Have you ever wondered about the intricate world of financial markets and the instruments used by seasoned investors to navigate volatility and profit from market trends? Two of these instruments, often mistaken for each other, are futures and options. These contract-based trading tools offer investors unique opportunities to speculate on the future price of an asset, but their approaches differ significantly. This article will delve into the nuances of futures and options, highlighting their similarities, and most importantly, the key distinctions that set them apart. Understanding these differences is crucial for any investor who seeks to capitalize on market opportunities while managing risk effectively.
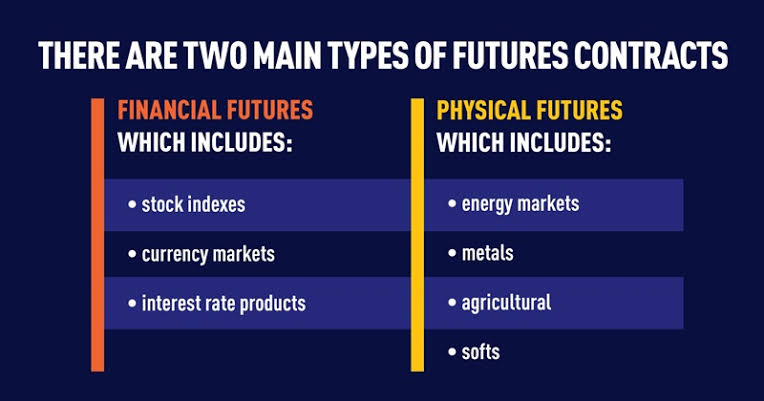
Image: buddymantra.com
A common misconception is that futures and options are interchangeable. While both offer opportunities to profit from future price movements, they achieve this through fundamentally different mechanisms. Imagine buying a ticket to a concert you want to attend. You’re essentially locking in the price beforehand, regardless of any price fluctuations later. Futures trading is similar, allowing investors to fix a price upfront for an asset they will buy or sell at a future date. This locks in a price for a future purchase or sale, offering certainty in a volatile market. Options, on the other hand, grant the *right* to buy or sell an asset at a predetermined price in the future, but without the obligation. It’s like having a call option for a concert ticket – the right, but not the obligation, to buy it at a pre-set price, even if the ticket prices increase later. This flexibility comes at a cost, as options contracts themselves have a price that needs to be factored into your strategy.
Navigating the World of Futures: A Deeper Dive
Futures trading centers around contracts that obligate both the buyer and seller to exchange a specific asset at a predetermined price and time. Think of it as a pre-arranged agreement to buy or sell a commodity like oil, gold, or a financial instrument like a stock index, in the future. This fixed price, regardless of the actual market price at the time of delivery, is what fuels the potential for profit or loss. Let’s illustrate this with a simple example:
Imagine you believe the price of crude oil will rise next month. You enter into a futures contract to buy oil at $80 per barrel in one month. If the price of oil does indeed climb to $85 per barrel by the contract’s expiration date, you can sell your contract for $85, making a profit of $5 per barrel. Conversely, if the oil price drops to $75, you’ll be obligated to buy at $80, incurring a loss of $5 per barrel. This illustrates the inherent risk and potential rewards of futures trading: the price of the underlying asset dictates your gains or losses.
Navigating the World of Options: The Right to Choose
Options trading, as the name suggests, provides buyers with the *right*, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an asset at a pre-defined price within a specified timeframe. Imagine having the option to buy a concert ticket at $50, but not being required to. If the ticket price skyrockets to $100, you can exercise your option and buy at the cheaper price, making a profit. However, if the ticket price drops to $30, you can choose not to exercise your option and simply let it expire, minimizing your potential loss. This flexibility makes options more appealing to traders seeking risk management strategies.
There are two main types of options: call options and put options. A call option grants the buyer the right to *buy* an asset at a set price, while a put option grants the buyer the right to *sell* an asset at a set price. These options are typically used for various purposes:
- Speculation: Options allow you to leverage your position and potentially capture significant gains if your prediction about the asset’s future price movement is correct.
- Risk Management: Options can help manage your risk by limiting your potential downside in case of an unfavorable market event.
- Income Generation: By selling options, you can generate income through premiums received, but this strategy also carries risks.
Unveiling the Similarities: A Shared Foundation
While their mechanisms and risk profiles differ, futures and options share several fundamental similarities:
- Leverage: Both contracts allow for leverage, amplifying potential profits but also magnifying losses.
- Volatility: Both benefit from volatile markets, as price fluctuations offer opportunities for profit.
- Speculation: Both futures and options can be used for speculation on the future price of an asset.
- Liquidity: Both instruments are generally highly liquid, making it easier to enter or exit a position.
Image: www.tdameritrade.com
Distinguishing Features: Diverging Paths
Despite their commonalities, futures and options diverge significantly in crucial aspects:
Obligation vs. Right:
The most significant difference lies in the **obligation vs. right** aspect. Futures contracts oblige both the buyer and seller to perform the transaction at the agreed-upon price and time. In contrast, options provide the **right**, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an asset at a predetermined price. This flexibility is a key differentiator.
Profit and Loss Potential:
Futures trading offers unlimited profit and loss potential, as the price of the underlying asset is uncapped. Option profits are capped at the difference between the strike price and the market price at expiration. However, options premiums offer a maximum loss potential, which is defined at the time of purchase.
Risk and Reward:
Futures trading involves greater risk compared to options. The unlimited profit potential also comes with the risk of unlimited losses, as the price of the asset can fluctuate significantly. Options trading allows for more controlled risk management, but the potential profit is limited.
Considerations for Choosing Between Futures and Options
The choice between futures and options depends entirely on your individual trading style, risk tolerance, and investment goals. Here are a few key considerations:
- Risk Tolerance: If you have a high risk tolerance and are comfortable with potentially unlimited losses, futures may be suitable. If you prefer limited risk, options offer more control over your potential downside.
- Investment Goals: Do you want to speculate on price movements or manage your exposure to risk? Futures provide leverage for aggressive speculation, while options allow for targeted risk management techniques.
- Time Frame: Futures contracts have a specific expiration date, while options offer flexibility in terms of expiration and exercise time. Consider your trading horizon and choose the instrument that aligns with your timeframe.
Is Futures Trading Same As Options
https://youtube.com/watch?v=WsTAgI2pyiM
Conclusion: Navigating the Financial Landscape
The world of financial trading offers a wide array of tools, each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. Futures and options, though often confused, are distinct instruments with unique characteristics. Understanding the differences between these financial instruments is crucial for any investor seeking to navigate the complex financial landscape. By considering your risk tolerance, investment goals, and trading style, you can select the most appropriate tool to achieve your desired outcomes. Ultimately, navigating the financial markets involves careful evaluation, calculated risk, and a constant pursuit of knowledge to gain an edge in this dynamic realm.






