Understanding Options Trading
Options trading is a complex yet versatile financial instrument that can be used to enhance portfolio returns, manage risks, and achieve specific investment goals. Unlike stocks, options do not represent ownership in a company but rather an agreement between two parties to buy or sell an underlying asset at a predetermined price on or before a specific date.
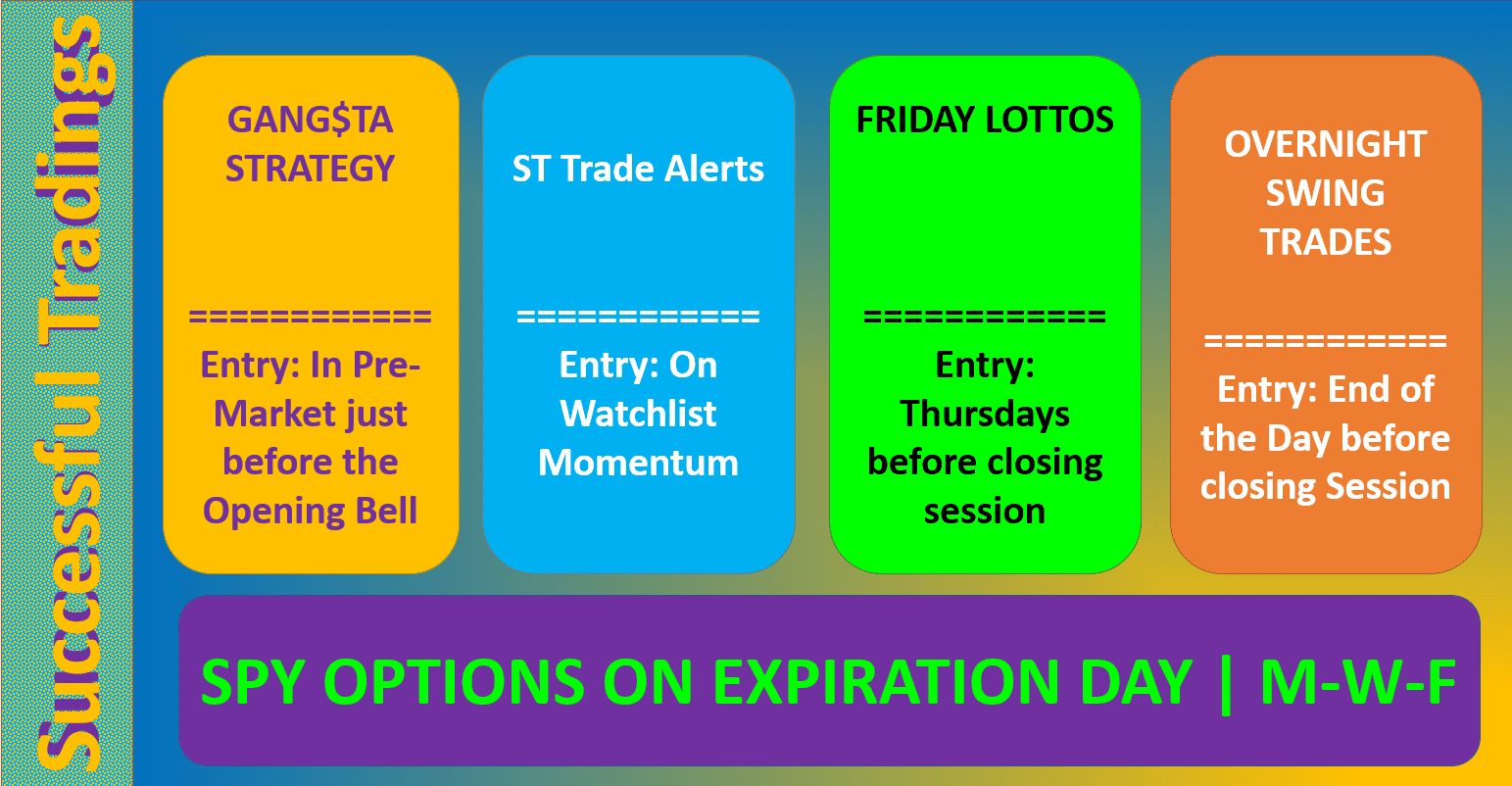
Image: successfultradings.com
Types of Options Transactions
1. Buying an Option (Call or Put):
Buying a call option gives the right, but not the obligation, to buy an underlying asset at the strike price before the expiration date. Conversely, buying a put option gives the right to sell an asset at the strike price before expiration.
