In the realm of options trading, where uncertainty reigns and opportunities abound, mastering the art of straddling can be a game-changer. A straddle is a neutral strategy that involves buying both a call and a put option with the same strike price and expiration date on the same underlying asset. This allows traders to profit from significant price movements, irrespective of the direction of the move.

Image: www.pinterest.com
Understanding Straddle Strategies
The key concept behind straddling is exploiting market volatility. By purchasing both a call and a put option, traders are essentially betting that the underlying asset’s price will fluctuate significantly within the option’s lifespan. When the price moves substantially in either direction, the value of one option will increase while the other will lose value, potentially generating a profit for the trader.
Elements of a Straddle Strategy
- Call Option: The call option grants the holder the right, but not the obligation, to buy the underlying asset at a specific price (the strike price) on or before a predetermined date (expiration date).
- Put Option: The put option grants the holder the right, but not the obligation, to sell the underlying asset at a specific price (the strike price) on or before a predetermined date (expiration date).
- Strike Price: The strike price is the specified price at which the trader can buy or sell the underlying asset using the call or put option.
- Expiration Date: The expiration date is the day on which the options contract expires. If the options are not exercised or closed before this date, they become worthless.
Benefits of Straddling
- Profitability in Both Market Directions: Straddling allows traders to benefit from significant price movements in either an upward or downward direction. This is a significant advantage, especially in volatile markets where the direction of the move is uncertain.
- Limited Risk: Unlike buying a standalone call or put option, straddling limits the downside risk. If the underlying asset’s price does not move significantly within the option’s lifetime, the trader’s loss will be limited to the premium paid for both options.
- Flexible Strategy: A straddle can be customized to match different market conditions and risk tolerances. Traders can adjust the strike price and expiration date to suit their specific trading goals.

Image: myjourneytomillions.com
Challenges and Considerations
While straddling offers attractive benefits, traders must also be aware of its limitations:
- High Premium Cost: Purchasing both a call and a put option can be expensive, especially in the case of highly volatile underlying assets.
- Time Decay and Volatility: The value of options decays over time. Additionally, straddles are more profitable in highly volatile markets. If volatility decreases, the value of the options may diminish quickly.
- Opportunity Cost: Buying a straddle ties up capital that could have been used for other trading opportunities.
Options Trading How To Straddle
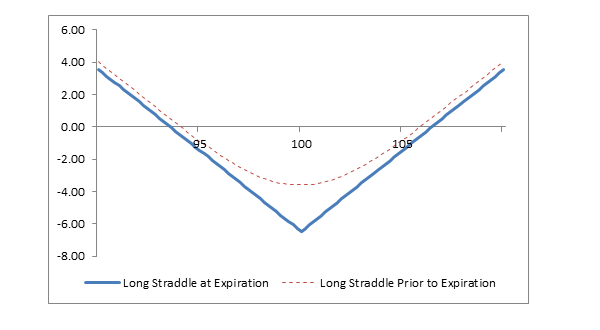
Image: www.fidelity.com
Conclusion
Mastering the art of straddling requires careful consideration, proper risk management, and a thorough understanding of the intricacies of options trading. By leveraging this versatile strategy, traders can enhance their ability to generate profits in volatile markets. However, it’s crucial to remember that the success of any options strategy, including straddling, depends on sound analysis, calculated decision-making, and a disciplined approach to trading.






