Introduction
The realm of investing enchants many, promising the prospect of multiplying wealth through calculated risks. Among the vast array of investment avenues, two prominent paths stand out: stock trading and options trading. Both offer unique opportunities and risks, making it crucial to grasp their fundamental differences before embarking on this financial journey.
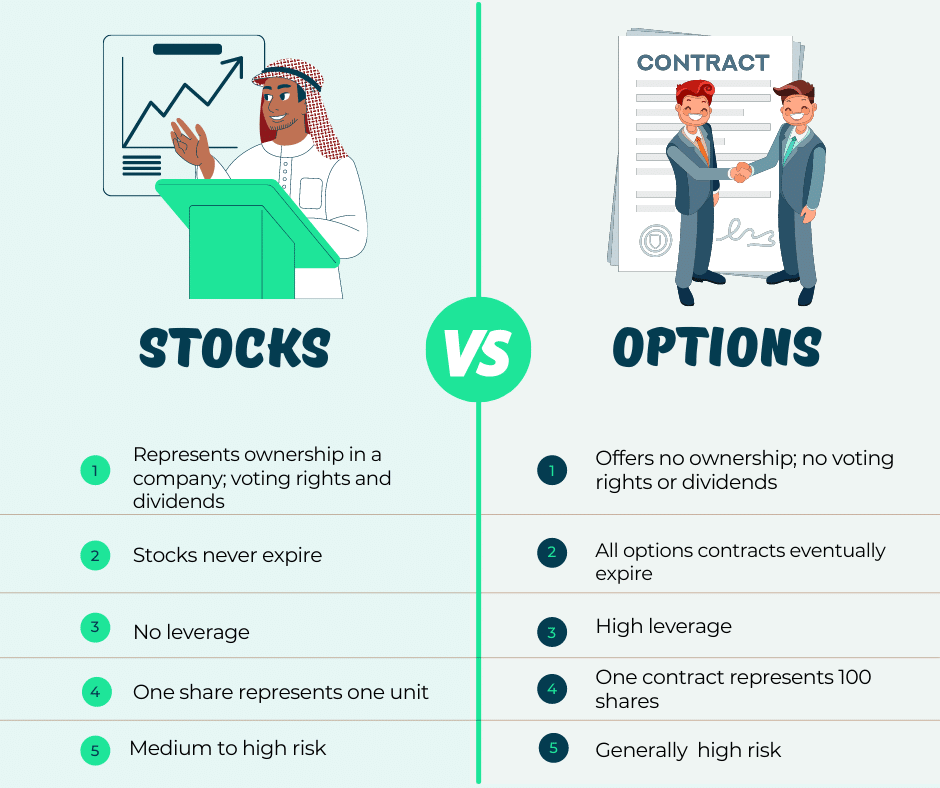
Image: www.projectfinance.com
Stocks: A Cornerstone of Investing
Stocks are slivers of ownership in publicly traded companies. By acquiring stocks, an investor becomes a shareholder with rights to a portion of the company’s earnings and assets. When the company thrives, the value of its stocks tends to rise, translating into capital gains for shareholders. However, stocks also carry the risk of depreciation if the company’s performance falters.
Options: Leveraging Volatility
Options, on the other hand, are contracts that convey the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a specific price within a predetermined time frame. They are often employed by investors seeking to profit from volatility in the underlying asset’s value without necessarily owning it. Options can be complex instruments, offering a wide range of strategies that can cater to varying risk appetites.
Key Differences: Unraveling the Dynamics
- Ownership vs. Contracts: Stocks represent ownership in a company, while options are mere contracts.
- Rights and Responsibilities: Stockholders have voting rights and are entitled to dividends, whereas options holders merely have the right to exercise their contracts within the specified timeline.
- Risk Exposure: Stocks expose investors to the full extent of the underlying company’s performance, while options provide limited risk, potentially resulting in losses only up to the premium paid for the contract.
- Potential Returns: Stocks have the potential to deliver substantial returns over the long term, but they also carry the risk of losing the invested capital. Options offer the possibility of amplified gains, but the potential for losses is capped at the premium paid.
