
Image: optionstradingiq.com
Introduction
In the ever-evolving world of investments, derivatives have become indispensable tools for savvy traders seeking to enhance returns and manage risks. Among the most popular derivative instruments are warrants and options. While both offer unique advantages, understanding their distinct characteristics is crucial for making informed investment decisions. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of warrants vs options, shedding light on their similarities, differences, and practical applications.
A Deeper Look: Trading Warrants vs Options
Warrants
Warrants are long-term derivative securities that provide holders the right, but not the obligation, to purchase a specified number of shares of an underlying asset at a pre-determined price (the exercise price) on or before a particular date (the expiration date). Unlike options, warrants typically have a longer maturity period, often ranging from several years to decades.
Options
Options, on the other hand, are short-term derivative contracts that grant buyers the right to buy (call options) or sell (put options) an underlying asset at a fixed price on or before a specific date. Options have a shorter duration than most warrants, usually expiring within a matter of months.
Key Differences
- Maturity Period: Warrants usually have a longer maturity period than options.
- Exercise Type: Warrants grant the right to purchase an underlying asset, while options offer flexibility in both buying and selling.
- Complexity: Options involve more complex strategies and calculations, whereas warrants are relatively simpler to trade.
- Leverage: Options often provide greater leverage, amplifying potential gains or losses, compared to warrants.
Applications in Investment Strategies
- Speculation: Both warrants and options offer opportunities for speculative trading, allowing traders to bet on potential price movements of the underlying asset.
- Hedging: Warrants and options can be employed to hedge against potential losses in a portfolio.
- Income Generation: Call option selling can yield premium income in anticipation of a rise in the underlying asset’s price.
Expert Insights
According to renowned investment strategist, Dr. Mark Merton, “Warrants offer investors a lower-leveraged, longer-term approach to speculating on stock price movements, while options provide more flexibility and higher potential for maximizing gains or limiting losses.”
Actionable Tips
- Consider your investment objectives and risk tolerance before trading warrants or options.
- Study the underlying asset and market conditions thoroughly to make informed decisions.
- Choose reputable brokers with expertise in derivative trading.
- Seek professional advice if navigating complex option strategies.
Conclusion
Warrants and options offer distinct advantages and applications in the world of derivatives. By understanding the key differences and practicing informed trading strategies, investors can harness the power of these instruments to enhance their portfolios and achieve financial success. The journey of trading warrants vs options is an exciting one, fraught with both risk and reward. Armed with knowledge and prudent decision-making, investors can unlock the full potential of these financial tools and navigate the markets with confidence.
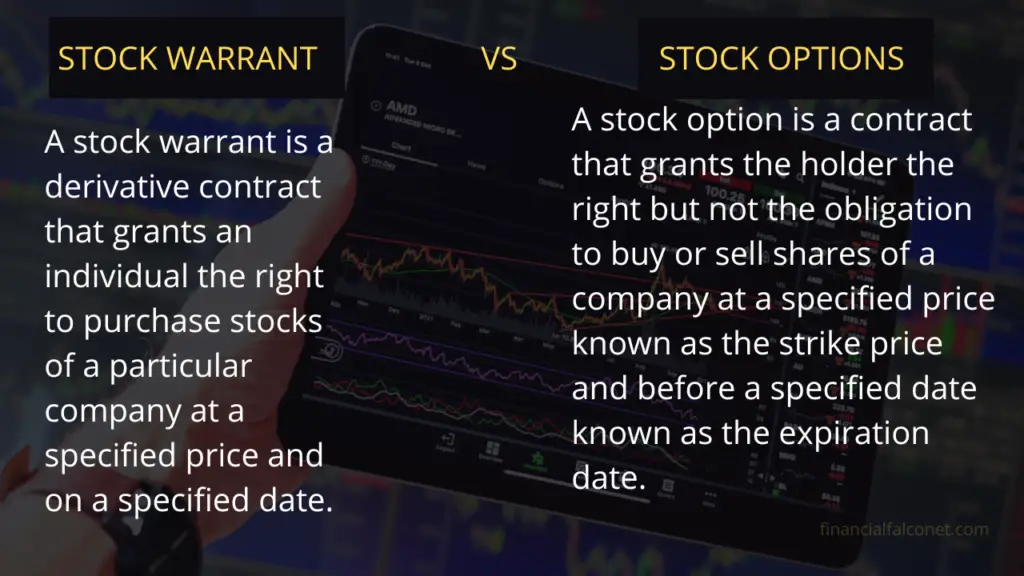
Image: www.financialfalconet.com
Trading Warrants Vs Options

Image: moneyandmarkets.com






