Introduction: Navigating the Ebb and Flow of Options
Options trading, a lucrative endeavor in the financial markets, is not without its complexities. The option trader’s success often hinges on their ability to anticipate the fluctuations of the underlying asset and the movement of market forces. Enter the options trading calendar, a valuable tool that sheds light on upcoming economic events and company disclosures that can significantly impact option prices. Embarking on an exploration of this trading calendar unravels a roadmap to the market’s heartbeat, empowering traders to align their strategies with the cycles that shape the options landscape.
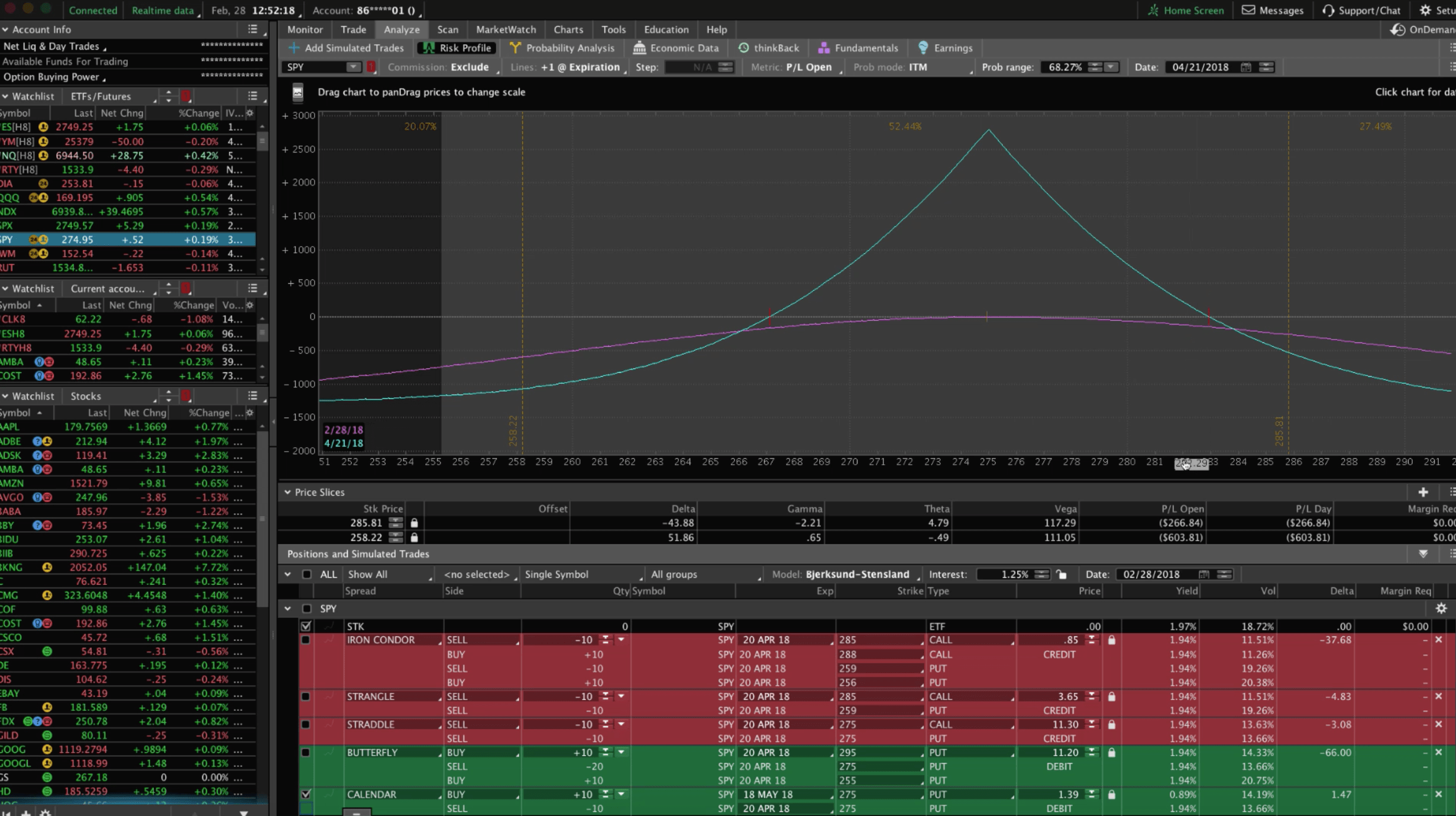
Image: navigationtrading.com
The options trading calendar serves as a central hub of information, meticulously curating a list of pertinent events that can influence the market’s direction. These events, spanning economic data releases, corporate earnings announcements, and central bank monetary policy decisions, each carry the potential to trigger market volatility and substantial price swings in underlying assets. By being privy to this forward-looking calendar, traders can pre-empt market reactions, positioning their options trades accordingly.
