Ever wondered what lies beyond the familiar world of buying and selling stocks? Have you ever been curious about a trading strategy that offers the potential for amplified returns but also carries a heightened risk? This is where options trading steps into the spotlight. Options, a type of financial derivative, provide traders with a powerful tool to navigate the complexities of the market, unlocking new opportunities while presenting challenges to master.

Image: financebreakout.com
Options trading, a derivative market teeming with complexity and opportunity, allows investors to assume a position based on their prediction of future price movements for underlying assets. Whether you’re a seasoned trader or a curious newcomer, understanding the fundamentals of options trading is paramount to navigating this intricate world. This article serves as your comprehensive guide, breaking down the key concepts, strategies, and nuances of this dynamic financial tool.
Unveiling the Essence of Options
At their core, options are contracts that grant the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a predetermined price (strike price) on or before a specific date (expiration date). This right comes at a cost, known as the premium. Picture it as a ticket that allows you to access a specific opportunity, but you aren’t required to use it.
Types of Options: The Call and the Put
The realm of options contracts is divided into two key categories: call options and put options.
- Call Options: A call option grants the holder the right to buy the underlying asset at the strike price. Call buyers are bullish, expecting the price of the underlying asset to rise.
- Put Options: A put option grants the holder the right to sell the underlying asset at the strike price. Put buyers are bearish, expecting the price of the underlying asset to decline.
The Dynamics of Options Pricing
The price of an option is influenced by a complex interplay of factors, including:
- Underlying Asset Price: A call option’s price increases as the underlying asset’s price rises, while a put option’s price increases as the underlying asset’s price falls.
- Strike Price: The further the strike price is from the current market price, the higher the premium. A higher strike price for a call option means it’s cheaper, while a lower strike price for a put option means it’s cheaper.
- Time to Expiration: As the time to expiration decreases, the value of an option decreases. This is because there is less time for the underlying asset to move in the desired direction.
- Volatility: Higher volatility in the underlying asset increases the price of options. This is because there is a greater chance of the price moving significantly, either in the direction the option holder is hoping for or against them.
- Interest Rates: Interest rates can influence options prices, particularly for long-term options. Higher interest rates generally favor call options, while lower interest rates favor put options.
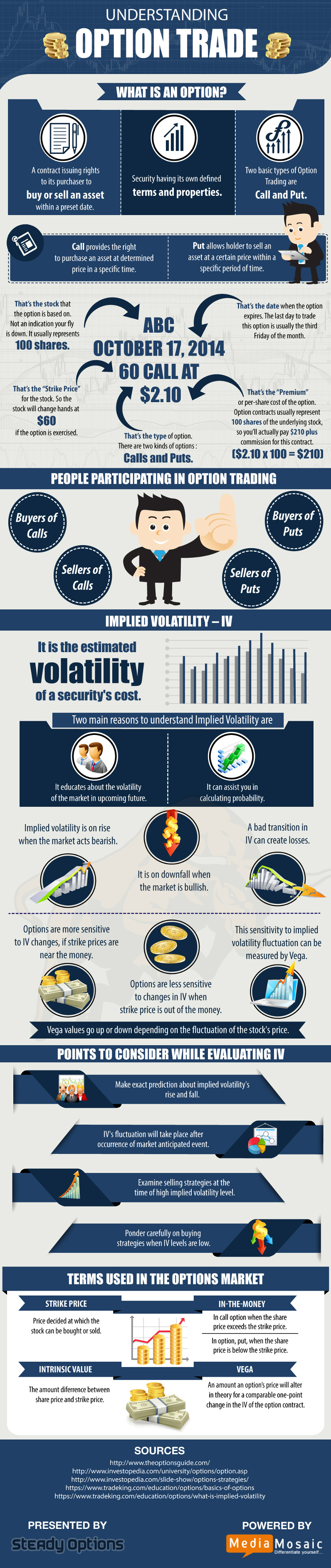
Image: www.visualcapitalist.com
A Practical Example: Navigating the Options Landscape
Imagine a scenario where you believe the price of Apple stock (AAPL) will rise in the next few months. You could buy shares of AAPL directly, but an alternative approach is to buy a call option. Let’s say AAPL is trading at $150 per share, and you purchase a call option with a strike price of $160 expiring in three months for $5 per share.
