Introduction
Options trading has gained significant traction in recent years, offering investors and traders a versatile way to manage risk and potentially profit from underlying assets. But what exactly is options trading, and how does it work? This article will delve into the intricate world of options trading, providing a comprehensive overview of its key concepts, strategies, and applications.
Image: www.youtube.com
Defining Options Trading
Options contracts are financial derivatives that provide the buyer (holder) the right, but not the obligation, to buy (call option) or sell (put option) an underlying asset at a predetermined price (strike price) before or on a specific expiration date. In exchange for this right, the buyer pays the option seller (writer) a premium.
Options trading offers flexibility and strategic advantages, allowing traders to speculate on the future price movements of underlying assets, hedge existing positions, and generate income from premiums. Understanding the mechanics of options trading is crucial for navigating this complex financial landscape.
Understanding Basic Options Concepts
Types of Options Contracts
There are two primary types of options contracts:
- Call options give the buyer the right to buy the underlying asset at the strike price.
- Put options grant the buyer the right to sell the underlying asset at the strike price.
.
Each type can be held either “in the money” (ITM), “at the money” (ATM), or “out of the money” (OTM) depending on the relationship between the market price and the strike price.
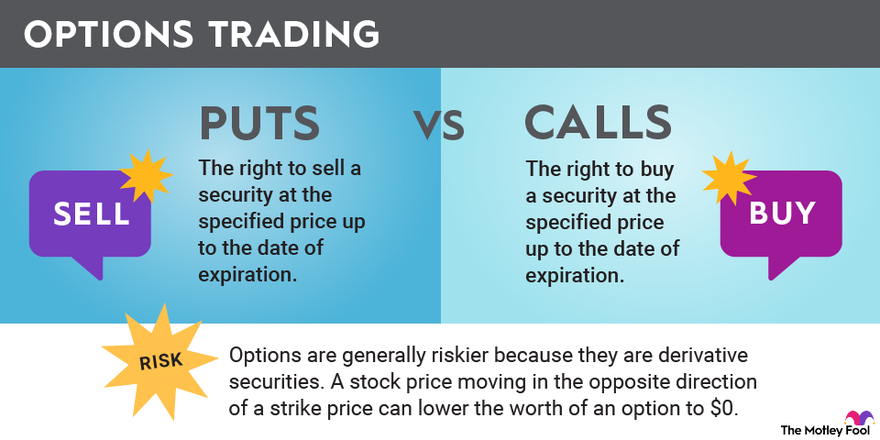
Image: www.fool.com
Participants in Options Trading
Two parties are involved in every options transaction:
- Option buyer: They acquire the right to exercise the option contract in exchange for paying a premium to the seller.
- Option seller: They transfer the right to exercise the option to the buyer, receiving the premium payments.
Expiration Dates
Options contracts have specified expiration dates. The buyer has the right to exercise the option before the expiration or let it expire worthless.
Demystifying Options Trading Strategies
Options trading strategies encompass a wide spectrum of techniques used to achieve specific investment goals. Common strategies include:
Buying Calls and Puts
Buying call options capitalizes on expectations of rising asset prices, while buying put options anticipates price declines.
Selling Calls and Puts
Selling call options conveys a bullish outlook and generates income from premiums. Conversely, selling put options implies a bearish view with premium income.
Spreads
Spreads combine multiple options contracts, allowing traders to refine their risk and profit potential in more sophisticated strategies.
Applications of Options Trading
Options trading finds diverse applications in the financial markets:
Risk Management
Options provide a powerful tool to hedge against potential losses in other investments.
Speculation
Traders can speculate on future asset price movements for potential profits, leveraging options’ high leverage.
Income Generation
Selling options premiums can generate income, especially during periods of sideways or volatile market conditions.
Wht Is Options Trading

Image: tradeoptionswithme.com
Conclusion
Options trading, though a sophisticated financial instrument, offers remarkable versatility for investors and traders. By understanding its core concepts, stratégies, and applications, you can effectively navigate the options market, manage risk, and pursue potential profit opportunities. As always, it’s essential to approach options trading with knowledge, sound judgment, and a comprehensive understanding of the risks involved.






