I’ve always been fascinated by the roaring excitement of the stock market. The surge of adrenaline as prices rise and the exhilaration of placing a winning trade. However, as I delved deeper into the world of investing, I encountered a pivotal lesson: the undeniable presence of taxes.

Image: capitalflow.info
Taxes play a crucial role in the world of option trading. Understanding the intricacies of tax implications is paramount for a successful and prudent investment strategy. In this comprehensive article, we’ll embark on a journey through the labyrinth of option trading and taxation, deciphering the complexities and providing expert advice to chart a clear path.
Decoding the Basics of Option Trading Taxation
Before delving into the specifics, let’s quickly establish the basics. Options, in essence, are financial instruments that grant the holder the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a predetermined price within a specified time frame. These options, when exercised or sold, incur tax implications.
Income from option trading is classified into two categories: short-term capital gains and long-term capital gains. Short-term capital gains arise from options held for a period of less than one year and are taxed at your ordinary income tax rate. Long-term capital gains, on the other hand, stem from options held for over a year and benefit from lower tax rates.
Unveiling the Impact of Different Strategies
The tax consequences of option trading vary depending on the strategy employed. Here’s a breakdown of the most prevalent strategies and their associated tax implications:
- Selling Call and Put Options (Covered or Naked): The premium received from selling covered calls or puts is taxed as long-term capital gain if the option expires unexercised. If assigned, the gain or loss on the underlying asset is netted against the premium received.
- Purchasing Call and Put Options (Long Calls, Long Puts): The premium paid for purchasing options is considered short-term capital loss if the option expires unexercised. Any gain realized upon exercising a profitable option falls under short-term capital gains.
- Writing Call and Put Options (Short Calls, Short Puts): The premium received from writing uncovered calls or puts is considered short-term capital gain if the option expires unexercised. If exercised, the resulting gain or loss is treated as a short-term capital loss or gain.
Steering Clear of Tax Pitfalls
To navigate the tax complexities of option trading, there are several key considerations to keep in mind:
- Establish a Trading Strategy: Clearly define your goals and risk tolerance to choose appropriate options strategies that align with your financial situation.
- Documentation is Key: Maintain detailed records of your trades, including the date, strike price, premium paid or received, and any gains or losses.
- Seek Professional Guidance: If you’re unsure about the tax implications of a particular transaction, consult a tax professional for personalized advice.

Image: dailytrademantra.com
Delving into Expert Insights
“Taxation can be a game-changer in option trading,” remarks Emily Carter, a seasoned financial advisor. “Understanding the tax laws and implications can significantly impact your investment decisions and ensure optimal outcomes.”
“Always consider the time horizon of your trades,” adds Mark Stevens, a tax attorney. “Planning ahead can potentially minimize tax burdens, allowing you to maximize your profits.”
Frequent Questions Unraveled
Q: Can I deduct losses incurred from option trading?
A: Short-term capital losses can be deducted up to $3,000 per year against other sources of income. Long-term capital losses can be carried forward indefinitely and offset against future capital gains.
Q: How are option premiums taxed?
A: Premiums received from selling options are taxed as capital gains, while premiums paid for purchasing options are treated as capital losses.
Q: Is it possible to avoid paying taxes on option trading profits?
A: While it may be possible to minimize taxes through various strategies, it’s generally not realistic to completely avoid paying taxes on profitable trades.
Option Trading And Taxes
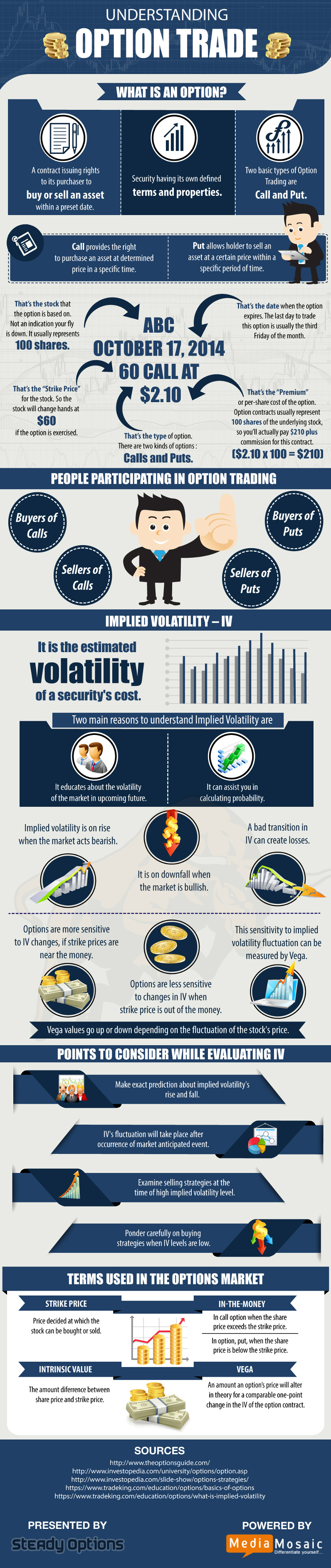
Image: www.visualcapitalist.com
Conclusion
Understanding the tax implications of option trading is a multifaceted aspect that demands consideration throughout your investment journey. By comprehending the tax laws, seeking expert guidance, and implementing strategic planning, you can optimize your trades, potentially minimize your tax burden, and maximize your profits. Remember, informed and savvy trading paves the way for greater financial success. Are you ready to venture into the world of option trading with newfound confidence and clarity?