Here’s how the call option works: If AAPL rises to $170 by the expiration date, you have the right to buy the stock at the strike price of $160. You can then sell your stock for $170, making a profit of $10 per share, minus your initial premium of $5. Your overall profit would be $5 per share. However, if AAPL stays below $160, your option will expire worthless, and you’ll lose the $5 premium.
This example highlights the potential for leveraged gains with options trading, as a small premium can control a large position in the underlying asset. However, it also showcases the downside: if the stock moves against your prediction, your entire initial investment (the premium) can be lost.
Probing the Strategies of Options Trading
The world of options trading offers a diverse range of strategies tailored to various market conditions and trader profiles. Here are some common strategies employed by options traders:
Covered Call Writing: A Blend of Income and Risk
This strategy involves selling a call option while simultaneously owning the underlying stock. This generates premium income, but limits potential gains on the stock. The downside is the potential for early assignment of the call option if the stock price rises, forcing you to sell at the strike price.
Cash-Secured Put Writing: A Conservative Approach
This strategy involves selling a put option while holding cash equal to the strike price. This generates premium income and provides downside protection, as you have the cash to buy the underlying stock if the put option is exercised. However, the downside is a limited return if the stock price goes up.
Bullish Call Spreads: Limiting Risk While Capturing Upside
This strategy involves buying a call option with a lower strike price and selling a call option with a higher strike price. The difference in the strike prices is the maximum profit potential. This strategy is bullish and suitable for those who expect a modest rise in the underlying asset price. However, if the price stays flat, the entire premium paid will be lost.
Bearish Put Spreads: Profiting from Declines
This strategy involves buying a put option with a higher strike price and selling a put option with a lower strike price. The difference in the strike prices is the maximum profit potential. This strategy is bearish and suitable for those expecting a decrease in the underlying asset price. However, if the price goes up, the entire premium paid will be lost.
Options Pricing Models: A Look Under the Hood
The process of determining fair market values for options is governed by complex mathematical models. Some of the commonly used models include:
- Black-Scholes Model: This widely adopted model employs a set of assumptions to calculate theoretical option prices based on the value of the underlying asset, volatility, time to expiration, interest rates, and dividends.
- Binomial Tree Model: This model uses a series of step-by-step calculations to assess the potential payoffs of an option in various price scenarios. It works by breaking down the future into a series of discrete time periods, each with a corresponding probability of an upward or downward move in the price of the underlying asset.
- Monte Carlo Simulation: This technique uses random numbers to generate multiple potential price paths for the underlying asset. By running numerous simulations, it provides estimations of the probability distribution of option payoffs and helps evaluate the risk associated with different investment strategies.
Navigating the Risks and Rewards: A Prudent Approach
The inherent nature of options trading presents both potential rewards and risks. Understanding the unique risk profile of options trading is crucial for any investor.
Leveraged Gains: A Double-Edged Sword
Options trading offers the potential for amplified returns, as a small investment can control a larger position in the underlying asset. However, this leverage also magnifies losses if the trade moves against you.
Time Decay: The Ticking Clock
Options have a limited lifespan and lose value as they approach expiration. This decay in value, known as time decay, is faster for options with shorter timeframes. Traders must consider how time decay influences their strategies.
Volatility: A Force Multiplier
Volatility in the underlying asset can significantly impact options prices. High volatility can lead to both larger potential profits and larger potential losses.
The Importance of Risk Management
To mitigate losses, successful options traders employ robust risk management strategies, including:
- Setting Stop-Loss Orders: Stop-loss orders limit potential losses by automatically selling an option if it reaches a certain price level.
- Diversifying Your Portfolio: Spreading your investments across various options contracts or asset classes can reduce overall risk.
- Understanding Your Risk Tolerance: Know your appetite for risk and choose strategies that align with your comfort level.
How Options Work In Trading
Embracing the Power of Options: A Final Word
Options trading presents a complex but rewarding avenue for investors seeking to leverage the market and potentially amplify returns. By comprehending the fundamental concepts, exploring various strategies, and prioritizing risk management, you can equip yourself to navigate this dynamic landscape and harness the potential of options trading.
Remember, options trading is best suited for experienced investors who have a solid understanding of financial markets and risk management principles. If you’re new to options trading, start with thorough research and consider seeking guidance from a qualified financial advisor. The world of options is vast, and continuous learning is key to success in this field.






