Navigating the Complex World of Options
Options trading has emerged as a powerful tool for retail investors seeking to amplify their returns or hedge against potential losses. However, the intricacies of options trading can often prove daunting for newcomers. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the fundamentals of options trading, empowering you with the knowledge and strategies to navigate the complex world of options like a seasoned professional.
Image: pyqudow.web.fc2.com
Understanding Options: A Primer
An option contract grants the holder the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a predetermined price on or before a specified date. Call options give the holder the right to buy, while put options give the holder the right to sell. The underlying asset can be stocks, bonds, commodities, or even currencies.
The price specified in the contract is known as the strike price, and the date on which the option expires is known as the expiration date. Each option contract represents 100 shares of the underlying asset.
The Lures and Pitfalls of Options Trading
Options trading offers enticing potential profits. By leveraging relatively small investments, investors can gain significant exposure to the underlying asset. However, it’s crucial to recognize the inherent risks involved. Options can expire worthless, resulting in total loss of the investment.
Types of Options Trading Strategies
Retail investors can employ a diverse range of options trading strategies to suit their individual risk tolerance and investment goals. Some popular strategies include:

Image: harshbijalwan.com
Bullish Strategies
- Buying Call Options: Acquire the right to buy the underlying asset at a higher price, anticipating a rise in its value.
- Writing Covered Calls: Sell call options while holding the corresponding number of shares in the underlying asset, expecting the stock price to remain below the strike price.
Bearish Strategies
- Buying Put Options: Acquire the right to sell the underlying asset at a lower price, anticipating a decline in its value.
- Writing Naked Puts: Sell put options without holding the corresponding number of shares in the underlying asset, seeking income or market neutrality.
Key Considerations for Options Trading
Volatility
Volatility measures the fluctuations in the underlying asset’s price. Increased volatility translates into higher option premiums, making them more expensive.
Time Decay
Option values erode over time as the expiration date approaches. This phenomenon is known as time decay.
Size of Investment
Retail investors should carefully consider the amount they are willing to risk on options trading, keeping in mind that it can result in substantial losses.
Options Trading Retail Investors
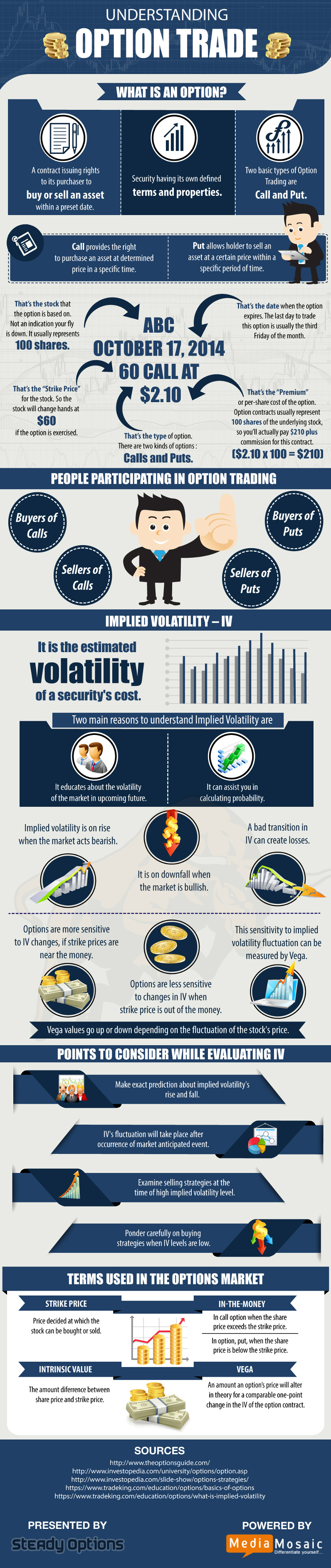
Image: www.visualcapitalist.com
Conclusion
Options trading presents ample opportunities for retail investors to enhance their portfolios. By understanding the nature of options contracts and implementing appropriate strategies, investors can harness the potential of options while managing risks. Thorough research, constant learning, and prudent execution are essential for success in the realm of options trading. Remember, knowledge and caution are your unwavering allies in this captivating financial landscape.






