Options trading is a powerful investment strategy that allows investors to enhance their returns and manage risk. Whether you’re new to the market or seeking to expand your trading skills, this beginner’s guide will provide you with a thorough understanding of options and how to trade them effectively.

Image: fintrakk.com
What is Options Trading?
In options trading, an investor enters into a contract with a financial institution, granting them the right (but not the obligation) to buy (in the case of a call option) or sell (in the case of a put option) a particular asset (stock, index, commodity, etc.) at a specified price (known as the exercise price) within a given period (known as the expiration date). This contract provides the investor with flexibility in their trading decisions and potential for both profit and loss.
Types of Options
There are two main types of options: calls and puts. Call options give the holder the right to buy an asset at a specified price, while put options give the holder the right to sell an asset at a specified price. Additionally, options can be further classified as:
- In-the-Money (ITM): When the current market price of the underlying asset is higher than the exercise price for call options (or lower for put options).
- At-the-Money (ATM): When the current market price of the underlying asset is the same as the exercise price.
- Out-of-the-Money (OTM): When the current market price of the underlying asset is lower than the exercise price for call options (or higher for put options).
Understanding Option Premiums
When an option is opened, the holder pays a premium to the seller. The premium is the price of the option contract and varies depending on several factors, including:
- Price of the Underlying Asset: The higher the price of the underlying asset, the higher the premium.
- Time to Expiration: Options with a longer time to expiration will generally have a higher premium.
- Volatility: Options on more volatile assets will have a higher premium.
- Interest Rates: Higher interest rates can lead to higher option premiums.

Image: worldmags.net
Advantages and Limitations of Options Trading
Advantages:
- Flexibility: Options allow investors to tailor their trading strategies to specific market conditions.
- Leverage: Options offer the potential for high returns with relatively small capital outlay.
- Risk Management: Options can be used to hedge against potential losses in other investments.
Limitations:
- Risk of Loss: If the market moves against the investor’s expectations, they could lose the entire premium paid for the option.
- Time Decay: Options premiums decrease in value as the expiration date approaches, even if the underlying asset price remains unchanged.
- Complexity: Options trading can be complex, especially for beginners, and requires a thorough understanding of the risks involved.
Getting Started with Options
To get started with options trading, consider the following steps:
- Educate Yourself: Familiarize yourself with the basics of options through books, articles, and courses.
- Open a Brokerage Account: Find a reputable broker that offers options trading services.
- Research and Analyze: Conduct thorough research on the underlying asset and its market trends before entering any options trades.
- Start Cautiously: Begin with small trades and gradually increase your exposure as you gain experience.
- Manage Risk: Develop a comprehensive risk management strategy and always have a plan for potential losses.
Options Trading A Beginne
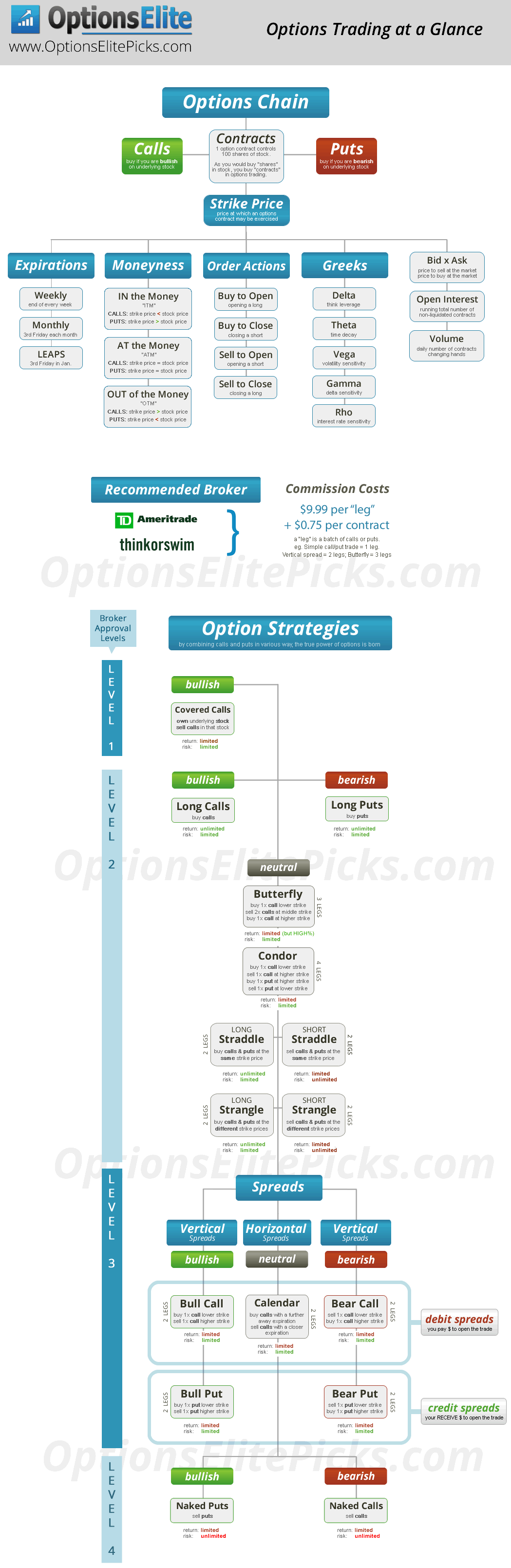
Image: thestockmarketwatch.com
Conclusion
Options trading can be a powerful tool for investors seeking enhanced returns and risk management capabilities. By understanding the types of options available, the factors that affect option premiums, and the potential risks and rewards involved, beginners can navigate the world of options trading with greater confidence. Remember to approach options trading with caution, conduct thorough research, and prioritize risk management strategies to achieve success in this dynamic financial arena.






