Options trading is a powerful investment strategy that allows individuals to speculate on the future movement of an underlying asset, such as a stock, index, or commodity. However, the world of options trading can be overwhelming for beginners due to its unique jargon and complex concepts. This comprehensive guide aims to demystify the language of options trading, empowering readers to navigate this complex arena with confidence.

Image: tradebrains.in
What is Options Trading?
An option is a financial contract that gives the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a specified price within a set period. There are two main types of options: calls and puts. A call option gives the buyer the right to buy an asset at a certain price, while a put option gives the buyer the right to sell an asset at a certain price. Options traders use these contracts to speculate on the future movement of prices, hedge against risk, or generate income through premiums.
Essential Options Trading Jargon
Here is a glossary of essential options trading jargon you need to know:
Call Option: An option that gives the buyer the right to buy an underlying asset at a set price within a specified period.
Put Option: An option that gives the buyer the right to sell an underlying asset at a set price within a specified period.
Strike Price: The price at which the underlying asset can be bought or sold with the option.
Expiration Date: The date on which the option expires and becomes worthless.
Premium: The price paid by the option buyer to the option seller for the right to buy or sell the underlying asset.
In the Money: An option is in the money when its intrinsic value is positive.
Out of the Money: An option is out of the money when its intrinsic value is zero.
Intrinsic Value: The difference between the market price of the underlying asset and the strike price of the option.
Time Value: The premium paid for an option that is not yet in the money.
Exercise: The act of buying or selling the underlying asset with the option.
Rollover: The strategy of buying a new option with a different expiration date and closing out the existing option.
Understanding Options Trading Concepts
In addition to the jargon, it is crucial to understand the key concepts of options trading. These concepts include underlying assets, leverage, and risk.
Underlying Asset: An options contract represents an obligation to buy or sell an underlying asset, such as a stock, index, or commodity.
Leverage: Options trading offers significant leverage, meaning traders can control a larger position with a relatively small investment.
Risk: Options trading involves risk, and traders can lose more money than their initial investment.
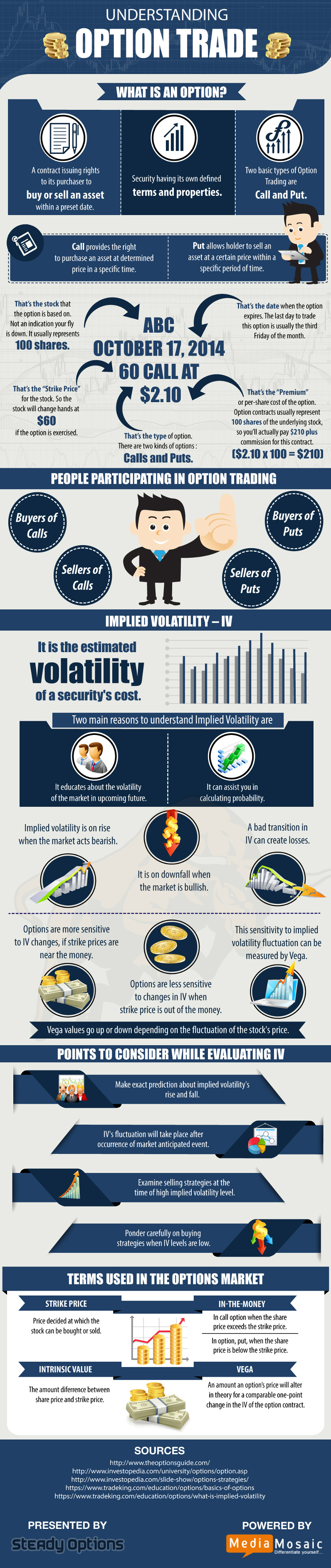
Image: www.visualcapitalist.com
Types of Options Trading Strategies
There are multiple options trading strategies to choose from, including long calls, short calls, long puts, and short puts. Each strategy has its own risk and reward profile and is used to achieve different investment objectives.
Long Call: Buy a call option, expecting the underlying asset price to rise.
Short Call: Sell a call option, expecting the underlying asset price to remain stable or fall.
Long Put: Buy a put option, expecting the underlying asset price to fall.
Short Put: Sell a put option, expecting the underlying asset price to remain stable or rise.
Options Trading Jargon

Image: traders-paradise.com
Conclusion
Understanding the jargon and concepts of options trading is essential for success in this complex and potentially lucrative investment strategy. By familiarizing yourself with the terms and nuances of options trading, you empower yourself to navigate the market with confidence, make informed decisions, and achieve your financial goals. Remember, education is key when it comes to options trading, so never hesitate to research, consult with experienced traders, and continuously expand your knowledge to maximize your success in this dynamic and rewarding financial arena.