- Complexity: Stocks are relatively straightforward, requiring an understanding of company fundamentals. Options, on the other hand, demand a deeper comprehension of market dynamics, price movements, and option strategies.
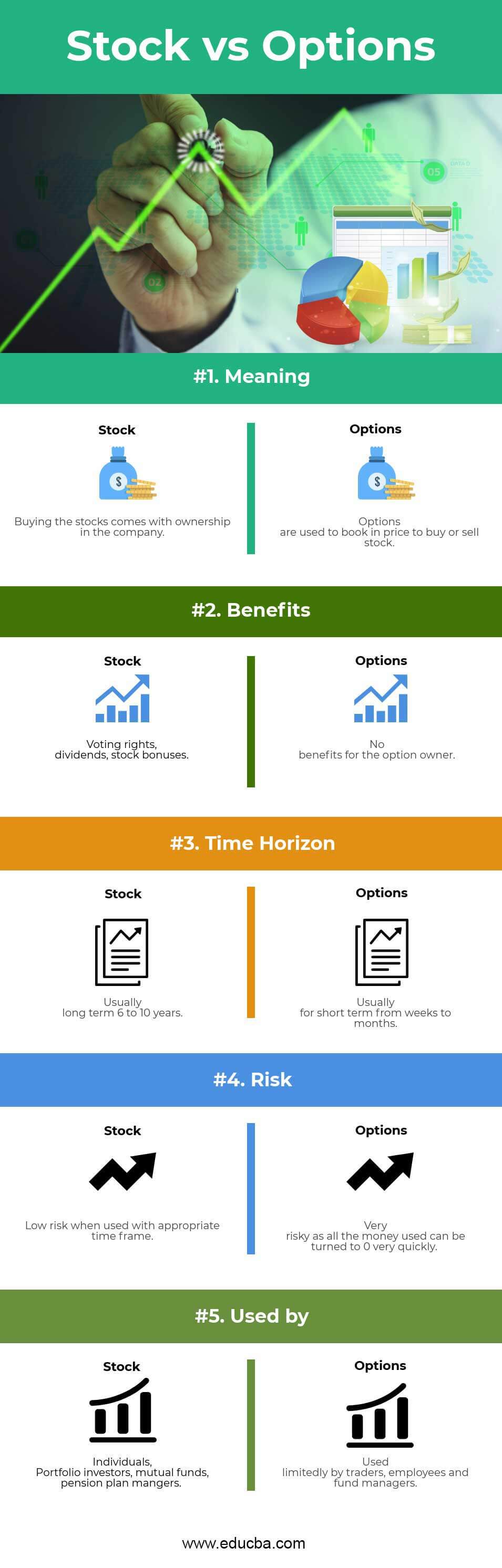
Image: www.educba.com
Suitable Paths: Aligning Objectives with Choices
The suitability of stocks or options hinges on individual investment goals, risk tolerance, and financial literacy.
- Stocks: For long-term investors seeking steady growth and dividends, stocks may be a sensible choice.
- Options: Options are more suited for sophisticated investors who navigate market volatility, seek leveraged returns, and are prepared for potential losses.
Trading Strategies: Navigating the Market
- Buy-and-Hold Strategy: This passive approach involves purchasing stocks or options with the intention of holding them for an extended period, aiming for capital appreciation or income generation.
- Day Trading: This active strategy executes trades within a single trading day, capitalizing on short-term price fluctuations.
- Hedging Strategies: Options can be employed to offset the risks associated with holding stocks or other assets, reducing overall portfolio volatility.
- Speculative Strategies: Options provide opportunities for speculative trades, aiming to profit from anticipated price movements in the underlying asset.
Trading Stock Vs Options

Image: www.samco.in
Conclusion:
The choice between stock and options trading depends on an investor’s goals, risk tolerance, and market expertise. Stocks offer a straightforward path to corporate ownership with the potential for long-term growth. Options, on the other hand, provide flexibility and leverage for sophisticated investors to navigate market volatility and pursue amplified returns. Understanding the nuances of each instrument is vital for making informed investment decisions and charting a prosperous financial course.






