Understanding the Basics
Options trading, an intriguing facet of financial markets, has garnered considerable attention in recent times. Options, derivative securities, empower traders to leverage underlying assets such as stocks, bonds, or commodities without owning them outright. It’s a powerful tool that can potentially enhance returns and manage risks, making it a valuable consideration for both seasoned investors and aspiring traders alike.
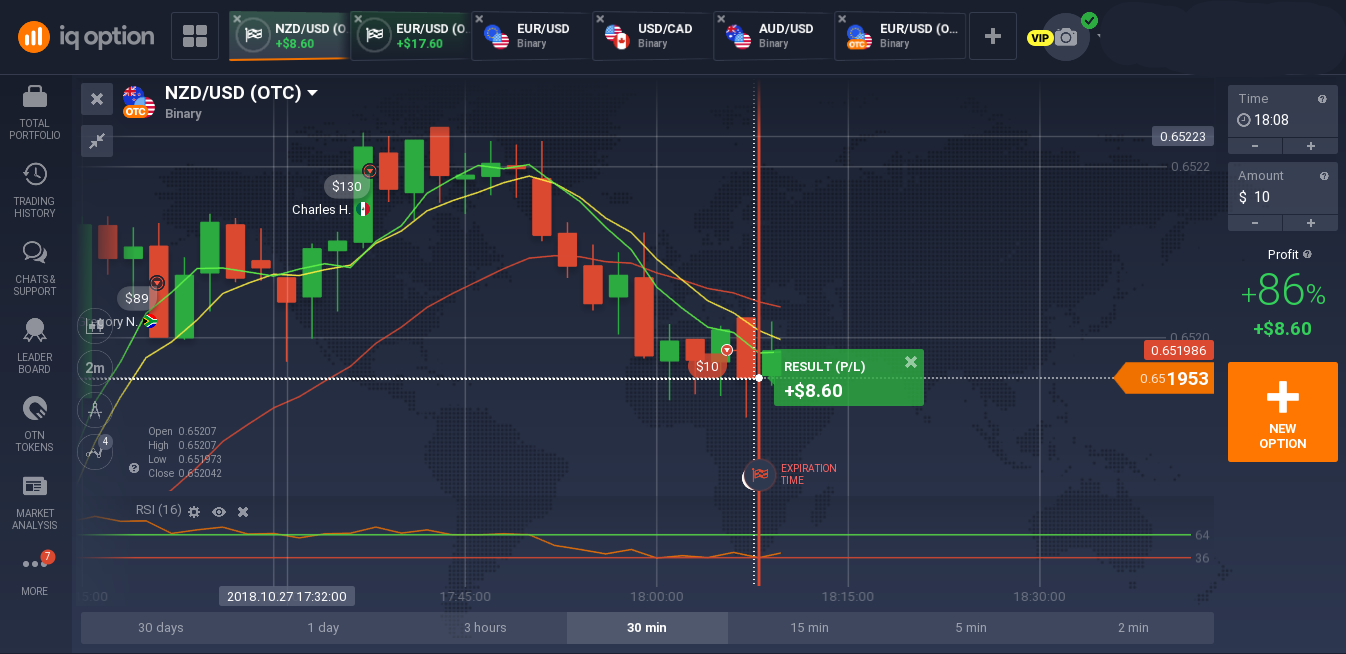
Image: www.plafon.id
Options trading hinges on the concept of contracts, granting buyers the ‘option’ or choice to buy (in the case of a ‘call option’) or sell (in the case of a ‘put option’) a specified number of shares of an asset at a predetermined price, referred to as the ‘strike price,’ on or before a set date, known as the ‘expiration date.’ By purchasing an options contract, a trader is not obligated to execute the trade, but retains the flexibility to do so if market conditions prove favorable.
Types of Options Contracts
The world of options trading offers two primary types of contracts: calls and puts. Call options grant buyers the right to purchase an asset at a specific price within a certain timeframe. They’re typically employed when traders anticipate an uptick in the underlying asset’s value. Conversely, put options grant buyers the right to sell an asset at a specified price within a certain timeframe. These are often utilized when traders expect a decline in the underlying asset’s value.
Within each of these categories, traders can choose between two distinct styles of options: American-style options and European-style options. American-style options afford holders the flexibility to exercise their option at any time up until the expiration date. European-style options, on the other hand, can only be exercised on the expiration date itself.
Strategies for Options Trading
Options trading presents a versatile array of strategies, enabling traders to tailor their approach to their unique risk tolerance and profit objectives. Covered calls involve selling call options while already owning the underlying shares. This strategy generates income from the sale of the option, but limits potential gains from price appreciation. Protective puts, on the other hand, are utilized to safeguard against downside risk. Here, traders buy put options to protect their existing stock holdings.
Hedging and Speculation
Options trading finds diverse applications in the financial realm, serving both hedging and speculative purposes. Hedging involves employing options to mitigate potential losses in existing investments. For instance, an investor holding a portfolio of stocks can purchase protective put options to limit downside risk in the event of a market downturn.
On the other hand, options trading presents opportunities for speculation, allowing traders to make educated predictions and potentially profit from price fluctuations. Skilled traders leverage options to capitalize on short-term market movements and generate impressive returns.
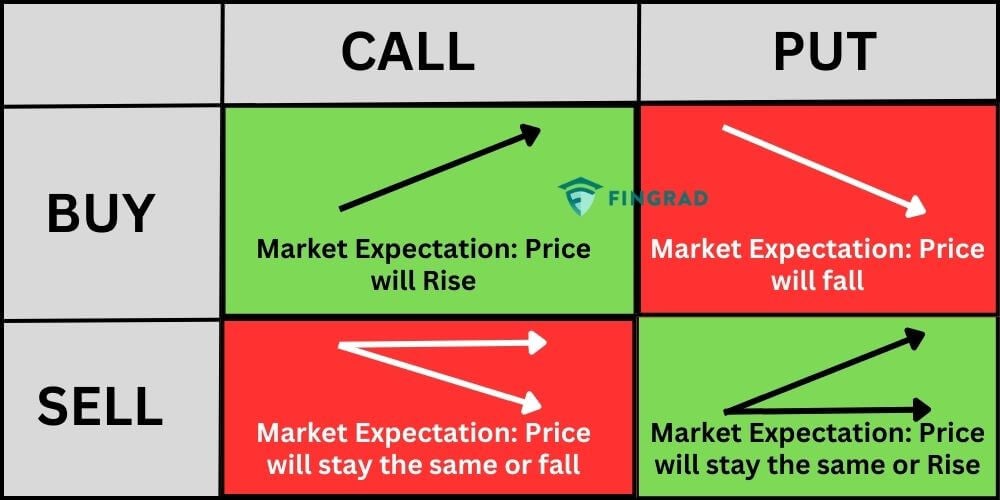
Image: tradebrains.in
The Importance of Research and Education
Embarking on the journey of options trading requires a solid foundation in financial knowledge and market dynamics. Investors should diligently study the underlying concepts, different strategies, and risk factors involved. Comprehensive research, coupled with a keen understanding of market trends, is crucial for making informed decisions while navigating the complexities of options trading.
Everything About Options Trading
Start Your Options Trading Journey Today
Options trading, with its inherent complexities and potential rewards, continues to fascinate investors seeking to enhance their financial acumen. If you’re intrigued by the world of derivatives and eager to explore the possibilities of options trading, know that a wealth of resources and learning opportunities await you. Dive into the markets with confidence, mindful of the risks and rewards, and uncover the transformative power of options trading.






