Have you ever wondered how seasoned investors can potentially amplify their returns in the stock market, while simultaneously managing their risk? The answer often lies in the fascinating realm of options trading. Unlike simply buying or selling shares directly, options provide a unique and complex leverage tool that can be both exhilarating and intimidating. This guide dives deep into the fundamentals of options trading, demystifying the concepts and equipping you with the knowledge to explore this dynamic world with confidence.
Image: malcolmxavier.gumroad.com
Understanding options trading is crucial for investors seeking to enhance their portfolio strategies. It allows for flexible and strategic approaches to market participation, offering the ability to capitalize on both bullish and bearish market sentiments. Whether you’re a seasoned trader or a curious newcomer, grasping the essence of options trading will provide you with a valuable tool to navigate the intricacies of the financial markets.
Understanding the Basics of Options
Defining Options Contracts
At its core, an option is a contract giving the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset, like a stock, at a pre-determined price within a specific timeframe. This price is known as the “strike price,” and the timeframe is the “expiration date.”
Call vs. Put Options: A Tale of Two Contracts
There are two primary types of options:
- Call options grant the holder the right to buy the underlying asset at the strike price.
- Put options grant the holder the right to sell the underlying asset at the strike price.
Visualizing these concepts helps illustrate their power. Imagine you own a call option on a stock currently trading at $100, with a strike price of $95. If the stock price rises to $110, you can exercise your option, buy the stock for $95, and immediately sell it in the market for $110, earning a profit of $15 per share (minus the cost of the option). Conversely, if the stock price drops below $95, exercising your call option would result in a loss.
Put options function similarly, but in a bearish scenario. They allow you to profit if the price of the underlying asset falls. Suppose you hold a put option on a stock trading at $100, with a strike price of $105. If the stock price dips to $90, you could exercise your option, sell the stock for $105, and simultaneously buy it in the market for $90, earning a profit of $15 per share (minus the cost of the option).
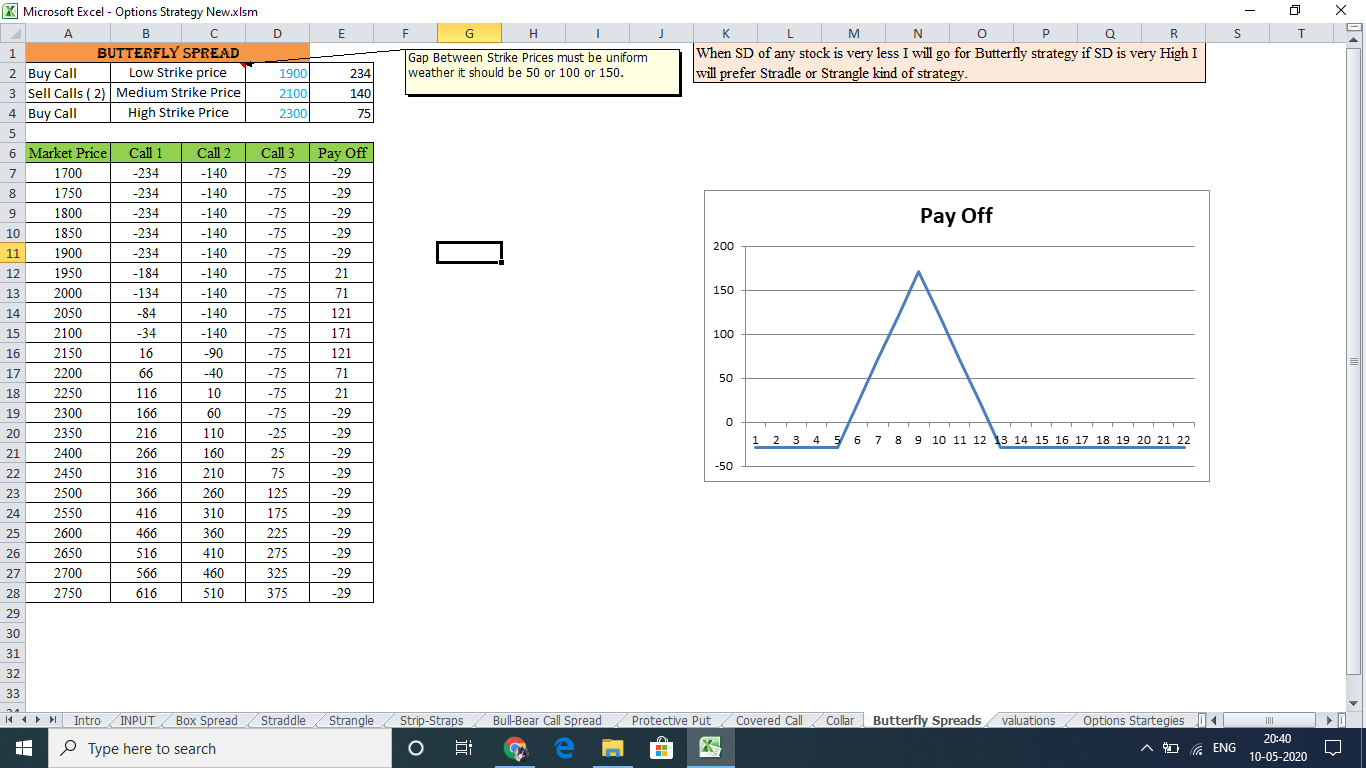
Image: www.eloquens.com
The Mechanics of Options Trading
Premium and Intrinsic Value
Options have a price, known as the “premium,” which is paid by the buyer to the seller. The premium reflects the value of the underlying asset, the time to expiration, and market expectations. It can be broken down into intrinsic value and time value.
