The stock market can be a daunting place, especially for novice investors. With so many different strategies and instruments to choose from, it’s easy to feel overwhelmed. But what if I told you that there’s a way to potentially profit from market movement, even if you’re not sure which direction it will go? This is where options trading comes in.

Image: erainnovator.com
I remember when I first started learning about options. It felt like deciphering a foreign language. But once I dug into the details, the possibilities started to open up. Options trading is a fascinating world with its own set of rules and strategies, and it can be a powerful tool for both seasoned traders and those just starting their journey.
Understanding Options: A Gateway to Market Flexibility
Options are essentially contracts that give you the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset (like a stock) at a predetermined price on or before a specific date.
Imagine you think the price of a company’s stock is going to rise soon. You could buy shares of that company, hoping to profit from the expected increase in price. But there’s another way: you could buy a “call” option. This option gives you the right, but not the obligation, to buy that stock at a specific price (the strike price) before a specific date (the expiration date). If the stock price goes up as you predicted, you can exercise your option and purchase the stock at the lower strike price, then sell it in the market at the higher current price. On the other hand, if the price goes down, you simply let the option expire worthless and lose only the premium you paid for it.
Diving Deeper into Options: Exploring the Different Types
There are two main types of options: calls and puts.
Call Options: Riding the Wave of Price Increases
Call options grant you the right to buy an underlying asset at a specified price.
As we discussed earlier, if you believe the stock price will rise, buying a call option can be a valuable strategy. You control the potential upside while limiting your downside risk to the premium paid for the option. Here’s an example:
Imagine you buy a call option for XYZ Corp. at a strike price of $50 with an expiration date of December 31st. The premium you pay for this option is $3. If the price of XYZ Corp. rises to $60 before the expiration date, you can exercise your option, purchase the shares for $50 each, and immediately sell them in the market for $60, making a profit of $7 per share (minus the $3 premium). However, if the price of XYZ Corp. stays below $50, you can let the option expire worthless and lose only the premium paid ($3).
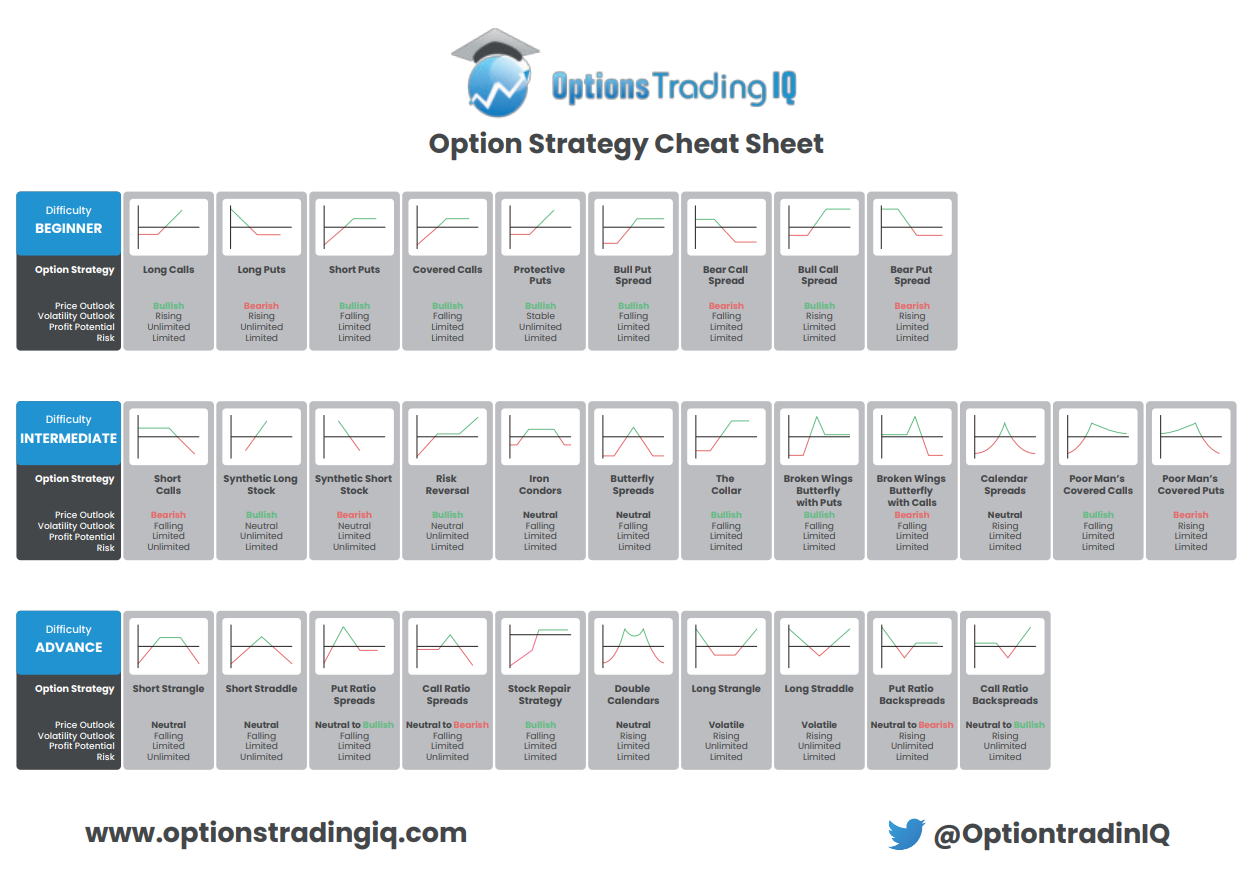
Image: www.newtraderu.com
Put Options: Playing Defense Against Declining Prices
Put options grant you the right to sell an underlying asset at a specified price.
