Have you ever wondered about the mysterious world of options trading, where investors seem to have a secret weapon for navigating the ups and downs of the market? It might sound intimidating, but it’s actually a powerful tool that can be utilized for both profit and risk management, opening up a whole new dimension in investing.
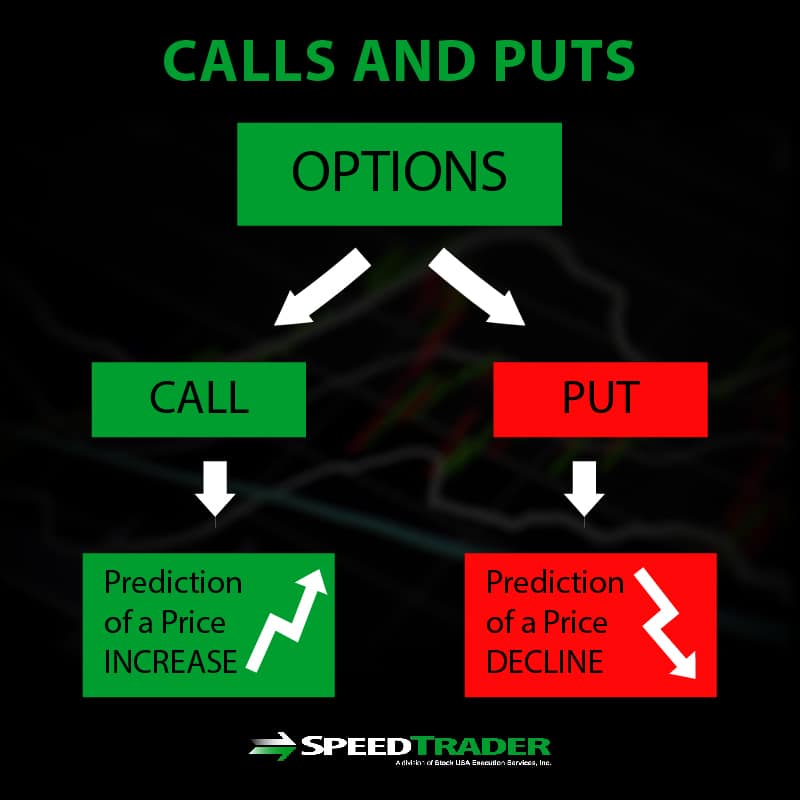
Image: speedtrader.com
Options trading is essentially a contract that gives the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a predetermined price on or before a specific date. This right, known as an option, is purchased for a price called the premium. The world of options can seem complex at first, but with the right approach and understanding, it can be an exciting and rewarding journey.
What are the different types of options?
There are two primary categories of options: **calls** and **puts**:
- Call options grant the buyer the right to buy the underlying asset at a specified price (the strike price). This is for investors who believe the asset’s price will increase.
- Put options grant the buyer the right to sell the underlying asset at a specified price. This is for investors who believe the asset’s price will decrease.
Further breakdowns include:
- American options can be exercised at any time up to the expiration date.
- European options can only be exercised on the expiration date.
Understanding the Language of Options
Before diving into the intricacies of options trading, it’s crucial to grasp the essential terminology:
- Strike price: The price at which the option buyer can buy or sell the underlying asset.
- Premium: The price the option buyer pays for the right to buy or sell the asset.
- Expiration date: The date when the option contract expires.
- Underlying asset: The asset that the option contract is based on, such as stocks, indices, or commodities.
- In-the-money: When the underlying asset price is above the strike price for a call option or below the strike price for a put option.
- Out-of-the-money: When the underlying asset price is below the strike price for a call option or above the strike price for a put option.
- At-the-money: When the underlying asset price is equal to the strike price.
Why Trade Options?
While it can be a complex endeavor, options trading offers a unique set of advantages that can be enticing to both novice and experienced traders.

Image: www.5paisa.com
1. Leverage
Options trading allows for leveraged exposure, meaning you can control a larger amount of value with a smaller investment. For example, with a small premium outlay, you can gain the potential for substantial profits if the underlying asset moves in your favor.
