In the realm of financial markets, there lies a captivating instrument that empowers investors to navigate market uncertainties and harness opportunities to enhance returns—options trading. Options are financial contracts that provide the holder the right, but not the obligation, to buy (call option) or sell (put option) an underlying asset at a predetermined price on or before a specific date. Understanding the intricate mechanism of option trading can equip you with the knowledge and confidence to participate effectively in this dynamic market.
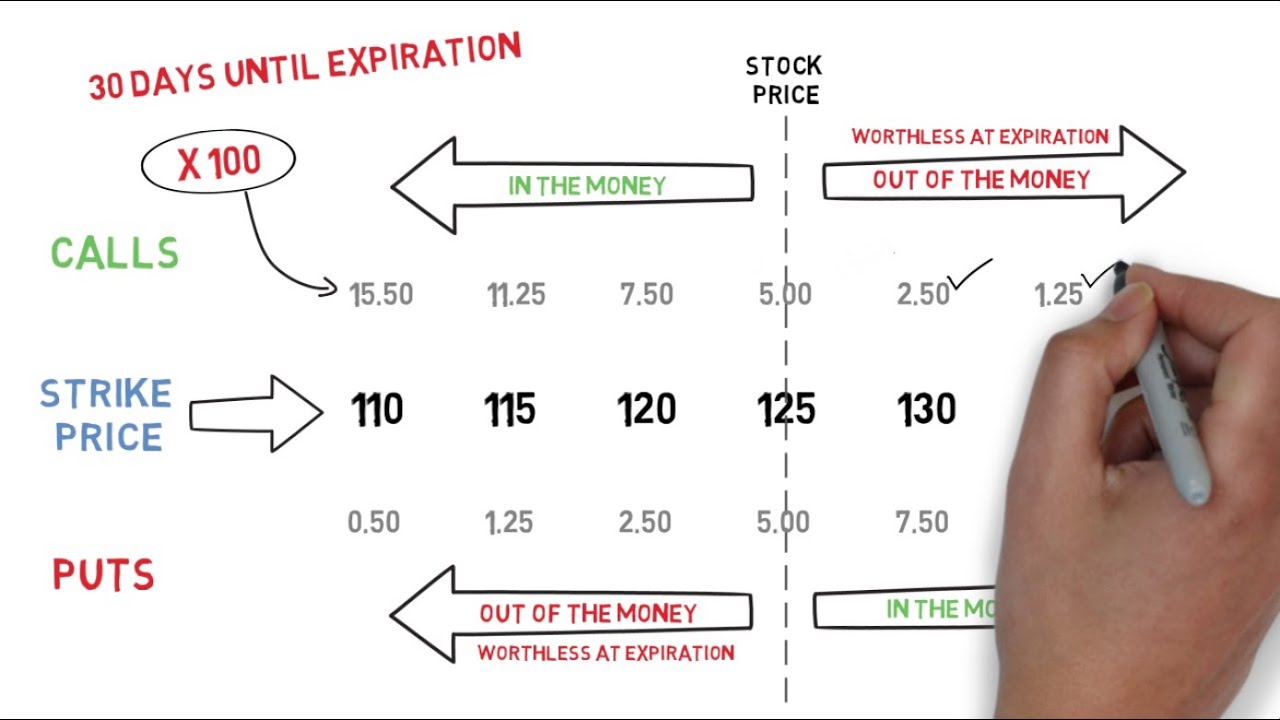
Image: m.youtube.com
The origins of option trading can be traced back to the 17th century, when traders in Amsterdam sought to mitigate risk and manage price fluctuations in the tulip market. Today, options are traded on a vast array of underlying assets, including stocks, bonds, indices, commodities, and currencies. They are an integral part of modern investment strategies, enabling investors to tailor their risk and return profiles according to their individual needs and market conditions.
Dive into the Fundamentals of Options
At the core of option trading lies a fundamental understanding of four key elements:
1. Underlying Asset: The underlying asset is the financial instrument, such as a stock or commodity, that the option contract references. Its price movements determine the value of the option.
2. Strike Price: The strike price is the price at which the holder can buy or sell the underlying asset.
3. Expiration Date: The expiration date specifies the last day on which the holder can exercise the option.
4. Premium: The premium is the price paid by the option holder to the option seller in exchange for the right to exercise the option.
Call and Put Options: Two Sides of the Market
Options are classified into two primary types: call options and put options. Call options give the holder the right to buy the underlying asset at the strike price, while put options provide the right to sell. Understanding the distinction between these two types is crucial for successful option trading.
1. Call Options: When an investor expects the underlying asset’s price to rise, they may purchase a call option. If the price does indeed increase and exceeds the strike price plus the premium paid, the call option becomes profitable.
2. Put Options: In anticipation of a decline in the underlying asset’s price, investors may buy a put option. If the price falls below the strike price minus the premium paid, the put option generates a profit.
Strategies for Profitable Option Trades
The versatility of option trading empowers investors to devise sophisticated strategies that cater to their risk tolerance and market outlook. Some common strategies include:
1. Covered Call: A covered call involves selling a call option against an underlying asset that you own. This strategy is employed when the investor expects the asset’s price to remain relatively stable or rise only modestly.
2. Protective Put: This strategy entails buying a put option on an underlying asset that you own. It serves as a hedge against a potential decline in the asset’s price, effectively reducing downside risk.
3. Straddle: A straddle involves buying both a call option and a put option with the same strike price and expiration date. This strategy is suitable for investors who expect significant volatility in the underlying asset’s price.
4. Strangle: Similar to a straddle, a strangle involves buying both a call option and a put option, but with different strike prices. This strategy allows for some flexibility in terms of the anticipated price movement.

Image: www.researchgate.net
Advanced Techniques for Seasoned Traders
As traders gain experience, they may explore more advanced techniques to enhance their option trading performance. These techniques include:
1. Delta Neutral Trading: This sophisticated strategy aims to create a portfolio that is unaffected by changes in the underlying asset’s price. It involves adjusting the positions in call and put options to maintain a neutral delta.
2. Volatility Trading: Volatility refers to the fluctuation in the price of an underlying asset. Skilled traders may employ volatility trading strategies to profit from expected changes in volatility levels.
3. Exotic Options: Exotic options are complex financial instruments that provide unique risk-return profiles. These options have additional features or variations that cater to specialized investor needs.
Option Trading Mechanism
Embark on the Journey of Option Trading
Option trading presents a dynamic and rewarding investment arena. However, it’s imperative to approach it with a fundamental understanding of the subject matter and a strong risk management strategy. By grasping the concepts outlined in this guide, you can embark on the journey of option trading with confidence and maximize your opportunities in the financial markets.