Section 1: Deciphering the Economic Calendar
The economic calendar serves as a compass in the ever-shifting terrain of financial markets. It charts the release of key economic indicators, meticulously compiled by statistical agencies around the globe. These indicators, ranging from employment figures to inflation data and consumer spending reports, paint a vivid picture of the economic landscape, often influencing the trajectory of the markets. For options traders, the economic calendar is an indispensable resource, enabling them to anticipate market sentiment and adjust their trading strategies accordingly.
Foremost among these economic indicators is the monthly employment report, a document that has the power to sway markets with its potent implications. The report’s unemployment rate and nonfarm payrolls figures provide crucial insights into the health of the labor market and the overall economy. Traders eagerly dissect this data, knowing that a robust labor market often fuels optimism, while a lackluster one can dampen sentiment.
Inflation data, as measured by the Consumer Price Index (CPI) and the Producer Price Index (PPI), is another market mover. These reports gauge the rate of increase in prices, providing insights into the potential impacts on purchasing power and consumer spending. Options traders closely monitor inflation data, as it can influence monetary policy decisions, which in turn can send ripples through the markets.
Retail sales reports, a barometer of consumer spending, are also highly anticipated by options traders. Robust retail sales figures often indicate a healthy economy, while weak numbers can raise concerns about consumer confidence and economic growth. Traders decipher these reports to ascertain the strength of consumer spending, a critical driver of economic activity.
In the realm of options trading, the Markit manufacturing and services Purchasing Managers’ Indices (PMIs) hold sway. These forward-looking indicators gauge the health of the manufacturing and service sectors, providing traders with a sneak peek into the future trajectory of economic activity. Positive PMI readings often bolster market sentiment, while negative readings can trigger caution.
Rounding out the economic calendar is a diverse array of other indicators, each with the potential to impact market direction. Trade balance reports, housing starts, and durable goods orders are but a few examples of the vast array of data points that options traders scrutinize to refine their trading strategies.
Section 2: Unraveling the Corporate Earnings Calendar
The corporate earnings calendar, a symphony of quarterly financial disclosures, offers options traders a glimpse into the inner sanctum of publicly traded companies. As companies release their earnings reports, traders eagerly dissect the numbers, assessing the financial health of these businesses and gauging their prospects for the future. These reports often come laden with insights that can substantially affect the prices of their underlying options.
Earnings per share (EPS), a metric that quantifies a company’s profitability, is a focal point for options traders. A company that surpasses its EPS estimates often elicits bullish sentiment, while a company that falls short may face the wrath of the bears. Traders use this information to adjust their positions, betting on the anticipated price movements of the underlying asset.
Revenue figures, another key component of earnings reports, provide insights into a company’s top line growth. Robust revenue growth often bolsters investor confidence, signaling the company’s ability to generate sales and expand its market share. Conversely, weak revenue growth can raise concerns about a company’s competitive advantage and its ability to sustain future growth.
Gross and operating margins, measures of a company’s pricing power and cost structure, are also closely scrutinized by options traders. Improving margins indicate a company’s ability to generate more profit from its operations, while declining margins can raise questions about its efficiency and its ability to maintain profitability in the face of competition.
Beyond the headline numbers, options traders also delve into the footnotes and management commentary of earnings reports, seeking additional insights into a company’s strategy, its competitive landscape, and its outlook for the future. This comprehensive analysis empowers traders to make informed decisions about their options trades, navigating the shifting currents of the market.