2. Selling an Option (Covered or Naked):
Selling an option involves granting the right to another party to buy (call) or sell (put) an asset. Covered options are secured by the underlying asset, while naked options are not.
Basic Concepts of Options Trading
1. Strike Price: The predetermined price at which the underlying asset can be bought or sold.
2. Expiration Date: The last day the option can be exercised.
3. Premium: The price paid to acquire an option.
4. Time Value: The portion of the option premium that reflects the amount of time until expiration.
5. Intrinsic Value: The profit that can be made by exercising the option immediately.
Strategies for Options Trading
Options traders utilize various strategies to manage risks and maximize returns:
1. Spread Option Trading: Combining two or more options with different strike prices and expiration dates to enhance profit potential.
2. Butterfly Spread: Buying one put option at a higher strike price, two call options at a middle strike price, and one put option at a lower strike price.
3. Collar Option Strategy: Buying a protective put option while simultaneously selling a call option with higher strike prices.
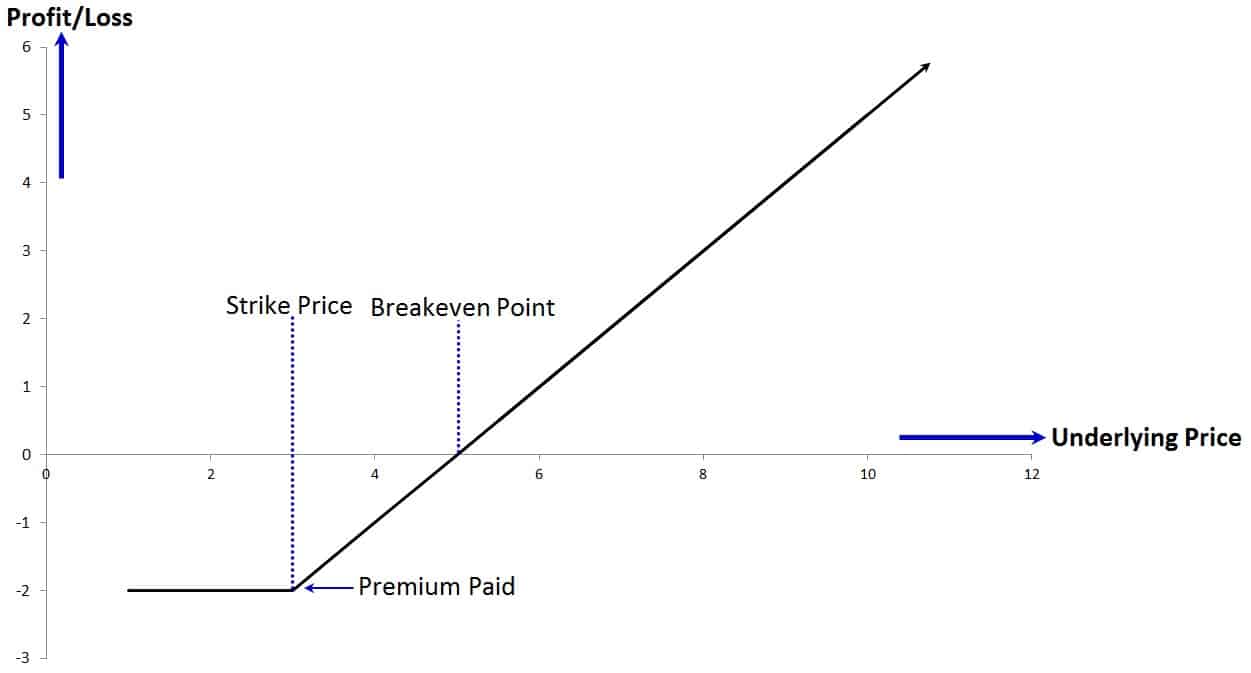
Image: www.netpicks.com
Benefits and Risks of Options Trading
Benefits:
- Enhanced Return Potential: Options can offer higher returns than traditional stock investments.
- Hedging Risk: Buying protective options can mitigate losses from holding other investments.
- Diversification: Options trading can diversify a portfolio and reduce overall risk.
