Introduction
The allure of financial markets beckons countless individuals seeking financial gain, but understanding the nuances of the trading landscape is essential. Two prominent investment avenues, options trading and stock trading, offer distinct characteristics, risks, and rewards. Navigating this complex terrain requires a thorough understanding of their respective pros and cons.

Image: speedtrader.com
Exploring the intricacies of options trading and comparing it to traditional stock trading unveils a fascinating dichotomy. Options trading, often perceived as a sophisticated realm, involves trading contracts that grant the holder the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a specified price on or before a predetermined date. This flexibility allows traders to speculate on price movements and potentially magnify their returns. In contrast, stock trading involves the direct purchase and sale of shares in a company, providing investors with a more straightforward path to potential capital appreciation.
Options Trading: Unveiling Its Advantages and Drawbacks
Advantages of Options Trading
- Leverage and magnification of returns: Options offer the potential for high leverage, allowing traders to control a large number of shares with a relatively small initial investment. This leverage can amplify potential profits, although it also magnifies potential losses.
- Hedging against volatility: Options provide investors with a powerful tool for hedging against market risk. By purchasing put options, traders can mitigate potential losses on underlying assets in the event of a market downturn.
- Flexible strategies: Options trading offers a wide range of strategies, enabling traders to tailor their risk and reward profiles to their investment goals. From simple long call or put strategies to complex multi-leg combinations, options provide flexibility to navigate diverse market conditions.
Downsides of Options Trading
- Complexity: Options trading can be complex, especially for beginners. Understanding the various option types, pricing models, and trading strategies requires a significant learning curve.
- Time decay: The value of options decays over time, particularly as the expiration date approaches. This time decay can lead to significant losses if the underlying asset’s price does not move in the trader’s favor.
- Liquidity risk: Liquidity risk, the difficulty in finding a buyer or seller for an option contract, can be a concern, especially for less-liquid options. This can make it challenging to exit positions quickly without incurring substantial losses.
Stock Trading: A Path to Capital Appreciation
Advantages of Stock Trading
- Simplicity: Stock trading is relatively straightforward, involving the purchase and sale of company shares. The underlying concept is intuitive, making it accessible to investors of all experience levels.
- Dividend income: Many companies pay dividends to shareholders, providing investors with a regular stream of passive income.
- Capital gains potential: Stocks offer the potential for capital appreciation as companies grow and their share prices rise. Long-term investors can benefit from compounding returns.
Downsides of Stock Trading
- Direct ownership: Unlike options trading, stock trading involves direct ownership of the underlying asset. This means that investors bear the full risk of price fluctuations, which can lead to significant losses if the stock price declines.
- Limited hedging strategies: Stock trading provides limited opportunities for hedging against risk. Unlike options, stock investors do not have the option to purchase contracts that provide downside protection.
- Market volatility: Stock prices can fluctuate significantly, and investors must be prepared for potential losses due to market downturns or unforeseen events.
Choosing the Right Path: Aligning Goals and Risk Tolerance
The decision between options trading and stock trading hinges on an investor’s individual goals, risk tolerance, and investment horizon. Those seeking leveraged returns, hedging strategies, and the potential for accelerated gains may find options trading appealing. However, they must be cognizant of the complexities and risks involved. Conversely, investors seeking a more straightforward approach, steady dividend income, and capital appreciation over time may prefer stock trading.

Image: www.experian.com
Options Trading Vs Stock Trading Pros And Cons
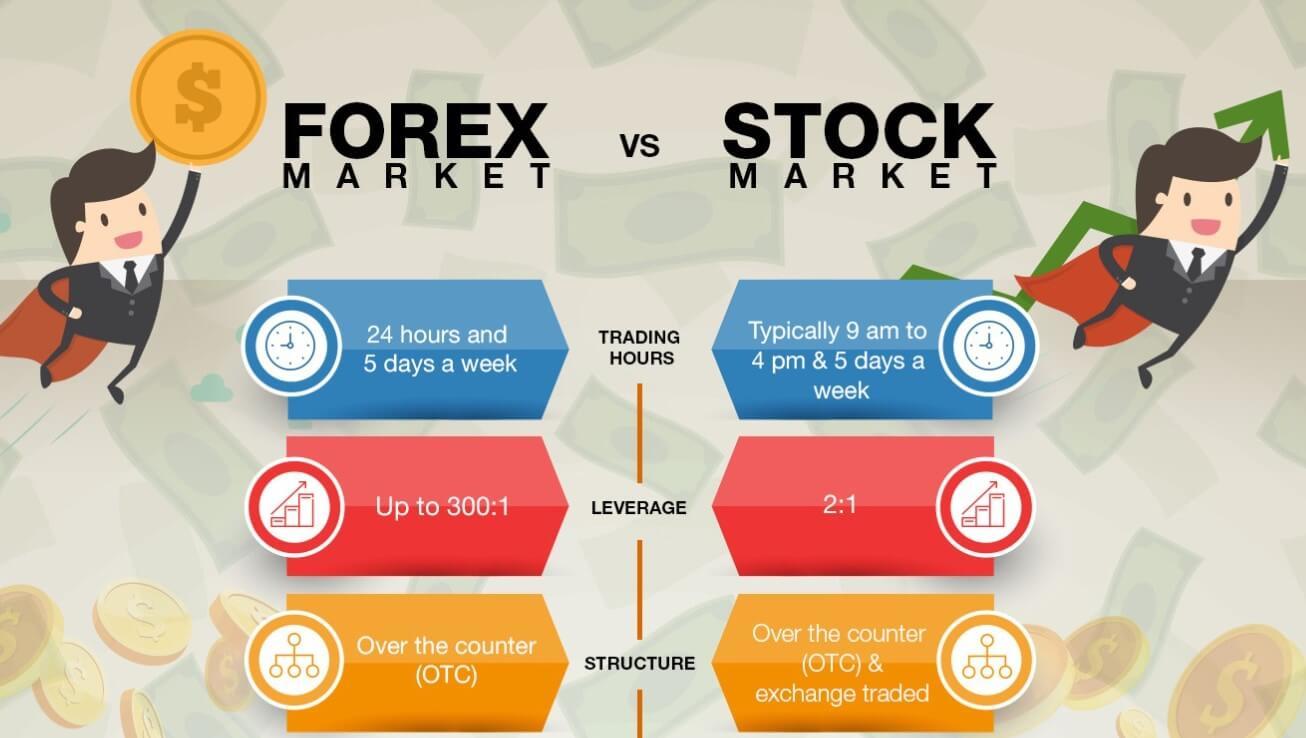
Image: www.keenbase-trading.com
Conclusion
Options trading and stock trading offer distinct opportunities and challenges in the financial markets. Understanding their respective pros and cons is paramount in making informed investment decisions. Options trading provides the allure of leverage, flexibility, and hedging strategies, but it requires a sophisticated understanding of options mechanisms and a high tolerance for risk. Stock trading, on the other hand, is more accessible, offers the potential for dividend income and capital appreciation, but it exposes investors to the full risk of market fluctuations. Ultimately, the choice between options trading and stock trading should be guided by an investor’s individual circumstances, financial objectives, and ability to withstand potential losses.






