Introduction
In the dynamic world of option trading, every trader seeks an edge to navigate market fluctuations. Pivot points emerge as a pivotal tool in this pursuit, offering insights into potential market reversals and providing a solid foundation for strategic decision-making. Understanding pivot points and their applications can elevate your option trading game, empowering you to identify lucrative opportunities and mitigate risks.

Image: muladharayogawear.com
Pivot points, originating from conventional technical analysis, serve as psychological levels where the markets establish critical support or resistance zones. They represent a hypothetical balance point around which prices tend to oscillate, providing traders with potential entry and exit points for their option trades.
Unveiling the Types of Pivot Points
Pivot point calculations vary based on specific formulas, each catering to different trading preferences. Among the widely recognized approaches are:
- Classic Pivot Points: Calculated using the high, low, and closing prices of the previous trading session.
- Fibonacci Pivot Points: A more refined version that incorporates Fibonacci ratios into the calculations.
- Camarilla Pivot Points: Emphasizes the importance of odd and even numbers.
- Woodie Pivot Points: Introduces time-based elements, dividing the day into four equal intervals.
Interpreting Pivot Point Signals
Pivot points provide valuable insights into potential market turning points, guiding traders in crafting their option strategies:
- Support and Resistance Levels: Pivots serve as dynamic support and resistance levels, which can be tested repeatedly. When the price approaches a pivot point, traders can anticipate potential reversals.
- Breakout Opportunities: Decisive breakouts above or below pivot points often signal a change in market trend. Traders can use such breakouts as entry points for trend-following option trades.
- Reversal Zones: Price action around pivot points can create reversal zones. When the price fails to break through a pivot point, it may indicate an impending trend reversal.
Trading Strategies Utilizing Pivot Points
Pivot points offer a versatile framework for both long and short trading strategies:
- Long Pivot Strategy: If the price breaks above a pivot point, traders can consider buying a call option, anticipating continued upward momentum.
- Short Pivot Strategy: Conversely, if the price breaks below a pivot point, buying a put option can capitalize on a potential downtrend.
- Range Trading: Pivot points can help identify potential trading ranges. Buying options at support levels and selling at resistance levels may yield profitable outcomes.
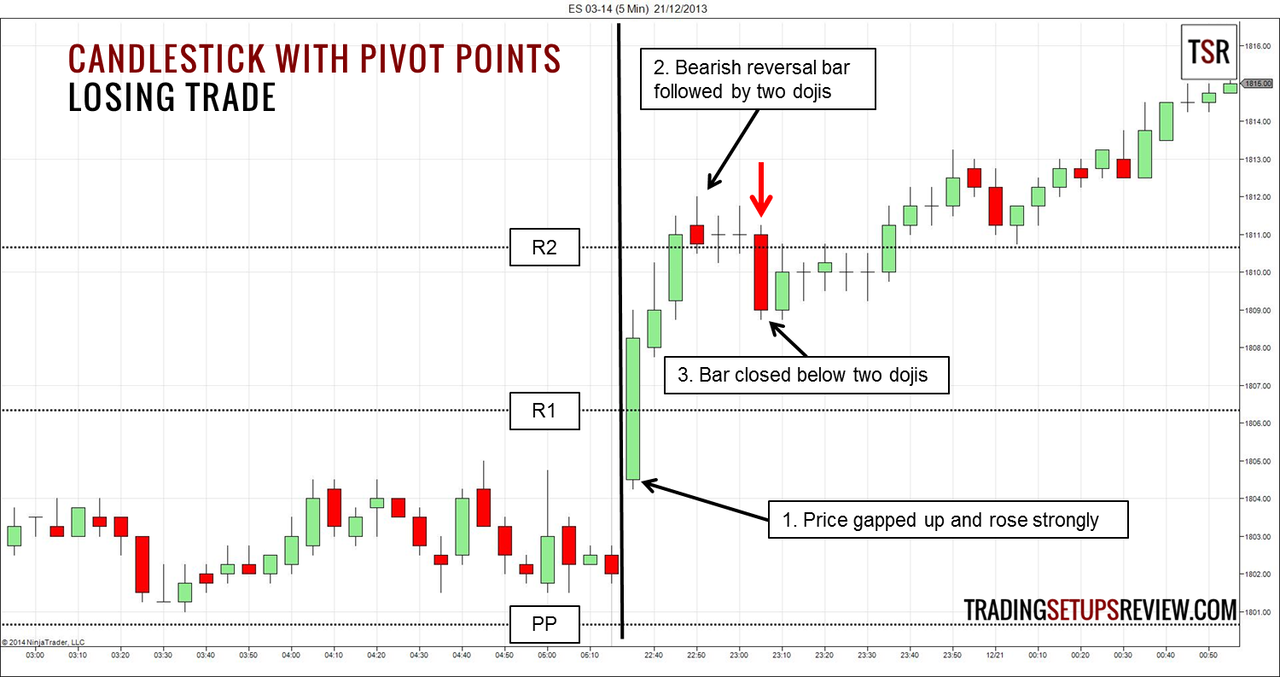
Image: www.tradingsetupsreview.com
Advanced Techniques for Leveraging Pivot Points
Seasoned traders employ advanced techniques to enhance their pivot point analysis:
- Multiple Time Frame Analysis: Examining pivot points across different time frames (daily, weekly, monthly) provides a comprehensive perspective on potential price movements.
- Candlestick Patterns: Combining pivot points with candlestick patterns can offer additional confirmation signals.
- Moving Averages: Incorporating moving averages into pivot point analysis can help identify underlying trends.
Pivot Point Option Trading
Conclusion
Pivot point option trading empowers traders to decode the intricacies of market movements and make informed decisions. By understanding pivot points, their types, interpretations, and trading strategies, traders can gain a competitive advantage in navigating the financial markets. Remember, the effective use of pivot points requires practice, patience, and a solid understanding of market dynamics. Embark on this journey of technical mastery and unlock the potential for exceptional option trading outcomes.