Risks:
- Loss of Capital: Options trading involves the risk of losing the entire investment if the underlying asset does not perform as expected.
- Time Decay: The value of options decays as the expiration date approaches.
- Volatility: Options are sensitive to changes in the underlying asset’s price and volatility.
Options Trading Options Transactions
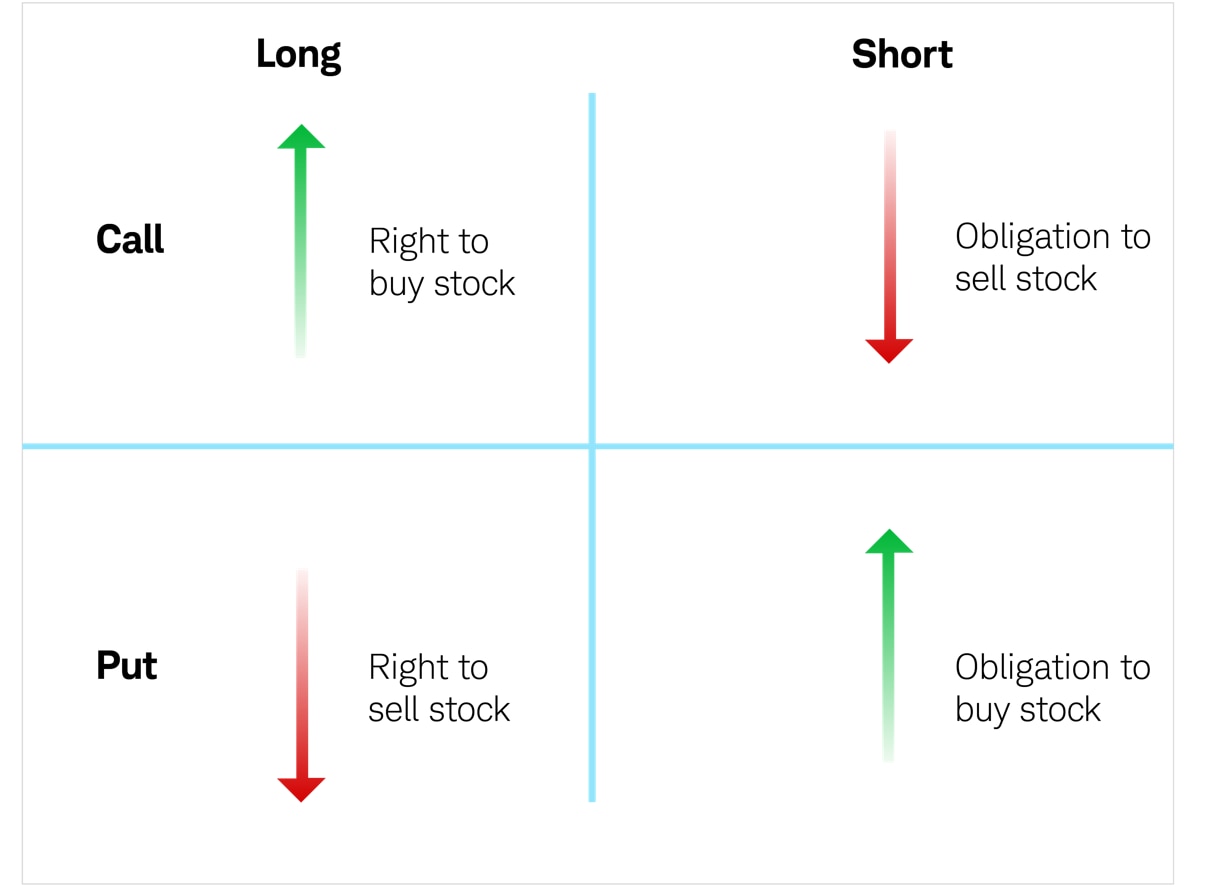
Image: www.schwab.com
Conclusion
Options trading is a powerful investment tool, but it requires a thorough understanding of the mechanics, strategies, and risks involved. By carefully evaluating options transactions, traders can potentially enhance their portfolio performance, manage downside risks, and achieve specific investment objectives. However, it is crucial to note that options trading is not suitable for all investors and should be approached with appropriate due diligence and in consultation with a qualified financial professional.






