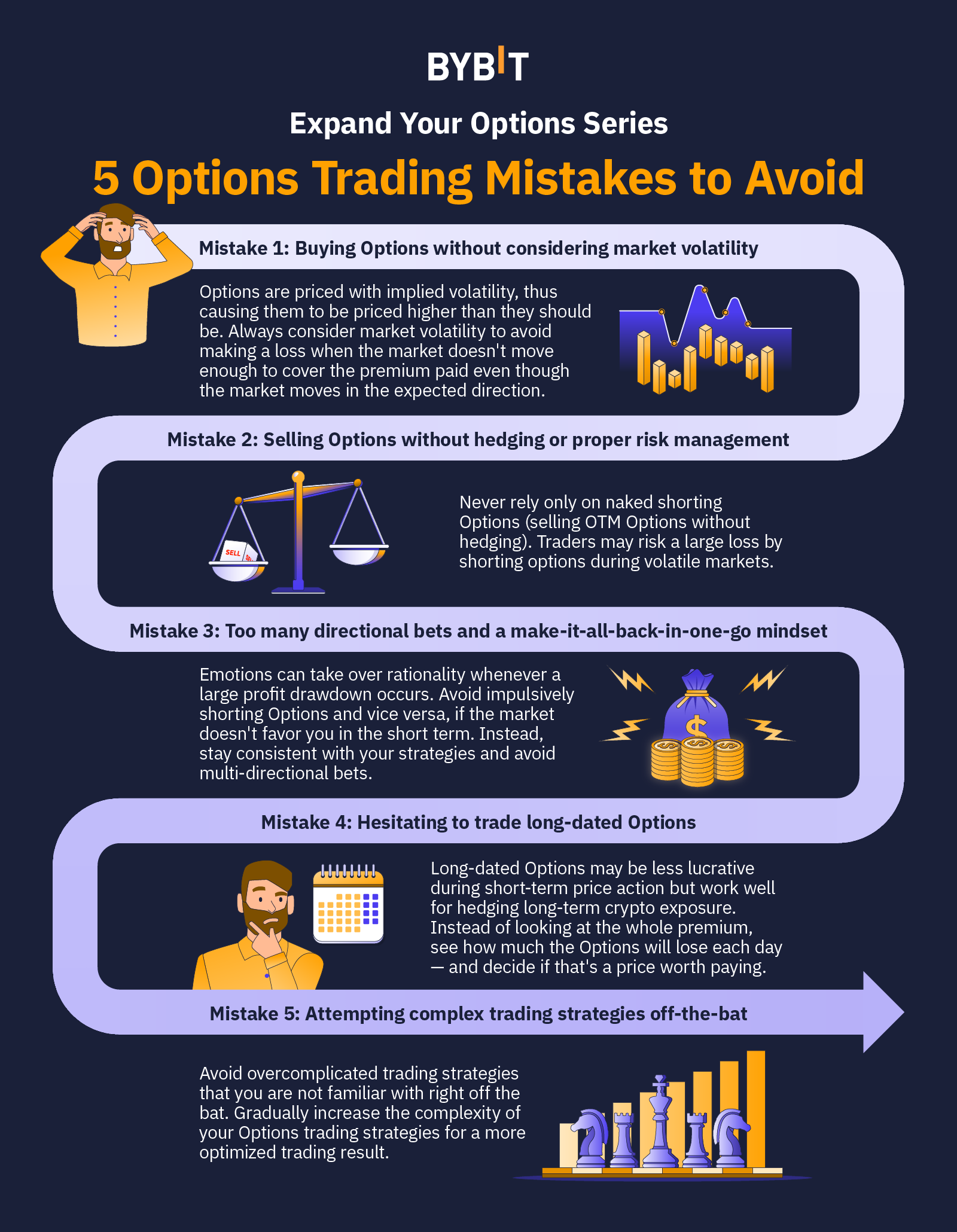
Image: ar.inspiredpencil.com
Gamma represents the rate of change in an option’s delta with respect to its underlying asset’s price. By understanding the intricacies of gamma and employing a gamma-hedging approach, traders can effectively control their risk exposure and enhance their overall trading performance.
Understanding Gamma and Why It Matters
Every option contract reacts differently to changes in the underlying asset’s price, influenced by its gamma value. Positive gamma characterizes call options, indicating that they gain sensitivity as the asset’s price rises. Conversely, negative gamma in put options signifies the opposite.
As the asset’s price deviates from the strike price, so too does the option’s delta, which measures its price responsiveness. Positive gamma amplifies this change, contributing to potential gains. However, as the option approaches expiration, gamma decays rapidly, rendering the strategy less effective.
Gamma-Hedging Technique: A Balancing Act
Gamma-hedging is a meticulous art of balancing long and short gamma positions. This interplay aims to maintain a close-to-zero net gamma, minimizing the volatility of an option’s delta and reducing the impact of price fluctuations on the trader’s portfolio.
To achieve this equilibrium, traders make adjustments by selling options with positive gamma (usually calls) against simultaneously buying options with negative gamma (typically puts). By offsetting these opposing forces, the net gamma remains relatively neutral, enhancing stability and reducing risk.
Types of Gamma-Hedging
Personalized hedging based on individual risk tolerance is a defining element of gamma-hedging. Different approaches cater to varying preferences:
- Delta-neutral hedging aims for zero net gamma, creating a stable position with minimal price sensitivity.
- Long gamma hedging, characterized by positive net gamma, seeks to amplify potential gains in rising markets.
- Short gamma hedging, with negative net gamma, aims to limit losses in falling markets.

Image: howtotradeonforex.github.io
Practical Applications of Gamma-Hedging
Beyond theoretical concepts, gamma-hedging finds practical use in a variety of scenarios:
- Reducing risk: By dampening the impact of price swings, gamma-hedging minimizes potential losses.
- Locking in gains: Hedged positions enable traders to capture profits in favorable markets while limiting the erosion of returns in adverse conditions.
- Volatility trading: Gamma-hedging allows traders to benefit from market volatility without exposing themselves to the full force of price fluctuations.
Prominent Gamma-Hedging Strategies
Traders employ diverse gamma-hedging strategies, each tailored to specific objectives:
- Delta-neutral overwriting: Selling portions of existing long stock positions as call options to generate income while maintaining a delta-neutral position.
- Collar strategy: A collar around a stock position involves buying protective put options (long gamma) and selling call options (short gamma) at higher strike prices.
- Synthetic long gamma: Creating a long gamma position by selling out-of-the-money puts combined with buying out-of-the-money calls.
Gamma-Hedging Option Trading Strategy

Image: www.awesomefintech.com
Conclusion
Gamma-hedging is a sophisticated risk management technique that empowers option traders to navigate market uncertainties with aplomb. Through the careful balancing of opposing gamma positions, traders can effectively control their risk exposure, enhance stability, and unlock the full potential of this powerful trading strategy. Embrace gamma-hedging today and embark on a path toward informed and profitable option trading.






