Options trading presents a unique opportunity for individuals to participate in the financial markets with varying levels of risk and potential rewards. In this comprehensive guide, we unveil the intricate world of options, covering their basics, strategies, and practical applications, empowering you with knowledge to navigate this dynamic arena.

Image: www.dvidshub.net
Options contracts, also known as financial options, confer the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a specific price (strike price) on or before a set date (expiration date). Buyers of options acquire these rights in exchange for paying a premium to the sellers, who in turn assume the corresponding obligations. Options provide investors with the flexibility to speculate on future price movements or hedge against potential losses.
Delving into Options Basics: Types, Rights, and Obligations
Options are broadly classified into two main types based on whether they give the buyer the right to buy or sell the underlying asset: call options and put options. Call options provide the right to buy, while put options grant the right to sell.
Each type of option comes with specific rights and obligations. Call option holders possess the right to buy the underlying asset at or below the strike price, while put option holders have the right to sell at or above the strike price. Sellers of call options bear the obligation to sell the asset if the buyer exercises their right, and sellers of put options have the obligation to buy.
Deciphering the Options Contract: Key Elements and Calculations
Options contracts are defined by essential characteristics, including premium, strike price, expiration date, and underlying asset. The premium is the price paid by the buyer to acquire the option. The strike price represents the price at which the buyer can exercise their right to buy or sell. The expiration date marks the last day the option can be exercised. Finally, the underlying asset is the financial instrument linked to the option, such as a stock, bond, commodity, or currency.
The intrinsic value of an option represents the potential profit that can be made by exercising the right immediately. For call options, intrinsic value is the difference between the strike price and the current market price of the underlying asset if the price is higher than the strike. For put options, intrinsic value exists when the strike price is above the current market price.
Strategies and Techniques for Options Trading: Maximizing Returns
Traders employ various strategies to optimize their options trading, each catering to specific trading objectives and risk tolerance. Covered calls involve selling a call option while already owning the underlying asset, seeking to generate additional income from the option premium. Protective puts are employed to hedge against potential downside risk, buying a put option to protect a long position in the underlying asset. Bull call spreads are crafted when an investor anticipates a bullish trend, purchasing a call option while simultaneously selling a call option at a higher strike price.

Image: northamericantrainingsolutions.com
Navigating Volatility and Risk Management in Options Trading
Volatility, often measured by the implied volatility index (VIX), plays a crucial role in options pricing and risk analysis. Implied volatility gauges market expectations of future price fluctuations, impacting option premiums. Traders must carefully consider the potential impact of volatility on their trading strategies and incorporate risk management measures, such as stop-loss orders and position sizing, to mitigate potential losses.
Benefits and Potential Pitfalls: Embracing the Opportunities and Challenges
Options trading offers a plethora of benefits, including leveraging opportunities for price speculation, hedging against downside risks, and generating additional income through premium collection. However, it is worth noting that options trading involves substantial risks, and traders must fully understand the potential for financial losses. Lack of knowledge, improper strategy selection, and insufficient risk management can lead to significant setbacks.
Ehat Is Options Trading
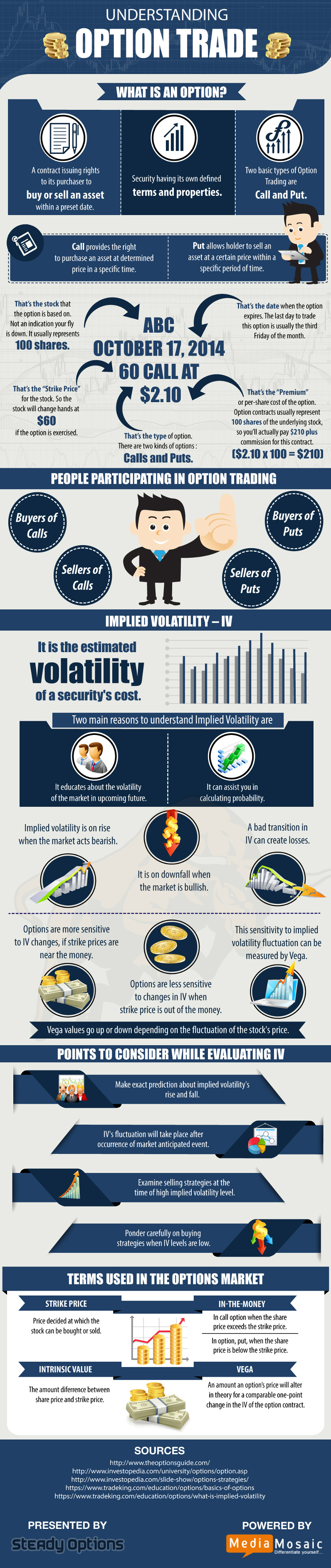
Image: www.visualcapitalist.com
Conclusion: Harnessing the Power of Options Trading
Options trading presents a complex and multifaceted investment arena, offering both opportunities and risks to participants. By thoroughly grasping the concepts, strategies, and risks involved, traders can harness the power of options trading to pursue their financial objectives, whether it’s capital appreciation, risk mitigation, or income generation. Remember, education and prudent risk management are the cornerstones of successful options trading.






