Introduction
The world of finance has long been captivated by the allure of options trading, a complex but potentially lucrative practice that grants investors the right but not the obligation to buy or sell an underlying asset at a predetermined price on or before a specified date. Throughout history, options trading has shaped markets and empowered countless individuals to navigate financial landscapes. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the captivating history of options trading, exploring its evolution, significance, and enduring impact on modern finance.
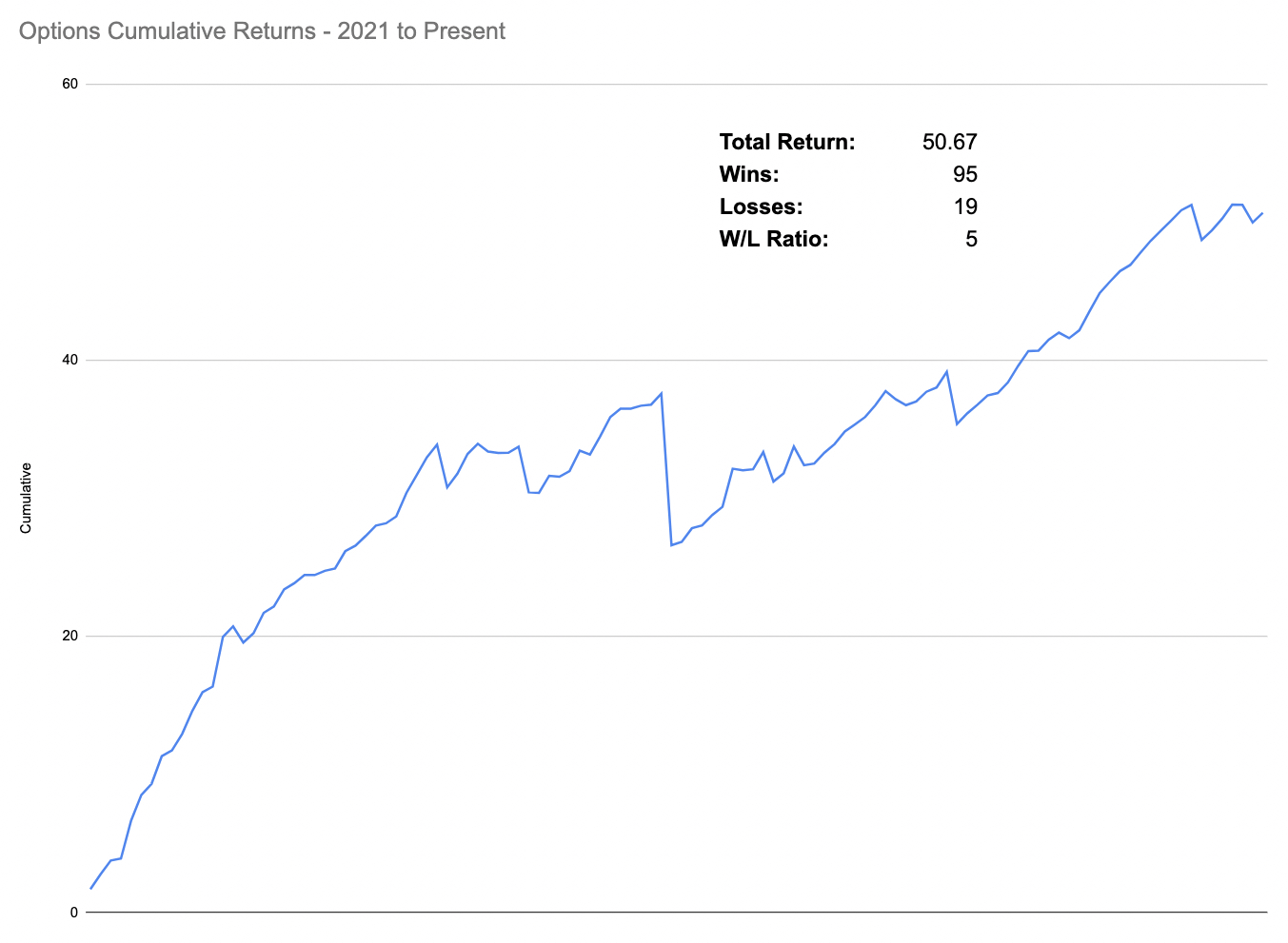
Image: evilspeculator.com
Origins and Evolution
The earliest recorded evidence of options trading dates back to ancient Greece, where merchants used forward contracts to lock in grain prices. These contracts allowed traders to secure future supplies at a fixed price, hedging against the vagaries of the market. In the 17th century, the Dutch introduced the concept of options to the Amsterdam Stock Exchange, further refining the practice and creating a more formal trading platform.
As commerce grew more complex, options evolved into versatile financial instruments that allowed investors to manage risk and speculate on market movements. The establishment of the Chicago Board Options Exchange (CBOE) in 1973 marked a significant milestone in the development of the options market, providing a centralized platform for the trading of standardized options contracts.
Basic Concepts and Terminology
Options trading involves two main types of contracts: calls and puts. A call option gives the buyer the right to buy an underlying asset at a set price (the strike price) on or before a certain date (the expiration date). A put option, on the other hand, gives the buyer the right to sell an underlying asset at the strike price on or before the expiration date.
The value of an option, known as its premium, is influenced by several factors, including the underlying asset’s price, volatility, the time remaining until expiration, and the risk-free interest rate. Options can be either long or short, depending on whether the investor is buying or selling the right.
Image: forex-station.com
Options Trading History
Real-World Applications
Options trading is widely employed by investors, speculators, and hedgers alike for various purposes. For instance, options can be utilized to:
- Speculate on Market Movements: Investors can speculate on the future price of an underlying asset by buying or selling call or put options. If the market moves in the predicted direction, the investor can profit from the corresponding price difference.
- Hedge Risk: Hedgers use options to reduce the risk of adverse price fluctuations in the underlying asset. For example, a farmer can buy a put option to protect against a potential decrease in crop prices.