Put options are useful when you expect the price of an asset to fall. If you think the stock price of a company will drop, you can buy a put option on that company. The put option gives you the right, but not the obligation, to sell those shares at a specific price, even if the market price falls below that level. Let’s say you buy a put option for XYZ Corp. at a strike price of $50 with an expiration date of December 31st. You pay a $3 premium for the option. If the price of XYZ Corp. falls to $40 before the expiration date, you can exercise your put option, sell the shares for $50, and then buy them back in the market at $40, making a profit of $7 per share (minus the $3 premium). However, if the price of XYZ Corp. rises above $50, you can let the option expire worthless and lose only the premium paid ($3).
Navigating the World of Options: Understanding Key Concepts
Here are some fundamental concepts to grasp as you delve into options trading:
- Premium: The price you pay for the option. This is your initial investment.
- Strike Price: The price at which you can buy or sell the underlying asset when exercising the option.
- Expiration Date: The last date you can exercise your option. If you don’t exercise it before this date, the option expires worthless.
- In the Money: An option is “in the money” if it’s profitable to exercise. For example, a call option is in the money if the current market price of the underlying asset is higher than the strike price, and a put option is in the money if the current market price is lower than the strike price.
- Out of the Money: An option is “out of the money” if it’s not profitable to exercise. For example, a call option is out of the money if the current market price is lower than the strike price, and a put option is out of the money if the current market price is higher than the strike price.
- At the Money: An option is “at the money” if the strike price is equal to the current market price of the underlying asset.
Current Market Trends and the Rise of Options Trading
Options trading has experienced a surge in popularity in recent years, driven by several factors:
- Increased accessibility: Online trading platforms have made it easier than ever to trade options, even for retail investors.
- Interest in Volatility: As markets become more volatile, options trading can offer attractive opportunities to profit from price swings, both up and down.
- Growth of meme stocks and short squeezes: Options have played a significant role in the recent phenomenon of meme stocks and short squeezes, attracting a new generation of traders to the options market.
Tips and Expert Advice for Successful Options Trading
While options trading can offer exciting possibilities, it’s important to approach it with due diligence and a sound understanding of the risks involved. Here are some key considerations:
- Start small: Don’t put more money into options trading than you can afford to lose.
- Educate yourself: Thoroughly research options trading strategies, risk management techniques, and the specific options you’re considering.
- Practice with paper trading: Before risking real money, use paper trading accounts to test your strategies and gain experience in a risk-free environment.
- Manage your risk: Options contracts have limited lifespans, and their value can expire quickly. It’s crucial to have a well-defined risk management plan in place before entering any options trades.
- Stay informed: Market conditions can change quickly, so it’s crucial to stay up-to-date on news and economic developments that could affect your options positions.
Remember, options trading is not suitable for everyone. It’s essential to assess your risk tolerance, investment goals, and level of financial sophistication before diving into this complex financial instrument.
Frequently Asked Questions about Options Trading:
- Q: What is the difference between buying and selling options?
A: Buying an option gives you the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a specific price. Selling an option (writing an option) gives you the obligation to buy or sell the underlying asset if the buyer of the option decides to exercise it.
- Q: Can I lose more than I invested in options trading?
A: Yes, options trading carries the potential for unlimited losses. While you lose only the premium paid when buying an option, selling an option (writing an option) exposes you to unlimited risk, as you are obligated to fulfill the contract if the buyer exercises it.
- Q: What are the biggest risks associated with options trading?
A: The biggest risks include the possibility of losing your entire investment, the rapid decay of option values as expiration dates approach, and the potential for unexpected market volatility to drastically impact your positions.
- Q: How can I learn more about options trading?
A: There are numerous resources available, including online courses, books, broker-provided education materials, and reputable financial websites. Additionally, it may be beneficial to consult with a financial advisor or experienced options trader.
What Are Trading Options
In Conclusion: Embracing the Flexibility and Potential of Options
Options trading offers a powerful way to manage risks and profit from market movements. Whether you’re a seasoned investor seeking to refine your portfolio or a newcomer interested in exploring different investment strategies, understanding the basics of options can unlock new opportunities. But remember, options trading requires a firm grasp of risk management and a commitment to continuous learning.
Are you interested in learning more about options trading? Do you have any questions about this complex but rewarding subject? This blog post has provided a broad overview of options trading, but there’s so much more to discover. Let’s continue the conversation!