Important Note: Leverage can amplify losses as well as profits, so it’s essential to understand and manage risk appropriately.
2. Risk Management
Options can be used to hedge against potential losses in your portfolio. Consider this example: If you own shares of a company and are worried about a price drop, you could purchase put options on that stock to protect your investment. If the price drops, the put options would offset your losses.
3. Income Generation
You can generate income through options selling. This involves selling call or put options and receiving the premium. If the option expires worthless, you keep the premium, but if it is exercised, you must buy or sell the underlying asset at the strike price.
Understanding the Risks
Despite the potential for profit, options trading comes with its share of risks that need to be acknowledged and managed wisely.
1. Time Decay
The value of options declines over time, a phenomenon known as “time decay.” The closer an option gets to its expiration date, the less value it holds, even if the underlying asset price is favorable. This means that time works against option buyers and in favor of option sellers.
2. Unlimited Loss Potential
In theory, there’s unlimited potential for losses on options trades, especially for options buyers, though it’s unlikely you’ll ever see it materialize in full. When compared to traditional stock trading, where potential losses are typically limited to the initial investment amount, options carry a risk factor that requires careful consideration.
3. Complexity
Options trading can be complex, involving various pricing models and strategies. Mistakes in understanding or implementing these strategies can lead to significant financial setbacks
Getting Started with Options Trading
If you’re considering dipping your toes into the realm of options trading, here are some key steps to take:
- Educate yourself: Start by gaining a thorough understanding of options fundamentals, strategies, and risk management principles. Consider reading books, articles, or taking online courses.
- Start small and practice: Begin with small, carefully calculated trades to gain experience and build confidence. Utilize a paper trading account to test your strategies and refine your approach without risking real money.
- Choose a reliable broker: Select a broker that offers robust options trading platform, educational resources, and excellent customer support. Make sure they are regulated and reputable.
- Establish a trading plan: Determine your trading goals, risk tolerance, and strategies before entering any trade. This will help you stay disciplined and manage your investments effectively.
- Manage your risk: Always use stop-loss orders to limit potential losses on your trades. Options strategies can be customized with risk measures in place.
Options Trading Strategies
Options trading offers a wide range of strategies, each with its own objectives and potential rewards. Each of these strategies involves varying levels of risk, so it is crucial to choose strategies that align with your experience level and financial goals.
Here are a few of the most popular option strategies:
- Covered call writing: A strategy involving selling a call option while owning the underlying shares, aiming to generate extra income.
- Cash-secured put writing: A strategy involving selling a put option and having sufficient cash in the account to cover the potential purchase of the underlying shares.
- Bullish call spread: A bullish strategy that involves buying a call option at a lower strike price and selling a call option at a higher strike price. It limits your potential profit while also limiting your potential loss.
- Bearish put spread: A bearish strategy that involves buying a put option at a higher strike price and selling a put option at a lower strike price. It also limits your potential profit and loss.
- Covered Put: This strategy involves selling a put option while owning the underlying shares.
Remember, each strategy has its unique characteristics and risks, so thoroughly understand each before you implement them. Consult a financial advisor for personalized guidance that aligns with your financial goals.
The Future of Options Trading
The options market continues to evolve. With the rise of online trading platforms and technological advancements, options trading is becoming more accessible to individuals. Furthermore, the introduction of fractional options allows investors to buy or sell portions of options contracts, lowering the entry barrier for smaller investors.
The options market is becoming increasingly dynamic and complex, requiring traders to adapt to the latest trends and technologies for success.
Options Trading Meaning
Conclusion
Options trading can be a powerful and rewarding investment tool, but it demands thorough education, disciplined risk management, and a commitment to ongoing learning. By carefully learning the fundamentals, understanding the risks, and utilizing appropriate strategies, individuals can navigate the exciting world of options trading and potentially unlock new possibilities for their financial success. Remember, consistency, planning, and a thirst for knowledge are essential for succeeding in this dynamic market. Explore resources, connect with experienced traders, and never stop learning – the world of options waits!






