Introduction
In the intricate world of financial markets, options trading stands as a versatile and potentially lucrative strategy for both individual investors and seasoned professionals. An option contract represents an agreement that grants the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a predetermined price within a specific time frame. Grasping the inner workings of option trading can empower you to harness its potential for substantial returns and mitigate financial risks.

Image: marketrebellion.com
Understanding Basic Concepts
An option contract involves two primary parties: the buyer and the seller. The buyer acquires the option in exchange for a premium paid to the seller. The premium represents the price of the option. The underlying asset can be a stock, bond, currency, commodity, or even an index. The strike price is the predetermined price at which the buyer can exercise their option to buy or sell the asset. The expiration date defines the time frame within which the option can be exercised.
Call Options vs. Put Options
Options fall into two primary categories: call options and put options. A call option grants the buyer the right to buy the underlying asset at the strike price. If the market price of the asset rises above the strike price, the call option holder can profit by exercising the option and purchasing the asset at a lower price than its current market value.
Conversely, a put option provides the buyer with the right to sell the underlying asset at the strike price. If the market price of the asset falls below the strike price, the put option holder can benefit by exercising the option and selling the asset at a higher price than its current market value.
Types of Option Trading Strategies
Option trading strategies can be broadly classified into three main types:
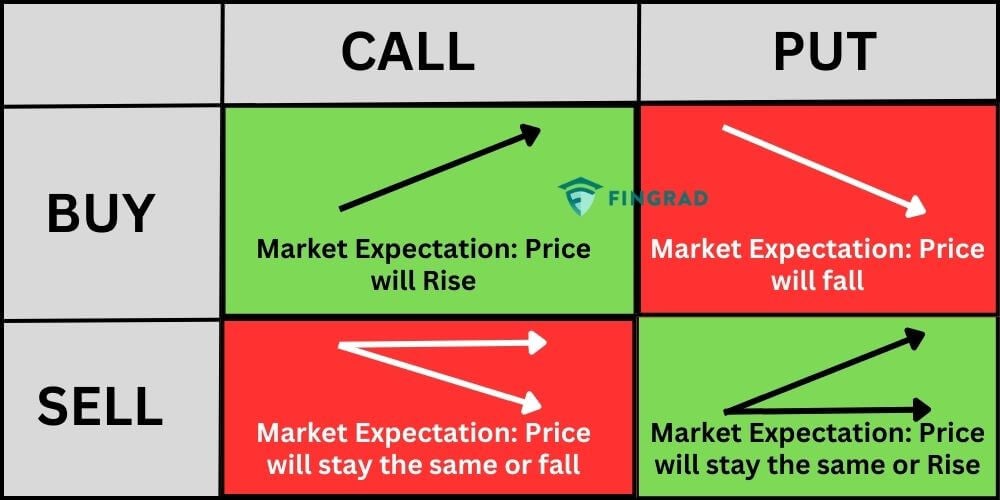
Image: tradebrains.in
Conservative Strategies
Conservative option strategies focus on minimizing risk and generating a steady stream of income. Examples include covered calls, where an investor sells a call option against an underlying stock they already own, or cash-secured puts, where the investor sells a put option and sets aside enough cash to purchase the underlying asset if the option is exercised.
Neutral Strategies
Neutral option strategies seek to maintain a neutral market position while profiting from fluctuations in volatility. A common example is the straddle, where the investor purchases both a call option and a put option with the same strike price and expiration date.
Speculative Strategies
Speculative option strategies involve taking on more risk in pursuit of potentially higher returns. Examples include naked calls or puts, where the investor sells an option without owning or having the cash to purchase the underlying asset, or bull or bear spreads, where the investor combines multiple options to capitalize on anticipated market movements.
Key Factors to Consider
Navigating the realm of option trading effectively requires careful consideration of several key factors:
Time Decay
Option premiums erode over time, even if the underlying asset’s price remains stable. This phenomenon, known as time decay, is particularly pertinent for short-term options with near-term expiration dates.
Price Volatility
The volatility of the underlying asset’s price significantly impacts option premiums. Higher volatility leads to more expensive options, as investors are paying a premium for the increased risk associated with price fluctuations.
Interest Rates
Interest rates can affect option pricing, especially for long-term options. Higher interest rates tend to lead to higher option premiums, as the value of the premium itself can generate interest over time.
How Does.Option Trading Work

Image: informationngr.com
Conclusion
Option trading can be an effective means of enhancing portfolio returns and mitigating risk. However, it is crucial to approach this complex financial instrument with a thorough understanding of its mechanisms, potential benefits, and inherent risks. By mastering the concepts outlined in this comprehensive guide, you can equip yourself to navigate the complexities of option trading with confidence and reap the rewards it offers.