- Intrinsic value is the difference between the current market price of the underlying asset and the strike price. It represents the immediate profit you could make if you exercised the option right now.
- Time value is the portion of the premium that reflects the remaining time until expiration. As time passes, the time value erodes until it eventually reaches zero at expiration.
Leverage: Magnifying Gains and Losses
One of the most significant aspects of options trading is leverage. This means that you can potentially control a larger position in the underlying asset with a smaller initial investment, effectively amplifying both gains and losses.
The Power of Time Decay
Time decay, or theta, is a crucial factor influencing the value of an option. As time passes, the time value of an option gradually reduces, eventually reaching zero on the expiration date. This decay can be advantageous for selling options, but detrimental for buying them.
For instance, if you’re selling a call option, you benefit from time decay as the value of the option diminishes, allowing you to potentially profit even if the underlying asset price stays relatively flat. Conversely, if you’re buying a call option, time decay works against you. The longer you hold it, the more value you lose. Comprehending time decay is essential for managing both your risks and your potential rewards.
Strategies: Maximizing Your Options
Covered Call Writing: Generating Income While Owning Shares
One common strategy is covered call writing. This involves selling a call option on a stock you already own. If the stock price rises above the strike price, you are obligated to sell the stock to the option holder. This strategy generates income from the premium received from selling the call, while simultaneously limiting potential upside gains.
Protective Put Buying: Insuring Your Portfolio
Protective put buying involves purchasing a put option on a stock you own. This strategy acts as a “safety net” for your investment by providing a guaranteed minimum selling price. If the stock price drops below the strike price, you can exercise the put option, effectively selling the stock for the higher strike price and limiting your potential losses.
Bullish and Bearish Strategies
Options offer flexibility to implement both bullish (expecting rising prices) and bearish (expecting falling prices) strategies.
Bullish strategies can involve buying call options, selling put options, or using combinations of options contracts. Bearish strategies can involve buying put options, selling call options, or using combinations designed to profit from declining prices.
Types of Options
American vs. European Options
Options come in two primary styles: American and European. American options can be exercised at any time before expiration, while European options can only be exercised on the expiration date. American options are more flexible but can be more expensive.
Index Options
Index options are based on market indices like the S&P 500 or the Nasdaq 100. They allow traders to make directional bets on the overall performance of these indices.
Futures Options
Futures options are based on futures contracts, which are agreements to buy or sell an asset at a specific price on a future date. These options allow traders to leverage their exposure to various commodities, currencies, and interest rates.
Managing Risk
Options trading can be incredibly lucrative, but it’s equally important to acknowledge the inherent risks. Understanding and managing these risks is crucial for responsible options trading.
- Time decay can significantly impact the value of your options, especially as expiration dates approach.
- Unlimited risk exists in buying options. If the underlying asset moves significantly against your position, your losses can exceed the premium you paid for the option. However, you can limit your potential losses on writing options by setting stop-loss orders.
- Volatility. Options pricing is highly influenced by market volatility. High volatility can inflate option prices, but it can also lead to unpredictable price movements, amplifying potential gains and risks.
Fundamentals Of Options Trading
https://youtube.com/watch?v=YyzqZPvCJTo
Conclusion
The world of options trading opens up a multitude of possibilities, allowing for sophisticated strategies and opportunities to potentially enhance your portfolio. By understanding the fundamental concepts of options contracts, leverage, time decay, and risk management, you can embark on a journey to unlock the potential of this dynamic trading world. Always remember to exercise due diligence, conduct thorough research, and seek professional guidance as you delve deeper into the realm of options trading. This guide has equipped you with the basic knowledge to start your journey, but remember that continued education and practice are key to navigating this exciting and challenging market.






