Introduction
Imagine a world where you could control the risk and potential reward of your investments with precision. That’s the power of options trading. Options are financial contracts that allow you to buy or sell an underlying asset, such as a stock, commodity, or currency, at a specified price on a specific date. They’re a flexible tool that can be used to protect your investments, amplify gains, and speculate on market movements. In this article, we’ll delve deep into the realm of option trading, equipping you with the knowledge you need to navigate this exciting market effectively.

Image: www.binaryoptions.com
Basic Concepts of Option Trading
An option contract consists of three key elements:
- Underlying Asset: The security that you’re buying or selling an option on.
- Strike Price: The price at which you can buy or sell the underlying asset.
- Expiration Date: The date on which the option contract expires.
There are two main types of options:
- Calls: Give the holder the right to buy the underlying asset at the specified price.
- Puts: Give the holder the right to sell the underlying asset at the specified price.
These options can be traded on exchanges like any other security, such as stocks or bonds.
How Option Trading Works
When you buy an option, you’re not obligated to complete the transaction, but you have the right to do so. If the price of the underlying asset moves in your favor, you can exercise the option and make a profit. If it moves against you, you can let the option expire worthless, losing only the premium you paid for it.
The value of an option contract depends on several factors, including the price of the underlying asset, the volatility (risk) of the asset, the interest rate, and the time remaining until expiration.
Trading Strategies Using Options
Options can be used in a variety of trading strategies, each with its own risk and reward potential:
- Buy Calls: Buy a call option if you expect the underlying asset to rise in price.
- Sell Calls: Sell a call option if you expect the underlying asset to fall in price.
- Buy Puts: Buy a put option if you expect the underlying asset to fall in price.
- Sell Puts: Sell a put option if you expect the underlying asset to rise in price.
By combining options in different ways, traders can create complex strategies to meet their specific investment goals and risk tolerance.
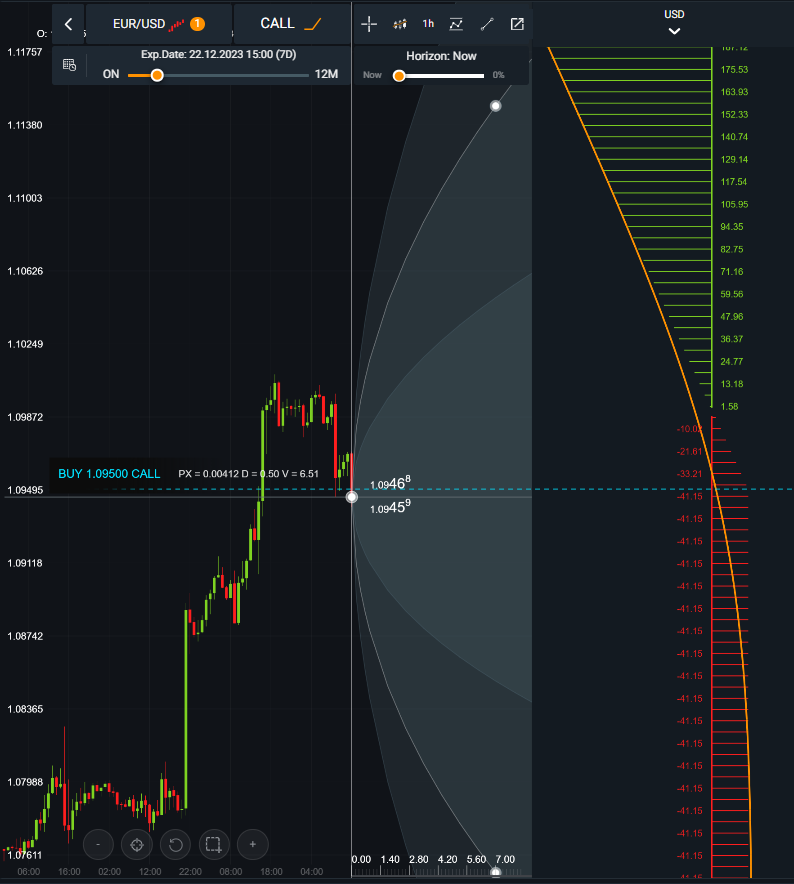
Image: tradersunion.com
Benefits of Option Trading
- Enhanced Risk Management: Options allow you to protect your investments by hedging against potential losses.
- Increased Return Potential: Options provide an opportunity to amplify potential gains.
- Flexibility: Options can be used in a variety of trading strategies, allowing you to tailor your approach to your individual needs.
Risks of Option Trading
- Loss of Premium: You can lose the entire premium you paid for the option if it expires worthless.
- Unlimited Risk: Selling options, particularly uncovered options, can result in unlimited risk.
- Complexity: Option trading can be complex, requiring a thorough understanding of the market and risk management principles.
Option Trading Articles
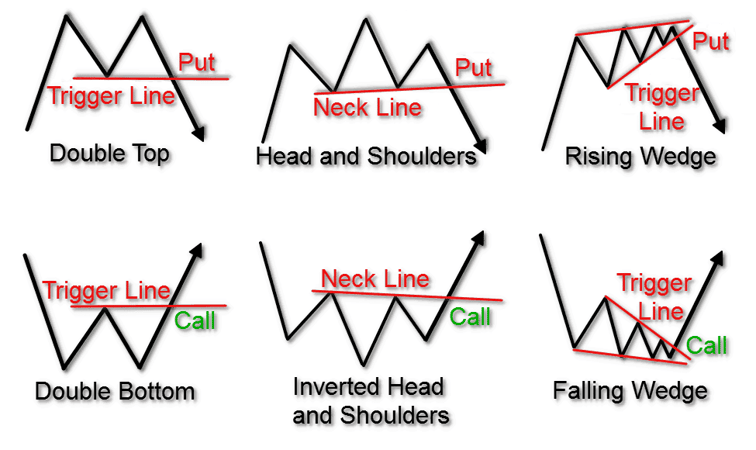
Image: www.tradingsim.com
Conclusion
Option trading offers a powerful tool for investors seeking to manage risk, amplify returns, and speculate on market movements. By understanding the basic concepts, trading strategies, benefits, and risks involved, you can harness the potential of options to enhance your investment portfolio. Remember, the key to successful option trading lies in thorough research, prudent risk management, and a deep understanding of the market.






