Have you ever felt the thrill of witnessing a stock soar, only to be left wishing you had jumped on board earlier? Or perhaps you’ve watched helplessly as a company you were invested in plummeted, wishing you could have mitigated the loss. In the realm of financial markets, a powerful tool exists that allows investors to navigate such scenarios with a strategic edge – option trading. This fascinating world of financial derivatives offers opportunities for both substantial gains and significant risks, and understanding its mechanics is paramount before embarking on this exciting journey.
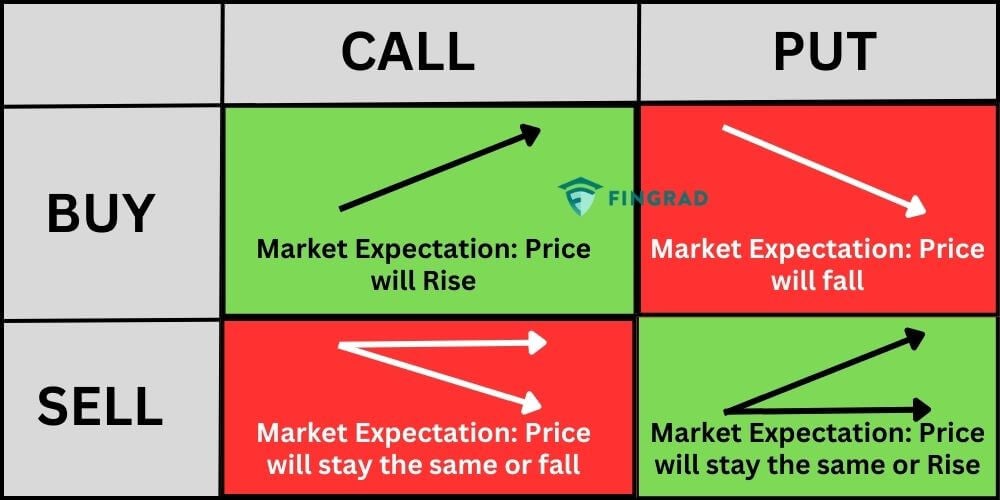
Image: tradebrains.in
Option trading, in essence, is a contract that grants the holder the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a predetermined price on or before a specific date. It’s a form of leverage that can amplify both potential profits and losses. The world of option trading can be complex, but with careful study and an understanding of its fundamental principles, you can unlock a powerful tool to manage risk and potentially enhance your investment strategy.
Delving into the World of Options: A Step-by-Step Guide
The Basics: Calls and Puts
Before diving into the intricacies of option trading, let’s first grasp the two fundamental types of options:
- Calls: A call option gives the holder the right to buy the underlying asset at a set price (the strike price), on or before the expiration date. Think of it as holding a ticket to purchase shares at a discount. Investors would buy a call option if they anticipate the asset’s price to rise.
- Puts: A put option, on the other hand, grants the holder the right to sell the underlying asset at the strike price, on or before the expiration date. This is like having the power to sell shares at a premium. Investors typically buy put options when they expect the asset’s value to decrease.
Understanding the Anatomy of an Option
Every option contract carries specific details, much like a well-structured agreement. Here are the key components:
- Strike Price: The price at which the option holder can buy or sell the underlying asset. It’s the agreed-upon price in the contract.
- Expiration Date: The date by which the option must be exercised (bought or sold). After this date, the option becomes worthless.
- Premium: The price an investor pays to acquire the option contract. It’s the fee for the right to exercise the option.
- Underlying Asset: The asset that the option contract is based on, such as a stock, index, or commodity.
Image: www.asktraders.com
Real-World Examples to Ignite Comprehension
- Example 1: Riding the Wave of a Rising Stock: You believe that the price of XYZ stock will rise to $100 by next month. You purchase a call option with a strike price of $95 and an expiration date of one month. If the stock price indeed rises to $100, you can exercise your option, buy the stock at $95, and immediately sell it in the market at $100, making a $5 profit per share. However, if the stock price falls below $95, your option becomes worthless, and you lose the premium you paid.
- Example 2: Navigating a Market Downturn: You’ve been watching ABC stock decline for weeks and anticipate further downward pressure. You buy a put option with a strike price of $80 and an expiration date of one month. If the stock price falls below $80, you can exercise your option and sell the stock at $80, mitigating potential losses. However, if the stock price stays above $80, you lose the premium paid.
The Leverage Effect: Amplifying Potential and Risk
One of the most significant aspects of option trading is the leverage it offers. A small price movement in the underlying asset can lead to a disproportionately larger gain or loss in the option’s value. This leverage makes option trading alluring, but it also makes it crucial to understand the inherent risks involved.
- Amplified Profits: If the underlying asset’s price moves in your favor, your option can generate significant gains. Imagine you bought a call option for $1 and the stock price rises by $10. Your option might be worth $50, yielding a 50-fold return on your initial investment.
- Increased Losses: Conversely, if the underlying asset’s price moves against your prediction, your losses can be substantial. The maximum loss on a bought option is limited to the premium paid. But, if you sold an option (writing an option), your potential losses can be unlimited, as the stock price can theoretically rise or fall indefinitely.
Expert Insights and Actionable Tips for Navigating the Option Landscape
Learning about option trading can feel overwhelming at first, but remember, mastering this skillset takes time, patience, and a willingness to embrace continuous learning.
- Consult with a Financial Advisor: Don’t hesitate to seek guidance from a qualified financial advisor who specializes in options. They can help you assess your risk tolerance, establish your investment goals, and create a personalized strategy that suits your unique circumstances.
- Start Small and Learn Through Practice: As with any new endeavor, start small and gradually increase your investment amounts as you gain confidence and experience. Consider using a paper trading account to practice trading strategies without risking real capital.
- Embrace Continuous Learning: The world of finance is dynamic. Keep yourself informed by staying updated on market trends, reading industry publications, and attending financial seminars or webinars.
- Control your risk: Option trading offers leverage and can amplify both profits and losses. Use stop-loss orders, consider selling covered calls or put options, and never invest more than you can afford to lose.
How Option Trading Works
The Final Word: Embracing the Potential of Options
While option trading can be complex and risky, it’s also an exciting avenue for experienced investors to potentially enhance their returns while actively managing risk. By understanding its fundamentals, you can equip yourself to make informed decisions, navigate the complexities of the market, and explore the potential benefits this powerful tool offers. Remember, knowledge is power, so start with careful research, a willingness to learn, and a solid grasp on your risk tolerance. As you embark on your journey into the world of options, embrace the possibilities while staying mindful of the inherent challenges.






