Introduction
The financial markets present a myriad of opportunities for savvy investors. Among these, options trading stands out as a versatile and lucrative strategy. Particularly intriguing is the concept of selling options, a sophisticated technique that allows traders to generate income and manage risk concurrently.

Image: bocahsaicoo.blogspot.com
Unveiling the Art of Selling Options
Options, financial instruments akin to insurance contracts, grant their holders the right, not the obligation, to buy (call option) or sell (put option) an underlying asset at a predetermined price (strike price) on a specified date. By selling an option, the option seller grants this right to another party (option buyer) in exchange for a premium.
Benefits of Selling Options
- Income Generation: The premium received by the option seller constitutes the primary source of income.
- Risk Management: Option sellers assume the role of the insurer, providing protection against price fluctuations to the option buyer.
- Limited Liability: The seller’s maximum potential loss is limited to the premium received.
Navigating the Options Landscape
To successfully implement this strategy, it is imperative to comprehend the nuances of selling options.

Image: howtotradeonforex.github.io
Key Concepts
- Expiration Date: The date on which the option contract expires, determining the time frame of the seller’s commitment.
- Exercise Price: The price at which the buyer can exercise their right to buy or sell the underlying asset.
- Implied Volatility: Market sentiment’s impact on the perceived likelihood of substantial price movements, directly influencing option prices.
Types of Options Contracts
Various types of options enable traders to tailor their strategies:
- Covered Call: Seller owns the underlying asset and sells a call option with a strike price above the current market price.
- Cash-Secured Put: Seller holds cash equal to the strike price and sells a put option with a strike price below the current market price.
- Naked Call: Seller does not own the underlying asset and sells a call option without holding the underlying asset.
Expert Insights and Strategies
Mastering the art of selling options requires a comprehensive understanding of market dynamics and optimal strategies:
Tips for Success
- Understand Options Greeks: Delta, gamma, theta, and vega provide valuable insights into an option’s price sensitivity.
- Manage Risk Effectively: Limit exposure by sizing positions appropriately and implementing prudent stop-loss orders.
- Stay Informed: Monitor market news, earnings reports, and economic data to make informed decisions.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is the difference between selling a covered call and a cash-secured put?
A: A covered call involves owning the underlying asset, while a cash-secured put requires holding cash equivalent to the strike price.
Q: How much money can I make selling options?
A: Earnings depend on various factors, including the premium, option type, and market conditions.
Q: Is selling options risky?
A: Yes, all options trading involves risk, but responsible risk management can mitigate potential losses.
Sell Options Trading
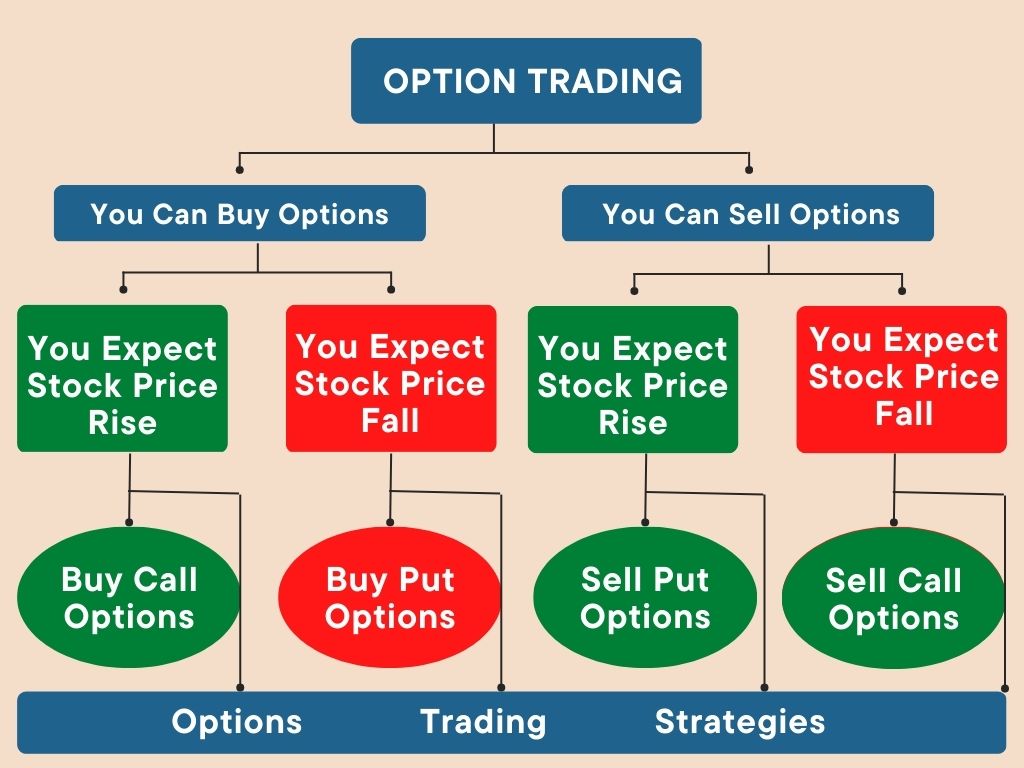
Image: www.ifmcinstitute.com
Conclusion
Selling options offers an alluring opportunity for savvy traders to enhance their financial portfolio. By harnessing the power of premiums and deftly managing risks, option sellers can capitalize on market volatility while simultaneously reducing their overall exposure. Whether you are an experienced trader or a budding enthusiast, delving into the world of selling options can be a rewarding and empowering endeavor. Embrace the intrigue of options trading today!






