**Introduction**
Amidst the bustling world of finance, where stocks dance to the whims of supply and demand, lies an intriguing force that subtly influences their movements: option trading. Options, with their alluring promises of potential profits and protective shields against losses, have become a ubiquitous part of the stock market ecosystem, leaving many to wonder how they leave their mark on stock prices.

Image: s3.amazonaws.com
Like an invisible thread, option trading weaves its way through the fabric of stock markets, impacting their trajectories in both subtle and profound ways. To fully unravel this intertwined relationship, we delve into the depths of how options trading affects stock prices, uncovering the mechanisms and dynamics that shape market behavior.
Understanding Options
Options, simply put, are contracts that grant the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to buy (call option) or sell (put option) a specific underlying asset, such as a stock or an index, at a predetermined price (strike price) within a particular timeframe. They offer investors a flexible tool to manage risk and speculate on price movements.
The Supply and Demand Dance
The impact of option trading on stock prices stems from the dance between supply and demand. When an investor buys an option, they are effectively betting on the future price of the underlying asset. If the option’s value increases due to a change in market expectations, it creates a demand for the option, driving its price higher. This, in turn, can push the underlying stock price up as traders believe the positive sentiment warrants an adjustment.
Conversely, when an investor sells an option, they are opening a position that benefits from a decline in the underlying asset’s price. Increased selling pressure on the option leads to a decrease in its value, which may translate into a reduction in the stock price if it signals a waning appetite for the stock.
The Implied Volatility Play
Implied volatility, a crucial concept in option pricing, measures the expected price fluctuations in the underlying asset. When implied volatility rises, it reflects heightened uncertainty and, therefore, an increased demand for options. This demand for protection against potential price swings can elevate option prices, adding an upward pressure to the stock price.
Convergence towards Strike Price
As options near their expiration date, a curious convergence occurs. Options that are in-the-money (ITM), meaning their strike price is more favorable than the current stock price, increasingly influence the stock’s behavior. ITM call options incentivize holders to exercise their right to buy the stock, creating buying pressure that can buoy the price. Similarly, ITM put options encourage holders to sell the stock, potentially leading to a downward price adjustment.
Liquidity and Market Depth
Option trading also impacts a stock’s liquidity and market depth. Options contracts, particularly those with shorter expiration dates, provide investors with increased flexibility and the ability to react swiftly to market developments. This enhanced liquidity can attract more investors, leading to a wider distribution of ownership and a more efficient price discovery process.
Conclusion
The relationship between option trading and stock prices is a complex symphony, where supply, demand, implied volatility, and convergence towards strike price orchestrate a dynamic dance. While options trading offers investors a wide array of opportunities for risk management and profit-seeking, its influence on stock prices is often subtle, requiring a discerning eye to fully appreciate its significance. By understanding these intricate mechanisms, investors can gain a deeper appreciation for market behavior and make more informed decisions in their financial endeavors.
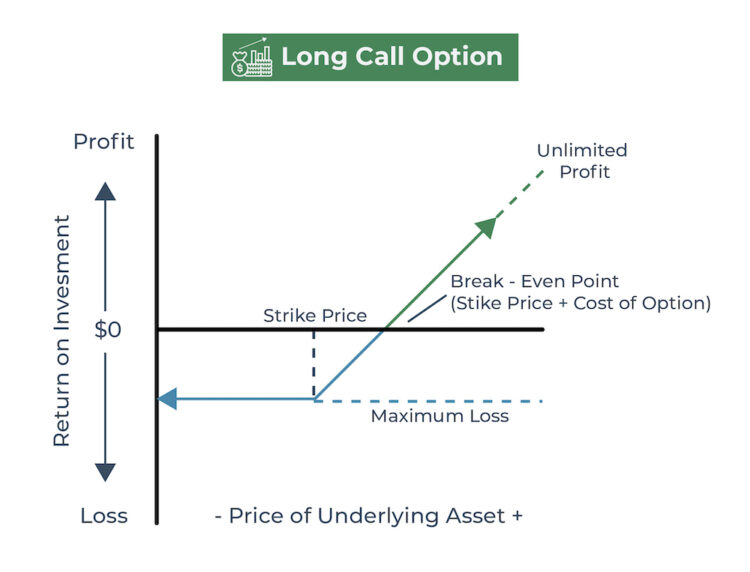
Image: investinganswers.com
How Does Option Trading Affect Stock Price
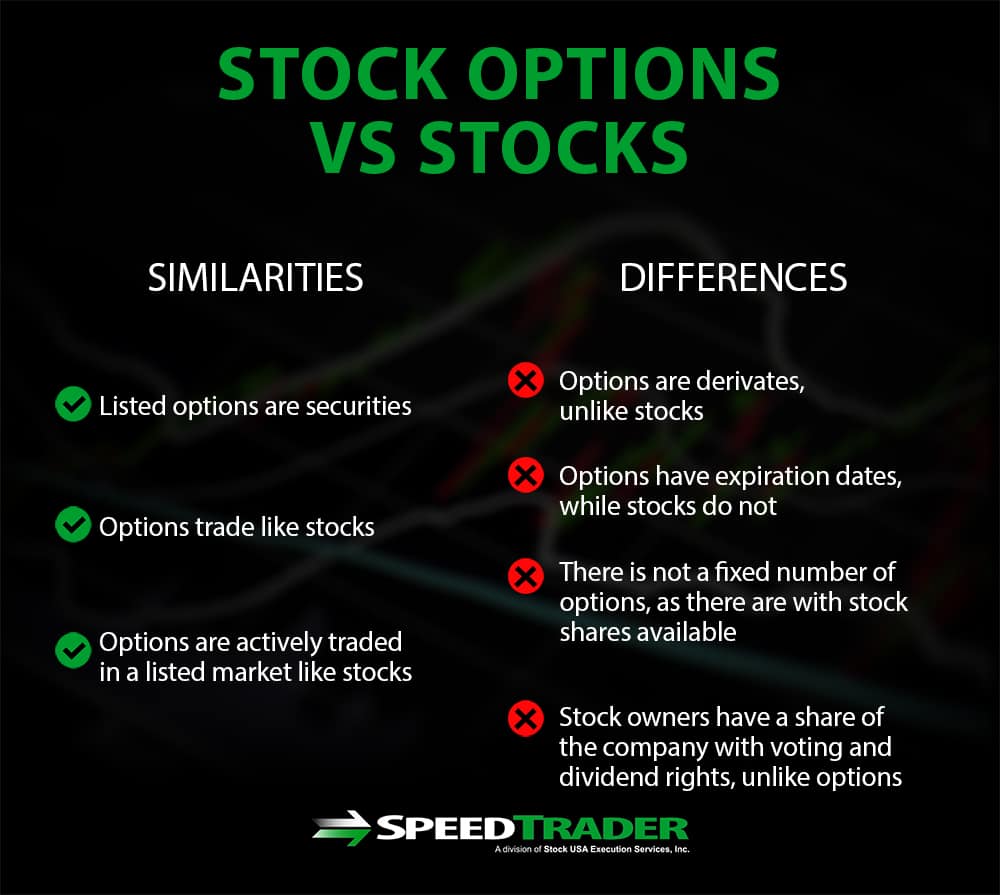
Image: speedtrader.com






