In the realm of financial investments, two distinct avenues beckon investors: options trading and securities. While both offer the potential for profit, they encompass unique characteristics and risk profiles that discerning investors must carefully consider. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the intricacies of options trading and securities, exploring their nature, advantages, and risks to empower investors with informed decision-making.
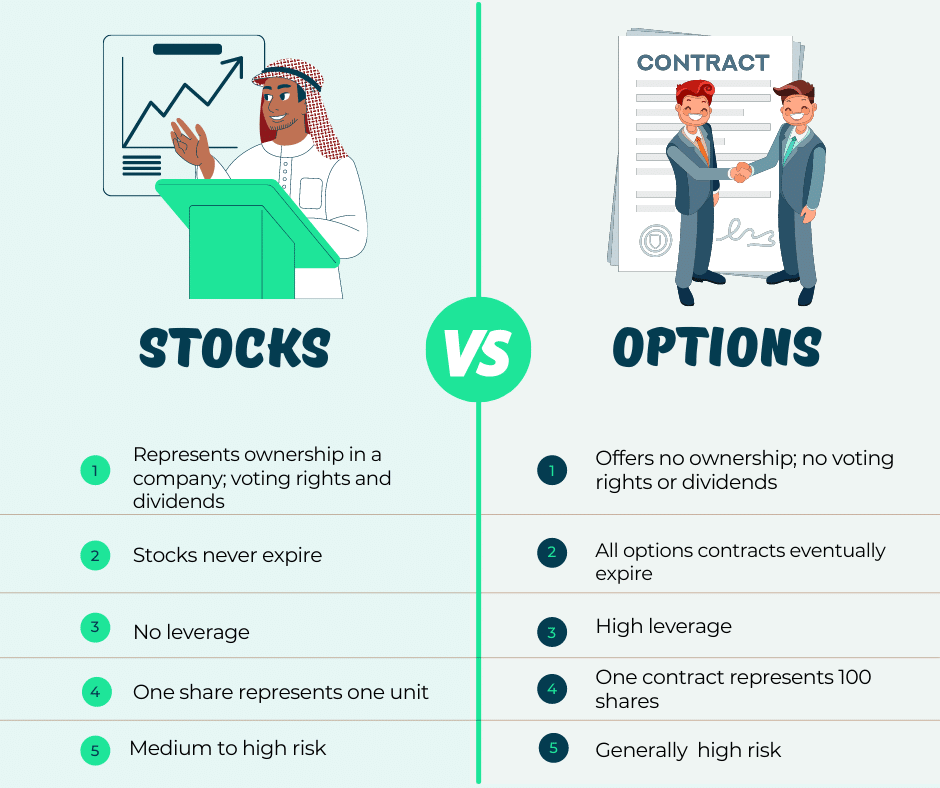
Image: www.projectfinance.com
Deconstructing the Options Trading Realm
Options trading introduces a specialized financial arena where investors engage in contracts that grant the right, but not the obligation, to buy (call options) or sell (put options) a specific underlying asset at a predetermined price (strike price) within a specified time frame. Unlike securities, options do not entail direct ownership of the underlying asset. Instead, they bestow the flexibility to exercise or relinquish the option contract as market conditions dictate.
Unveiling the Advantages of Options Trading
Options trading holds several alluring advantages for investors seeking to navigate market fluctuations strategically. These include:
- Leverage and Flexibility: Options offer substantial leverage, amplifying potential returns while also limiting downside risk. The flexibility to buy or sell options contracts allows investors to tailor their strategies to specific market scenarios.
- Income Generation: Options can generate income through various strategies, such as writing covered calls or selling premium. These approaches enable investors to capitalize on market volatility and time decay to their advantage.
- Risk Management: Options provide a powerful tool for managing risk in investment portfolios. Hedging strategies, such as buying protective puts, can mitigate downside risks and preserve capital.
Exploring the Risks Associated with Options Trading
Despite the allure of potential rewards, options trading also carries inherent risks that investors must acknowledge:
- Time Decay: The value of options decays over time, especially as the expiration date approaches. This factor exerts downward pressure on option prices, particularly when markets exhibit low volatility.
- Unlimited Losses: Investors in call options bear the risk of unlimited losses if the underlying asset price falls significantly below the strike price. Similarly, put option sellers face unlimited losses if prices rise sharply above the strike price.
- Complex Strategies: Options trading encompasses a wide range of strategies, some of which are highly complex. Understanding and implementing these strategies requires considerable knowledge and experience.
Image: biz.libretexts.org
Navigating the World of Securities
Securities, in contrast to options, represent direct ownership interests in specific companies or assets. They encompass a vast spectrum, including stocks, bonds, mutual funds, and exchange-traded funds (ETFs). Investors acquire securities with the primary objective of long-term capital appreciation, dividend income, or a combination of both.
Delving into the Benefits of Securities
Securities offer investors a multitude of benefits, including:
- Diversification: Securities provide ample opportunities for diversification, enabling investors to spread risk across multiple asset classes and sectors. This strategy reduces portfolio volatility and enhances overall returns.
- Passive Income: Dividends are a common feature of many securities, providing investors with a steady source of passive income. Bonds, in particular, offer fixed income payments over their lifespan.
- Long-Term Growth Potential: Securities, particularly stocks, have historically demonstrated long-term growth potential. By investing in the right companies, investors can benefit from the growth of the underlying businesses.
Understanding the Risks Associated with Securities
While securities can offer alluring returns, they also carry certain risks:
- Market Risk: Securities are subject to market fluctuations, which can lead to price declines and capital losses. Economic downturns and geopolitical events can exacerbate market volatility.
- Company-Specific Risk: Investments in individual securities are vulnerable to company-specific risks, such as poor management, financial distress, or industry headwinds. These factors can significantly impact stock performance.
- Inflation Risk: Inflation erodes the purchasing power of fixed-income investments, such as bonds. As prices rise, the real return on bonds declines, potentially offsetting any nominal income gains.
Matching Investment Objectives to Options vs. Securities
The suitability of options trading or securities for a particular investor depends on their individual investment objectives, risk tolerance, and time horizon.
- Short-Term Speculation: Options trading is better suited for short-term speculation or hedging strategies. It provides greater flexibility and leverage, but it also carries higher risks.
- Long-Term Investing: Securities, such as stocks and bonds, are generally more appropriate for long-term investing. They offer diversification, passive income, and the potential for capital appreciation over extended periods.
- Risk Tolerance: Investors with a higher tolerance for risk may find options trading attractive, while those with a lower risk tolerance should focus on securities or consider conservative options strategies.
Options Trading Vs Securities

Image: www.pinterest.com
Conclusion
Options trading and securities present distinct avenues for financial investments, each with unique characteristics, advantages, and risks. Understanding the intricacies of both options allows investors to make informed decisions that align with their investment goals and risk appetite. Whether pursuing short-term speculation or long-term growth, investors must carefully weigh the potential rewards and risks associated with each strategy. By embracing a diligent approach, investors can navigate the financial landscape with confidence and capitalize on the opportunities that await.






