Trading options, often shrouded in complexity, presents a dynamic and rewarding opportunity for investors seeking to navigate the financial markets with precision and strategy. This comprehensive guide aims to demystify the intricate landscape of options trading, empowering you with the fundamental knowledge and insights necessary to make informed decisions.

Image: www.tradestation.com
Options trading involves acquiring contracts that grant you the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a predetermined price on or before a specific date. This flexibility provides traders with a unique toolkit to manage risk, enhance returns, and speculate on market movements. Understanding the nuances of options trading can unlock a world of possibilities, empowering you to make calculated bets and potentially reap substantial rewards.
Foundation of Options Trading
At the core of options trading lies the fundamental division between call options and put options. Call options confer the right to buy an underlying asset, while put options grant the right to sell. These contracts are traded on exchanges, wherein buyers pay a premium (cost) to the seller to secure the right to exercise the option. Each option contract represents an underlying asset, which can be a stock, index, commodity, or currency. As the value of the underlying asset fluctuates, so does the value of the option.
Understanding the interplay between the strike price and the expiration date is crucial. The strike price represents the agreed-upon price at which the buyer can exercise the option to buy or sell the underlying asset. The expiration date, on the other hand, determines the timeframe within which the option can be exercised. It’s important to assess the market conditions and your investment goals when selecting the strike price and expiration date for your options contracts.
The Metrics of Options Trading
Navigating the options market requires a grasp of key metrics that measure the value and potential of an option contract. These include:
- Premium: Cost paid by the buyer to the seller for the right to exercise the option.
- Intrinsic Value: In-the-money option’s difference between the underlying asset’s current price and the strike price.
- Time Value: Premium paid for the option’s time until expiration.
- Volatility: Measure of the underlying asset’s price fluctuations, directly affecting option premiums.
Analyzing these metrics enables informed decisions when pricing and executing options trades.
Strategies for Success
Options trading presents a myriad of strategies tailored to different risk appetites and investment goals. Some commonly employed strategies include:
- Covered Call: Selling a call option against an underlying asset you own.
- Protective Put: Buying a put option to hedge against potential losses in the underlying asset.
- Bull Call Spread: Buying a call option at a lower strike price and selling a call option at a higher strike price with the same expiration date.
- Bear Put Spread: Buying a put option at a higher strike price and selling a put option at a lower strike price with the same expiration date.
Selecting the appropriate strategy hinges upon a thorough understanding of your risk tolerance, market outlook, and investment objectives.
Image: forex-station.com
Expert Insights
“Options trading offers a powerful tool for risk management and return enhancement,” says renowned financial strategist Mark Douglas. “However, it’s imperative to approach it with a disciplined approach, understanding the underlying concepts and managing risk effectively.”
“Thorough research and continuous market monitoring are vital for successful options trading,” adds options expert Karen Firestone. “Stay informed about factors influencing the underlying asset and adjust your strategy accordingly.”
Cautions and Considerations
While options trading offers immense potential, it’s crucial to exercise caution and consider the following:
- Risk of Loss: Options trading carries the potential for significant financial losses.
- Complexity: Options trading involves intricate strategies that require a comprehensive understanding of the market.
- Time Sensitivity: Options have a limited lifespan, and their value decays as the expiration date approaches.
It’s advisable to seek guidance from experienced professionals and thoroughly educate yourself before venturing into options trading.
Min For Options Trading
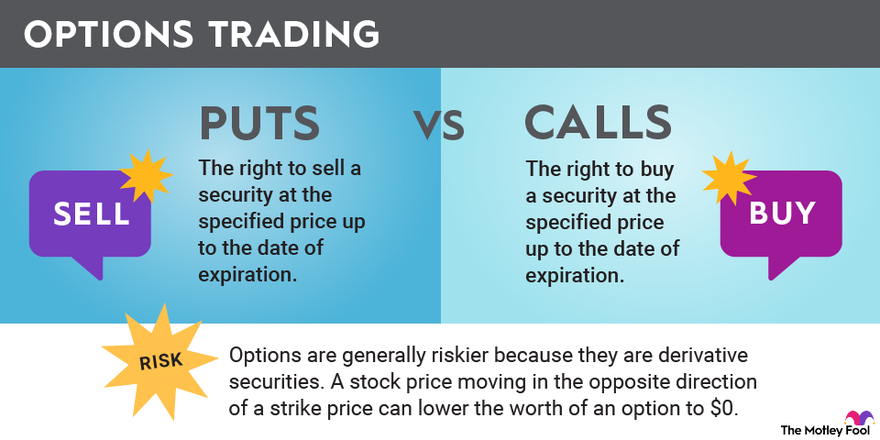
Image: www.fool.com
Conclusion
Embarking on the journey of options trading requires a blend of knowledge, strategy, and prudent risk management. By understanding the fundamentals, embracing proven strategies, and exercising due diligence, you can harness the power of options to navigate the complexities of financial markets with increased confidence and potential reward. Remember, investing in options is not a get-rich-quick scheme but a path towards disciplined and informed financial decision-making.
Embrace the learning curve, stay attuned to market dynamics, and seek guidance from trusted sources. The world of options trading awaits those willing to delve into its depths and unlock its transformative potential.






