Options Trading: The Ultimate Guide to Unleashing the Power of Leverage

Image: fintrakk.com
Options trading, a sophisticated investment strategy, offers boundless opportunities to savvy investors seeking to elevate their returns within the financial markets. Encompassing intricate concepts and nuanced market dynamics, options trading requires a comprehensive understanding to maximize its potential and minimize risks. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of options trading, empowering you with the knowledge and strategies to confidently navigate this complex landscape.
Comprehending the Basics of Options Trading
Options are financial instruments that grant holders the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a specified price (strike price) on or before a predetermined date (expiration date). Call options convey the right to purchase an asset, while put options grant the right to sell a certain asset. By trading options, investors speculate on the future price movements of stocks, currencies, commodities, and other underlying assets.
Unlike stocks, options do not represent ownership in the underlying asset. Instead, they offer the potential for significant returns based on the accuracy of price predictions and the time value of decay. The value of an option is influenced by factors such as the underlying asset’s price, time to expiration, strike price, interest rates, and market volatility.
Types of Options Trading Strategies
The vast world of options trading accommodates diverse strategies tailored to different risk tolerances and investment objectives. Here are some of the most commonly employed strategies:
- Long Call: The investor purchases a call option, anticipating an upward movement in the underlying asset’s price.
- Long Put: The investor purchases a put option, anticipating a downward movement in the underlying asset’s price.
- Short Call: The investor sells a call option, expecting the underlying asset’s price to remain below the strike price.
- Short Put: The investor sells a put option, expecting the underlying asset’s price to stay above the strike price.
- Covered Call: The investor sells a call option against a stock they already own, potentially generating additional income.
- Protective Put: The investor purchases a put option to hedge against potential losses on a long stock position.
Understanding the Greeks: Quantifying Option Risk and Volatility
The Greeks, a set of metrics, assist investors in quantifying the risk and sensitivity of options to changes in underlying variables. The most commonly used Greeks include:
- Delta: Measures the change in option price for every $1 move in the underlying asset’s price.
- Theta: Represents the decline in option value due to the passage of time.
- Vega: Measures the change in option price for every 1% change in implied volatility.
- Rho: Measures the change in option price for every 1% change in interest rates.
Image: trademetria.com
Advanced Strategies for Seasoned Options Traders
As expertise grows, options traders can explore more advanced strategies, such as:
- Straddles: Buying both a call and put option with the same strike price and expiration date.
- Strangles: Buying both a call and put option with the same expiration date but different strike prices.
- Butterflies: A combination of call and put options with varying strike prices and expiration dates.
Iron Condors: A neutral strategy involving selling both a call and put spread simultaneously, profiting from low volatility within a certain price range.
The allure and Pitfalls of Options Trading
Options trading offers an alluring blend of potential rewards and risks. The leverage inherent in options enables investors to amplify their returns, but it also magnifies potential losses. It’s imperative to exercise caution and manage risks prudently, utilizing appropriate stop-loss orders and understanding the nuances of options Greeks.
Options Trading Complex
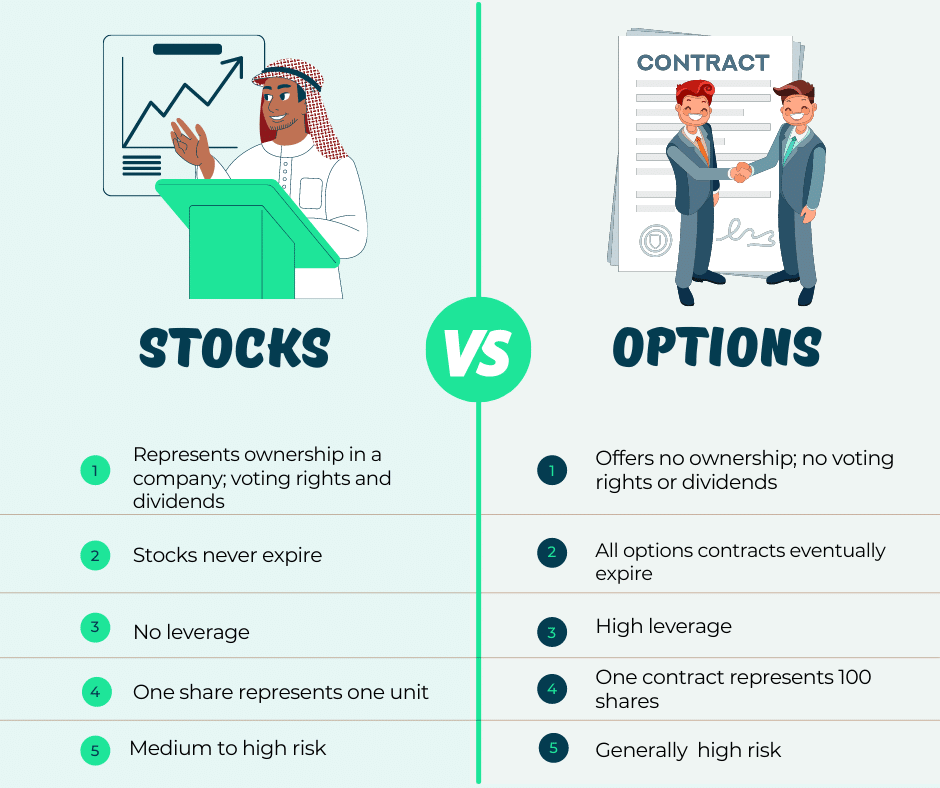
Image: www.projectfinance.com
Conclusion
Options trading represents an advanced financial strategy that can significantly augment investment portfolios. However, embracing this complexity requires a thorough comprehension of options concepts, strategies, and risk management techniques. By grasping the insights and techniques expounded in this guide, you can navigate the dynamic landscape of options trading with confidence, maximizing returns, and mitigating potential pitfalls astutely.






