Introduction
In the high-stakes world of option trading, managing risk is paramount. A stop-loss formula serves as a crucial tool to protect your capital and minimize potential losses. By establishing predefined parameters, you can automatically exit a trade when unfavorable market conditions arise. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of stop-loss formulas, empowering you to make informed decisions and enhance your trading strategy.

Image: scalablesolutions.io
Understanding Stop-Loss Formulas
A stop-loss formula is a mathematical equation that determines the point at which a trade should be closed to limit potential losses. It typically involves setting a threshold price below (for long positions) or above (for short positions) the current market price. When the price reaches this threshold, the stop-loss order is triggered, and the trade is automatically exited.
The formula for a stop-loss order is:
Stop-Loss Price = Entry Price ± Margin of Error
The margin of error represents the tolerance level you are willing to accept before exiting the trade. It should be based on your risk tolerance and the volatility of the underlying security.
Types of Stop-Loss Formulas
There are various types of stop-loss formulas, each with its own advantages and disadvantages:
1. Percentage Stop-Loss:
Sets the stop-loss price as a percentage below (for long positions) or above (for short positions) the entry price. This method is straightforward and easy to implement.
2. ATR Stop-Loss:
Utilizes the Average True Range (ATR) to determine the margin of error. ATR is a measure of volatility, and this formula adjusts the stop-loss price based on market fluctuations.
3. Volatility Stop-Loss:
Sets the stop-loss price based on the historical volatility of the underlying security. This method is more sophisticated but can provide greater accuracy.
4. Trailing Stop-Loss:
Adjusts the stop-loss price as the position moves in your favor. This strategy allows you to capture more profits during positive price movements.
Choosing the Right Formula
The optimal stop-loss formula depends on your individual trading style and risk tolerance. Consider the following factors:
- Risk Tolerance: How much potential loss are you willing to accept?
- Volatility of Underlying: How volatile is the security you are trading?
- Trading Strategy: Do you prefer aggressive or conservative trades?
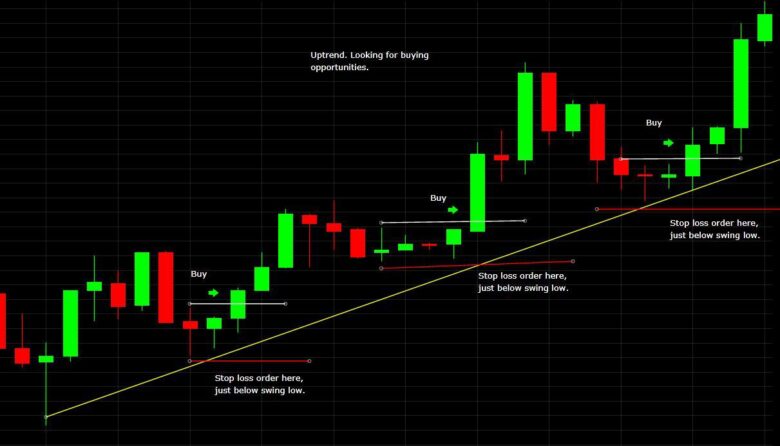
Image: www.the-pool.com
Guidelines for Using Stop-Loss Formulas
- Set Realistic Margins of Error: Avoid setting stop-loss prices too close to the entry price, as this can result in premature exits.
- Consider Market Conditions: Market volatility can impact the effectiveness of stop-loss orders. Adjust margins of error accordingly.
- Do Not Overtrade: Using overly aggressive stop-loss formulas can lead to frequent trades and potential losses.
- Review and Adjust Regularly: Regularly monitor your stop-loss orders and make adjustments as needed based on market conditions and trade performance.
Stop Loss Formula For Option Trading
Image: blog.elearnmarkets.com
Conclusion
A well-crafted stop-loss formula is an essential risk management tool for option traders. By understanding the different types of formulas and applying them effectively, you can protect your capital, minimize losses, and enhance your trading strategy. Remember to consider your risk tolerance, market conditions, and trading style when choosing the appropriate formula. By implementing these guidelines, you can navigate the unpredictable waters of option trading with greater confidence and a higher probability of success.






