The world of options trading presents immense opportunities, but understanding the nuances of taxation can be daunting. Skilled traders seek every advantage, and tax deductions are one such strategy. This guide will empower you with knowledge about the tax deductions available for options trading, allowing you to maximize your earnings and feel confident in your financial decisions.

Image: fincalc-blog.in
Options Trading: A Brief Overview
Options trading involves contracts that give the buyer (option holder) the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset (e.g., a stock, bond, or index) at a specified price by a certain date. Traders use options to speculate on future price movements or hedge against risks in their portfolio.
Navigating the Tax Maze: Deductible Expenses
The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) recognizes various expenses incurred in options trading as tax-deductible. These include:
- Commission Fees: Fees paid to a broker for executing trades are fully deductible as ordinary business expenses.
- Subscription and Information Services: Subscriptions to financial newsletters, data platforms, and research reports that provide timely information crucial for trading decisions can be deducted.
- Market Data: Costs associated with obtaining real-time market data (e.g., streaming quotes, historical charts) to trade effectively qualify for deductions.
- Investment Conferences and Seminars: Attending educational events focused on options trading can be written off as business expenses if related to improving your trading skills.
- Home Office Expenses: If you designate a portion of your home as your primary business office, you may deduct expenses such as rent, utilities, and depreciation.
Capital Gains: Where Tax Savings Shine
Options trading can generate capital gains (income from selling financial assets), which are subject to different tax rates depending on the holding period. Short-term capital gains held for less than a year are taxed at ordinary income tax rates, while long-term capital gains held for over a year enjoy preferential rates.
Understanding this distinction is critical when deciding when to close your positions. Holding options longer can result in significant tax savings on profits.

Image: www.indiafilings.com
Maximizing Deductions: An Astute Trader’s Approach
- Keep Accurate Records: Document all expenses related to options trading meticulously. Proper record-keeping allows you to claim deductions confidently and avoid IRS scrutiny.
- Categorize Expenses Wisely: Distinguish between deductible business expenses and personal expenses to optimize your tax savings.
- Maximize Long-Term Holdings: Strategic traders avoid frequent trading and aim for long-term capital gains to benefit from lower tax rates.
- Seek Professional Guidance: Consulting a tax accountant or financial advisor who specializes in options trading can provide invaluable insights for minimizing tax liability.
Tax Deductions For Options Trading
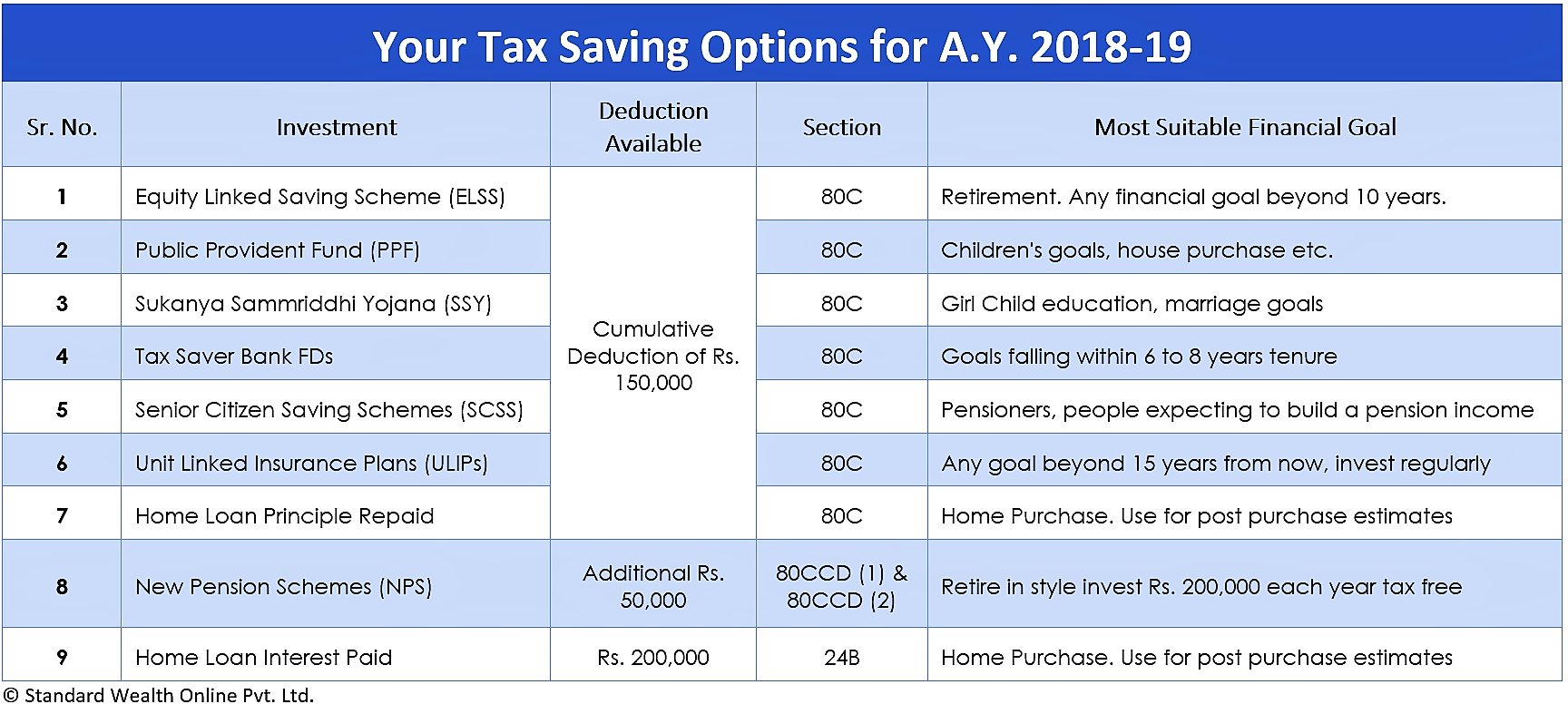
Image: www.standardwealthonline.com
Conclusion: Empowered Trading, Enhanced Savings
Mastering the intricacies of tax deductions for options trading is not a mere exercise in saving money; it’s an investment in your financial freedom. By leveraging this knowledge, you can unlock the full potential of options trading, knowing that your hard-earned earnings are protected and your tax burden is optimized. Embrace the opportunity, make informed decisions, and let tax deductions fuel your trading success.






