Unveiling the Labyrinth of Option Contracts
Option trading, a realm of strategic investment and risk management, has the potential to amplify financial returns. It’s not just about gambling; it’s about mastering the art of calculated risks and exploring the depths of financial markets.
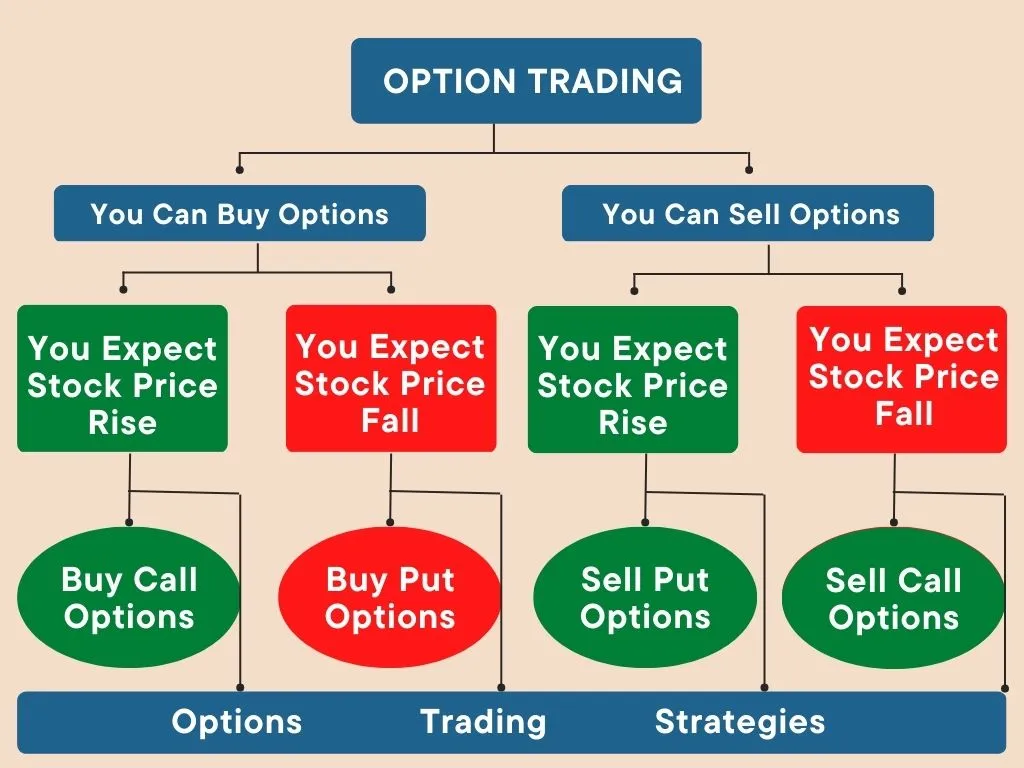
Image: changehero.io
Defining Options: The Bedrock of Trading Contracts
Options, unlike stocks or bonds, do not represent ownership shares in a company. Instead, they confer the right, not the obligation, to buy (in the case of call options) or sell (in the case of put options) an underlying asset at a predetermined price on a specific date. This flexibility is the cornerstone of option trading, affording investors the power to execute strategic maneuvers in response to market fluctuations.
Understanding the Mechanics: A Guided Tour through the Option Cycle
-
Initiation: The journey begins when an option is bought or sold between two parties: the buyer and the seller. It represents a contractual agreement for a future transaction.
-
The Waiting Game: After initiation, options have a specific lifespan, known as “time to expiration.” During this period, the option holder may choose to exercise their right to buy or sell the underlying asset (exercise) or let the contract expire, rendering it worthless.
-
Execution: The Moment of Truth If the price of the underlying asset aligns favorably with the terms of the option contract, the holder may decide to execute their right to buy or sell. For call options, the holder purchases the asset below market value; for put options, they sell above it.
-
Settlement: Exchanging Assets Executing an option involves a financial settlement. In the case of a call option, the buyer pays the seller the strike price of the underlying asset and receives the asset in return. For put options, the process is reversed, with the buyer receiving payment from the seller.
Navigating Option Strategies: Navigating the Options Map
-
Covered Calls: Generate income by selling (or “writing”) call options against an existing position in the underlying asset.
-
Protective Puts: Offer a safety net by purchasing (or “buying”) put options as insurance against potential price declines.
-
Married Puts: Combine a covered call with a protective put, enhancing downside protection while allowing for potential upside gains.
-
Straddles: A neutral strategy involving the simultaneous purchase of both a call and a put option at the same strike price and expiration date.
-
Strangles: Similar to a straddle, but with strike prices that differ (higher for calls, lower for puts).

Image: www.jlcatj.gob.mx
Expert Advice: Wisdom from the Trading Trenches
-
Start Small and Gradual: Don’t jump into the deep end; begin cautiously with smaller investments until you’ve developed a solid foundation.
-
Seek Understanding: The Path to Mastery Don’t trade blindly; educate yourself about options, market fundamentals, and risk management techniques.
-
Manage Risk Vigilantly: Options trading involves inherent risks. Implement strict risk management measures, such as stop-loss orders, to safeguard your capital.
-
Embrace Flexibility: Options provide versatility, allowing you to adapt to changing market conditions. Don’t hesitate to adjust your strategies when necessary.
-
Consult a Professional: The Guiding Light Don’t hesitate to consult with a financial advisor or experienced trader for guidance and support.
FAQ: Illuminating Option Trading Mysteries
Q: Who are option contracts suitable for?
A: Option trading is generally suited for knowledgeable investors with an understanding of market dynamics and risk tolerance.
Q: How much capital is required to trade options?
A: The minimum capital needed varies depending on the options strategy, the underlying asset, and market conditions.
Q: What are the potential risks associated with options trading?
A: Options trading involves significant risks, including the potential loss of investment capital.
Q: Can options trading generate income?
A: Yes, options trading can offer income-generating opportunities through selling premium (receiving payment from the option buyer).
Q: What are the benefits of trading options?
A: Options offer versatility, leverage, and risk management capabilities that enable investors to pursue diverse investment strategies.
How Do Option Trading Work

Image: www.plafon.id
Conclusion: The Option to Empower
Mastering option trading is a journey of calculated risks, strategic decision-making, and continuous learning. It’s not just about making money; it’s about empowering oneself with the knowledge and tools to navigate the complex financial landscape. So, delve into the world of options, embrace the challenges, and discover the hidden potential that lies within these fascinating contracts.
Let us know in the comments below if you have any further questions or thoughts on options trading.






