In the enigmatic world of options trading, a reverse split occurs when a company reduces the number of outstanding shares while proportionately increasing the share price. This maneuver can have significant implications for traders, and understanding its intricacies is crucial for informed decision-making.

Image: tradejanis.com
Reverse Split: An Overview
A reverse split is essentially a stock consolidation, where a company reduces the number of shares held by each shareholder. For instance, in a 1:2 reverse split, shareholders would receive one new share for every two shares they previously owned. Simultaneously, the stock price would double, maintaining the company’s market capitalization.
Rationale Behind Reverse Splits
Companies typically initiate reverse splits for strategic reasons. These may include:
- Enhancing Share Price: By increasing the share price, companies can make their stocks more accessible to retail investors who may prefer higher-priced shares.
- Meeting Exchange Requirements: Some exchanges impose minimum share prices for listing and trading, and reverse splits can help companies meet these criteria.
- Signaling Financial Strength: Reverse splits can give the impression of improved financial health, as they imply a higher share price.
Impact on Options Trading
Reverse splits have direct consequences for options traders:
- Contract Adjustments: Options contracts are adjusted accordingly. For a 1:2 reverse split, an existing option with a strike price of 100 would have its strike price adjusted to 200.
- Value Implication: While the underlying share price increases, the premium of options contracts decreases proportionately. This is because the reduced number of shares affects the contract’s underlying value.
- Exercise and Assignment: Exercise and assignment of options become more challenging, as traders may need to purchase or deliver a higher number of shares.
Image: ubawyzo.web.fc2.com
Factors to Consider
Before acting on a reverse split announcement, traders should consider:
- Company Fundamentals: Assess the company’s overall financial health and the rationale for the reverse split.
- Technical Analysis: Study the stock’s historical price action and technical indicators to gauge its potential performance after the split.
- Market Conditions: Consider the broader market environment and the impact it may have on the stock’s post-split trajectory.
Options Trading Reverse Split
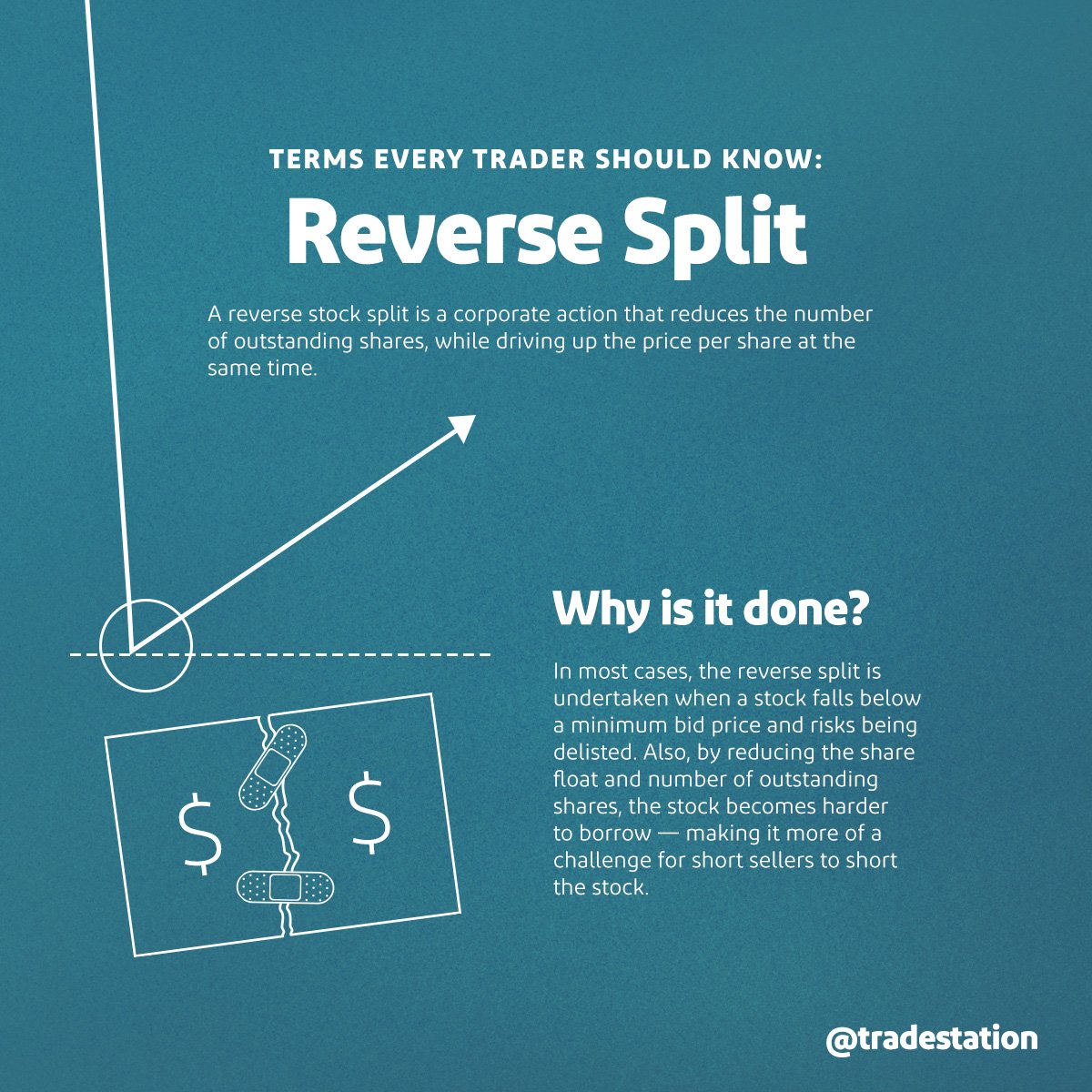
Image: cookinglove.com
Conclusion
Understanding the nuances of options trading reverse splits is essential for navigating these market events strategically. By carefully evaluating the reasons behind a reverse split and considering its impact on option contracts, traders can make informed decisions that align with their investment goals. Remember, while reverse splits can influence option trading dynamics, they should not be viewed in isolation when making investment decisions.