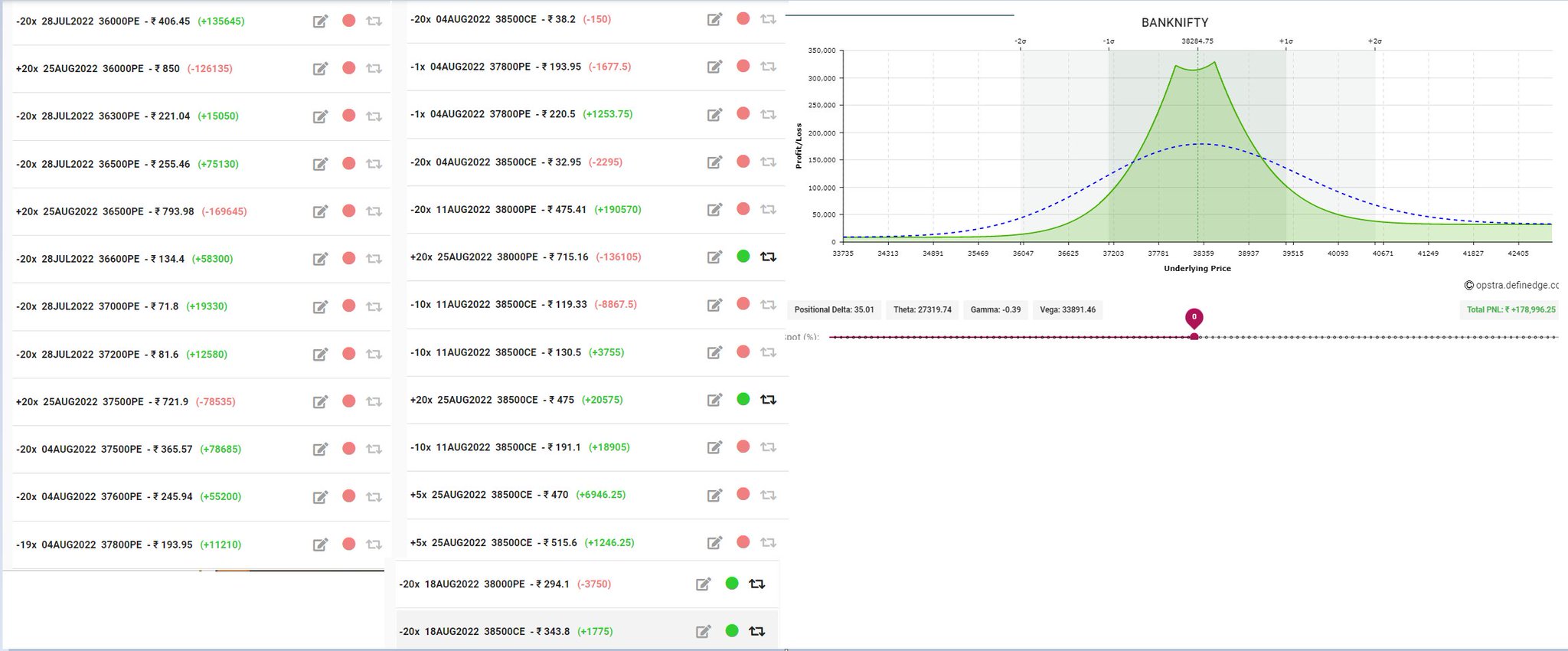 Image: twitter.com
Image: twitter.comOptions Trading Calendar
Section 3: Monitoring Central Bank Monetary Policy Decisions
The tapestry of the options trading calendar is intricately woven with the monetary policy decisions of central banks around the world. These decisions, often highly anticipated by market participants, have the power to shape the entire financial landscape, impacting interest rates, currency values, and the overall direction of the markets. Options traders, attuned to the nuances of monetary policy, carefully dissect these decisions, seeking clues to the future trajectory of the economy and the financial markets.
Interest rate decisions, a cornerstone of monetary policy, are paramount for options traders. Central banks, such as the Federal Reserve in the United States and the European Central Bank in the Eurozone, wield the power to raise or lower interest rates, influencing the cost of borrowing and the flow of money in the economy. An interest rate hike often signifies the central bank’s intention to combat inflation, while an interest rate cut suggests a desire to stimulate economic growth.
Quantitative easing (QE) and quantitative tightening (QT), unconventional monetary policy tools, also find their place on the options trading calendar. QE involves expanding the central bank’s balance sheet by purchasing government bonds and other assets, while QT entails reducing the balance sheet by selling those assets. These policies can significantly impact






