Are Options Trading Profits Taxable? A Comprehensive Guide
The stock market offers a multitude of investment avenues, one of which is options trading. However, one crucial consideration for any savvy investor is how tax laws impact their trading strategies. In this article, we delve into the taxation of options trading, providing a comprehensive guide to help you understand your tax obligations and optimize your returns.
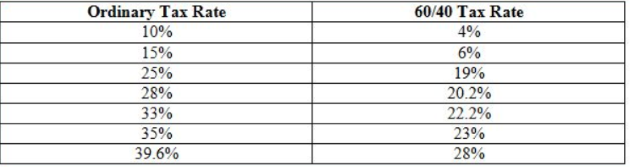
Image: alpari.com
Options trading falls under the realm of income tax. The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) classifies options premiums as either ordinary income or capital gains, depending on how long the options are held.
Short-Term Options Trading: Ordinary Income
When an option is held for less than a year (short-term), the profits or losses from its sale are taxed as ordinary income. This means they are subject to your regular income tax rate, which can be as high as 37%.
For example, if you purchase an option for $100 and sell it for $200 within a year, the $100 profit would be considered ordinary income and taxed accordingly.
Long-Term Options Trading: Capital Gains
If an option is held for more than a year (long-term), the profits from its sale are taxed as capital gains. Capital gains taxes are typically lower than ordinary income tax rates, ranging from 0% to 20% depending on your income level.
The holding period for options begins on the day after you acquire the option and ends on the day you sell or dispose of it. If you exercise the option, the holding period begins on the day after you exercise it.
Tax Implications of Option Strategies
The tax treatment of options trading can vary depending on the type of strategy you employ. Here are a few common strategies and their tax implications:
- Covered Calls: Profits from covered calls are generally taxed as capital gains, assuming you hold the stock underlying the option for more than a year.
- Cash-Secured Puts: Similar to covered calls, profits from cash-secured puts are typically taxed as capital gains if you hold the cash for more than a year.
- Naked Options: As premiums received from the sale of naked options are considered ordinary income, any profits or losses from these strategies are taxed accordingly.
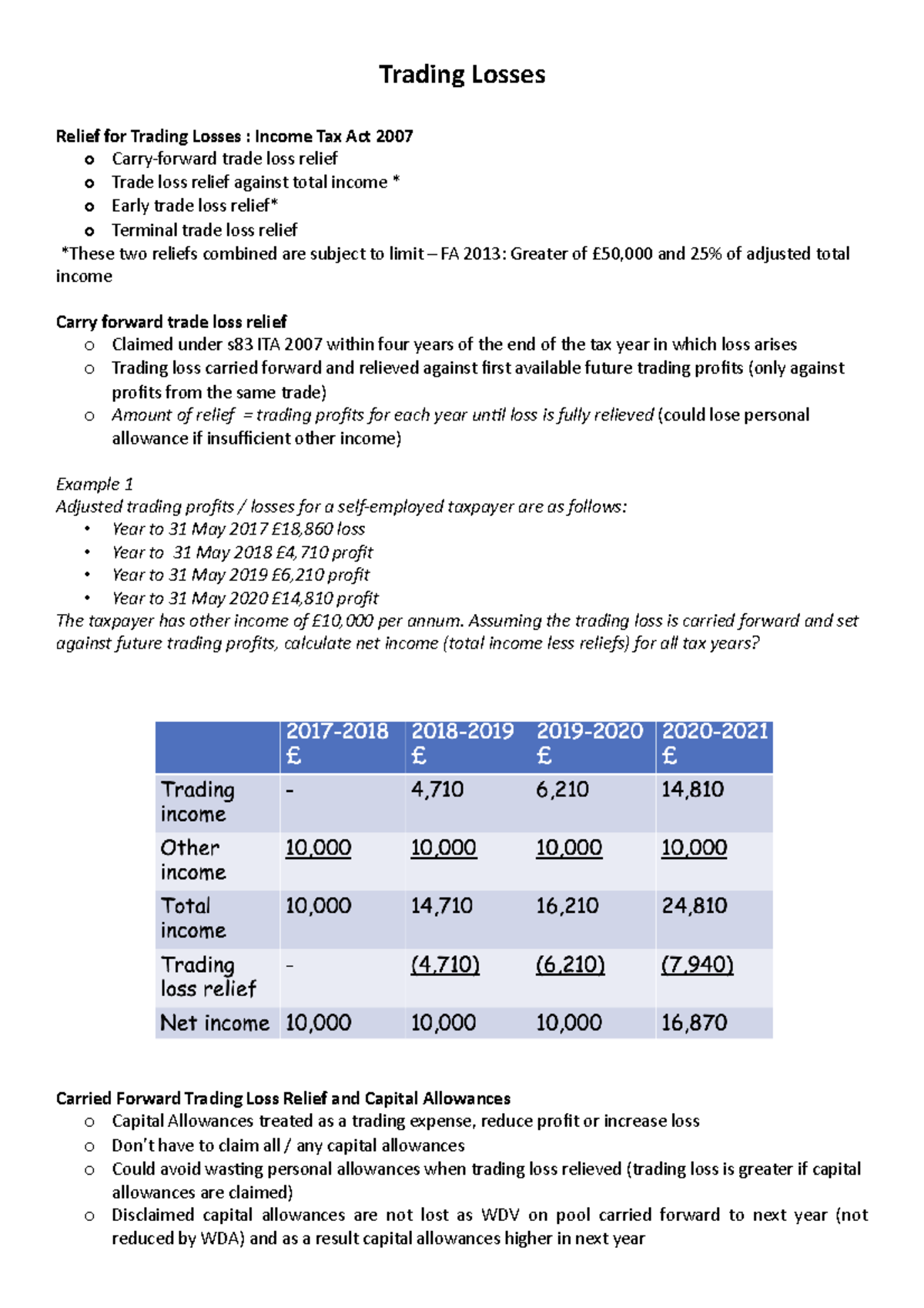
Image: www.studocu.com
Tips for Tax-Efficient Options Trading
To optimize your tax returns from options trading, consider the following tips:
- Hold Options Long-Term: If you anticipate a profit, consider holding your options for more than a year to benefit from the lower capital gains tax rates.
- Use Tax-Advantaged Accounts: Consider trading options in a tax-advantaged account, such as an IRA or 401(k), to defer or potentially avoid paying taxes on your profits.
- Offset Losses: If you incur losses from options trading, you can offset them against your other taxable income, potentially reducing your overall tax liability.
FAQs on Options Trading Taxation
Q: How are option premiums taxed if I exercise the option?
A: The premium paid for the option is not taxed when you exercise it. However, the profit you make from the underlying asset is taxed according to the holding period.
Q: Can I deduct option premiums from my taxes?
A: You can deduct premiums paid for options that expire unexercised. The amount you can deduct is subject to certain limitations.
Does Options Trading Fall Under Income Tax

Image: prajnacapital.blogspot.com
Conclusion
Understanding the tax implications of options trading is crucial for optimizing your returns and minimizing tax liabilities. By carefully navigating the tax code and implementing tax-efficient strategies, you can maximize your profits and minimize your worries come tax time.
Are you interested in pursuing a career in options trading? If so, we encourage you to explore the numerous online and offline resources available to expand your knowledge. With the right combination of research, practice, and a solid understanding of taxes, you can confidently embark on your trading journey.






